随着腔镜甲状腺手术的快速发展,各种并发症也越来越受到关注,喉上神经外支的保护日益受到重视,虽然其显露困难和损伤引起的后果不被重视,但随着患者对发音要求的提高,如何更好显露和保护喉上神经需要进一步探索,而术后颈部粘连皮肤联动越来越受到患者诟病,为更好解决这些问题,我院2018年1月—2018年10月开展了腔镜免缝合肌间隙入路(sutureless intermuscular space approach,SISA)甲状腺手术20例,效果满意,现报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
我院2018年1月—2018年10月行腔镜SISA甲状腺手术20例,其中男1例,女19例;年龄21~48岁,平均29.8岁;甲状腺腺瘤3例,结节性甲状腺肿13例,原发性甲状腺功能亢进4例;依据超声检查结果肿瘤大小2.1~4.8 cm,平均3.75 cm;手术方式为单侧甲状腺大部分切除术8例,双侧甲状腺大部分切除术12例。患者一般临床资料见表1。
1.2 手术方法
气管插管全麻。患者取仰卧位两腿分开,颈肩部略垫高,术者站在患者的两腿之间,监视器放在患者的头部,助手站在患者右边。用生理盐水100 mL加入肾上腺素0.5 mL在胸骨上窝下方3 cm处预造空间区做皮下注射。于右侧乳晕4点、11点位置分别切约10 mm和5 mm切口,左侧乳晕上缘切10 mm的皮肤切口,置入Trocar,注入CO2,压力至8 mmHg(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa)。用电凝钩或超声刀沿深筋膜浅层分离皮下疏松结缔组织,沿颈阔肌深面分离至甲状软骨上缘平面,两侧显露胸锁乳头肌,颈前带状肌间隙打开步骤:第一步:打开胸锁乳突肌与颈前带状肌的间隙到甲状软骨上缘水平;第二步:游离肩胛舌骨肌上腹;第三步:打开胸骨舌骨肌与胸骨甲状肌之间自然间隙。显露并游离甲状腺(图1A),应用拉钩或缝合牵拉胸骨舌骨肌与胸骨甲状肌,显露甲状腺峡部,气管前游离离断甲状腺峡部后,从甲状腺下级进行钝性分离,显露甲状腺下极血管,从下极紧贴甲状腺被膜钝性游离整个腺体,显露喉返神经及甲状旁腺(图1B),应用四步法检测神经信号,避免损伤,用超声刀凝固切断甲状腺下极血管。根据上极位置高低通过两种方法显露上极:上极位置高则通过肩胛舌骨肌与胸骨甲状肌的间隙(图1C);否则可通过胸骨甲状肌与环甲肌的间隙,显露上极血管及喉上神经(图1D),用神经检测检测喉上神经信号,保护喉上神经,离断上极血管。将上极脱帽游离。根据疾病情况用超声刀完成甲状腺大部分切除或全切。将切除的标本装入标本袋从左侧乳晕10 mm切口取出,根据疾病情况即可送冷冻病理检查,本组无甲状腺癌,再次检查创面,探查喉返神经及喉上神经和甲状旁腺,保证神经的完整和甲状旁腺的血供良好。通过肌间隙放置引流管。手术结束。
1.3 术后疼痛评分
采用视觉模拟评分法(VAS)对患者术后疼痛程度进行评分,0分:无痛;3分以下:有轻微的疼痛,能忍受;4~6分:患者疼痛并影响睡眠,尚能忍受;7~10分:患者有渐强烈的疼痛,疼痛难忍,影响食欲,影响睡眠。
表1 20例患者的一般资料
Table 1 General data of the 20 patients
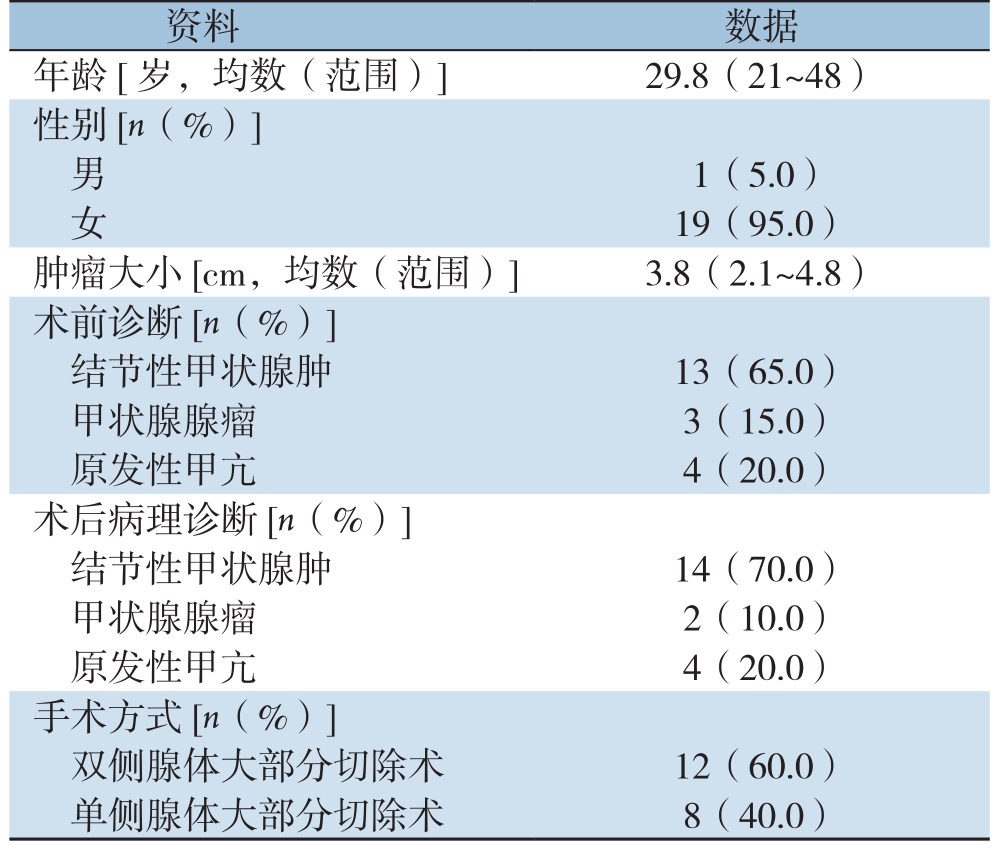
资料 数据年龄[岁,均数(范围)]29.8(21~48)性别[n(%)]男1(5.0)女19(95.0)肿瘤大小[cm,均数(范围)]3.8(2.1~4.8)术前诊断[n(%)]结节性甲状腺肿 13(65.0)甲状腺腺瘤 3(15.0)原发性甲亢 4(20.0)术后病理诊断[n(%)]结节性甲状腺肿 14(70.0)甲状腺腺瘤 2(10.0)原发性甲亢 4(20.0)手术方式[n(%)]双侧腺体大部分切除术 12(60.0)单侧腺体大部分切除术 8(40.0)
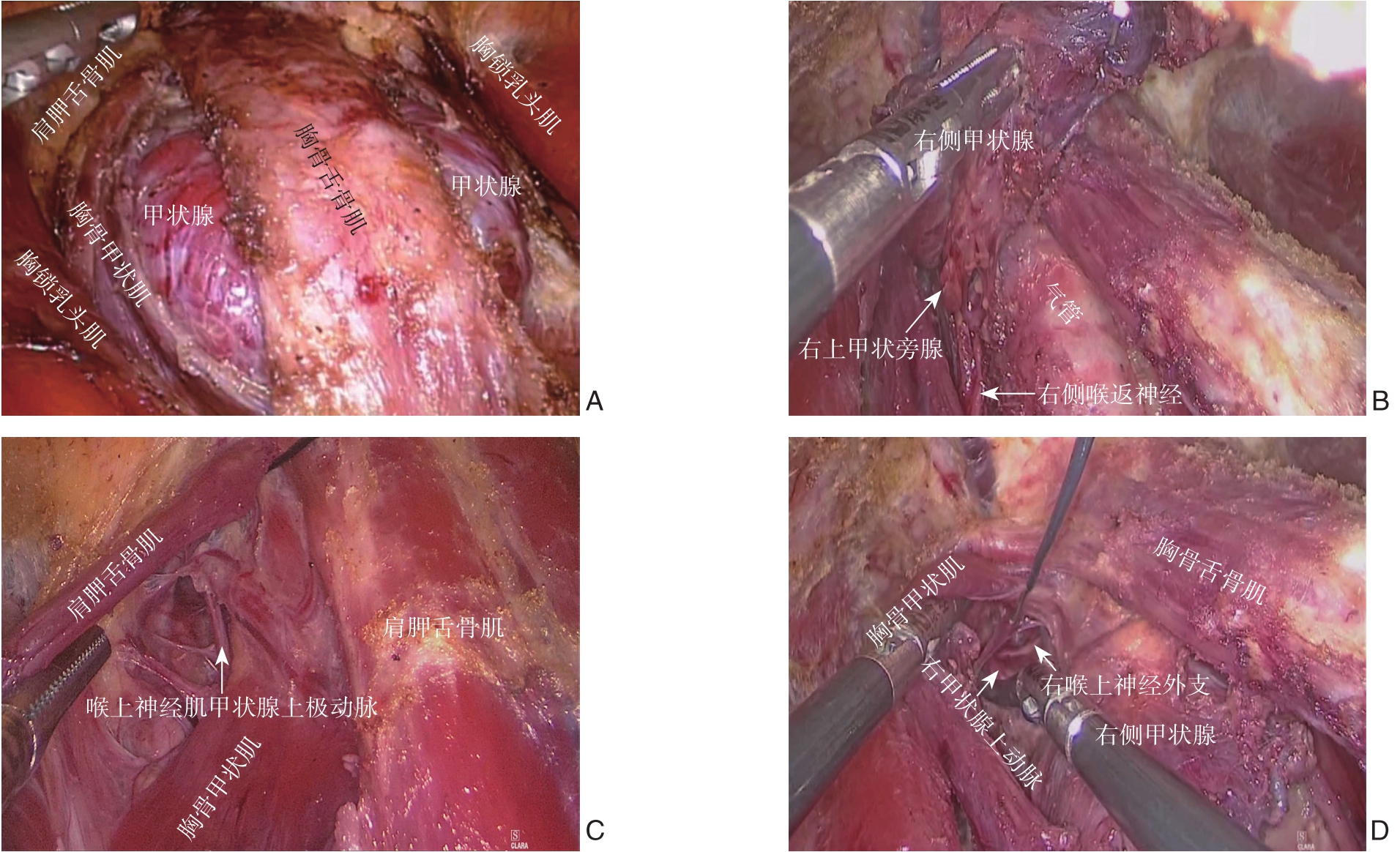
图1 术中照片 A:分离颈前肌间隙显露甲状腺;B:显露喉返神经及甲状旁腺;C:胸骨甲状肌与肩胛舌骨肌间显露喉上神经;D:胸骨甲状肌与环甲肌间显露喉上神经
Figure 1 Intraoperative views A:Separation of the space of the cervical anterior muscles to expose the thyroid;B:Exposure of the recurrent laryngeal nerve and parathyroid glands;C:Exposure of the superior laryngeal nerve between the sternothyroid muscle and the omohyoid muscle;D:Exposure of the superior laryngeal nerve between the sternothyroid muscle and the cricothyroid muscle
2 结 果
2.1 患者手术情况
20例均在完全腔镜下成功完成手术,无中转。3例甲状腺腺瘤,行单侧腺叶大部分切除术;13例结节性甲状腺肿,其中单侧甲状腺大部分切除术5例,双侧甲状腺大部分切除术8例;4例为原发性甲亢,行双侧甲状腺大部分切除术。手术时间(65±23.3)min;术中出血量(5.5±1.9)mL,手术需要显露喉返神经和喉上神经共32侧,本组显露喉上神经外支26侧(81.2%,26/32),喉返神经30侧(93.7%,30/32)。
2.2 患者术后情况
术后手术及神经损伤的相关症状,术后第1天引流量(54.5±32.5)mL。术后住院时间2~3 d,术后第1天VAS疼痛评分0~1分,术后随访3个月,无复发,术后1个月仅1例患者出现颈部压迫感和吞咽连动现象,患者对美容效果满意。
3 讨 论
近年来,由于甲状腺疾病的发病率呈上升趋势,且多见于女性,其对手术的美容效果要求高,腔镜甲状腺手术满足了患者对美容效果的需求,自应用该技术以来,得到了广大患者的欢迎,特别受到青年女性的青睐。并得到不断的发展和完善,各国学者探索了多种腔镜甲状腺手术的方法,如全乳晕径路[1-2]、腋窝径路[3-4]、腋窝乳晕联合径路[5-10]、经口腔径路[11-12]等,各种手术方法都有其优缺点和适应证,也是安全可行的,其突出的美容效果和大量患者的需求使得该手术广泛的开展,手术适应证也不断扩大[13-15],对预防相关并发症提出更高的要求:如怎样更好的保护神经和甲状旁腺,减少相关并发症;怎样减少术后吞咽时颈部皮肤牵拉连动现象和发紧压迫感。神经和旁腺的保护关键是显露和辨认,这在腔镜手术有时候是困难的,特别是喉上神经的显露。而颈部皮肤牵拉连动和压迫感往往出现在气管前区域,与颈白线的切开和缝合存在很大的关系,缝线作为异物必然增加粘连程度。为改善目前腔镜甲状腺手术的一些不足,笔者初步探索开展了腔镜SISA甲状腺手术。
SISA是通过打开颈部带状肌肉自然间隙显露甲状腺进行手术,游离胸骨甲状肌、胸骨舌骨肌及肩甲舌骨肌之间的自然间隙,通过牵拉显露双侧甲状腺,进行手术,不切开颈白线,颈部创面免缝合,可明显缩短手术时间。本组病例手术时间(65±23.3)min,比同一手术者所开展的所报道双侧腋窝同侧乳晕径路甲状腺手术[16]的手术时间[(85.5±23.2)min]和双侧乳晕同侧腋窝径路甲状腺手术的手术时间[(74.4±11.9)min]缩短[17],术中出血少,说明其操作并不难,出血少。颈前肌间隙径路不切断任何肌肉,手术结束时肌肉自然封闭创面,对机体创伤小,术后第1天疼痛评分为0~1,术后疼痛轻微。不需要应用镇痛药物。SISA不切开颈白线,不用缝合,术后颈部粘连轻,术后1个月仅1例患者出现颈部压迫感和吞咽连动现象。当然对粘连的评估需要对比研究,随着例数的积累,笔者将开展一系列的对比研究。
神经和甲状旁腺的损伤是内镜甲状腺手术常见也是最严重的并发症,其发生率对不同的作者存在很大的差异,目前对喉返神经损伤的预防关键是手术显露神经并应用神经检测(IONM)检测保护其功能完整,使其损伤的几率大大下降,喉上神经外支由于术中显露困难和损伤后对患者的影响较小,目前大多重视喉返神经的保护而忽视喉上神经的保护,由于喉上神经与甲状腺上血管的紧密解剖关系,大多医生多未能解剖而是选择避开[18-19]。
喉上神经外支损伤可引起环甲肌功能障碍,导致音质、音调的改变,影响生活质量,特别是对音质、音调特殊要求者。因此,近几年对喉上神经的辨认和功能保护越来越受到重视。喉上神经外支的保护可通过IONM检测进行保护,由于仅有34.9%可显露喉上神经[20],因此仍有一定的损伤几率,因此许多学者[21-23]通过横断胸骨甲状肌可达到80%~86%的显露喉上神经外支。此方法损伤肌肉,加大创伤和术后粘连。SISA通过胸骨舌骨肌和胸骨甲状肌的间隙可以充分显露喉返神经和下甲状旁腺,而喉上神经的显露和保护可以通过胸骨甲状肌和环甲肌的间隙进行寻找保护,如果上极位置高或者肿瘤位于上极且肿瘤较大导致显露困难,则可通过胸锁乳突肌、胸骨甲状肌和肩胛舌骨肌的间隙进行寻找保护,本组显露喉上神经达81.2%,而显露喉返神经达93.7%,充分显示肌间隙入路对神经显露和保护的优势,同时联合IONM,能更好的保护神经的功能,本组术后无神经损伤的相关症状。
因此笔者认为该手术具有以下优点:⑴不切开颈白线,免缝合,可能减少术后颈部粘连和吞咽皮肤联动现象。⑵能充分显露喉返神经及喉上神经,联合IONM可做到神经的解剖和功能的保护。⑶操作容易,可以处理双侧病变,易推广。
总之。SISA手术选择合适的病例是安全可行的,具有免缝合、易显露神经、颈部粘连轻、操作容易优点。是值得推广的内镜甲状腺手术径路。
[1]Ohgami M,Ishii S,Arisawa Y,et a1.Scarless endoscopic thyroidectomy:breast approach for better cosmesis[J].Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech,2000,10(1):1-4.
[2]Park YL,Han WK,Bae WG.100 cases of endoscopic thyroidectomy:breast approach[J].Surg Laparosc Endosc PercutanTech,2003,13(1):20-25.
[3]Ikeda Y,Takami H,Niimi M,et a1.Endoscopic thyroidectomy by the axillary approach[J].Surg Endosc,2001,15(11):1362-1364.doi:10.1007/s004640080139.
[4]Cho J,Lee D,Baek J,et al.Single-incision endoscopic thyroidectomy by the axillary approach with gas inflation for the benign thyroid tumor:retrospective analysis for a single surgeon's experience[J].Surg Endosc,2017,31(1):437-444.doi:10.1007/s00464-016-5093-5.
[5]Shimazu K,Shiba E,Tamaki Y,et a1.Endoscopic thyroid surgery through the axillo-bilateral-breast approach[J].Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech,2003,13(3):196-201.
[6]Bärlehner E,Benhidjeb T.Cervical scarless endoscopic thyroidectomy:Axillo-bilateral-breast approach(ABBA)[J].Surg Endosc,2008,22(1):154-157.doi:10.1007/s00464-007-9393-7.
[7]Choe JH,Kim SW,Chung KW,et al.Endoscopic thyroidectomy using a new bilateral axillo-breast approach[J].World J Surg,2007,31(3):601-606.doi:10.1007/s00268-006-0481-y.
[8]Koh YW,Kim JW,Lee SW,et a1.Endoscopic thyroidectomy via a unilateral axillo-breast approach without gas insufflation for unilateral benign thyroid lesions[J].Surg Endosc,2009,23(9):2053-2060.doi:10.1007/s00464-008-9963-3.
[9]Jeryong K,Jinsun L,Hyegyong K,et al.Total endoscopic thyroidectomy with bilateral breast areola and ipsilateral axillary(BBIA)approach[J].World J Surg,2008,32(11):2488-2493.doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9693-7.
[10]Choi JY,Lee KE,Chung KW,et al.Endoscopic thyroidectomy via bilateral axillo-breast approach(BABA):review of 512 cases in a single institute[J].Surg Endosc,2012,26(4):948-955.doi:10.1007/s00464-011-1973-x.
[11]Anuwong A.Transoral Endoscopic Thyroidectomy Vestibular Approach:A Series of the First 60 Human Cases[J].World J Surg,2016,40(3):491-497.doi:10.1007/s00268-015-3320-1.
[12]Schardey HM,Barone M,Pörtl S,et al.Invisible scar endoscopic dorsal approach thyroidectomy:a clinical feasibility study[J].World J Surg,2010,34(12):2997-3006.doi:10.1007/s00268-010-0769-9.
[13]Lee MC,Park H,Lee BC,et al.Comparison of quality of life between open and endoscopic thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid cancer[J].Head Neck,2016,38(Suppl 1):E827-831.doi:10.1002/hed.24108.
[14]Li Y,Zhou X.Comparison between endoscopic thyroidectomy and conventional open thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma:A meta-analysis[J].J Cancer Res Ther,2016,12(2):550-555.doi:10.4103/0973-1482.157353.
[15]Park KN,Jung CH,Mok JO,et al.Prospective comparative study of endoscopic via unilateral axillobreast approach versus open conventional total thyroidectomy in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma[J].Surg Endosc,2016,30(9):3797-3801.doi:10.1007/s00464-015-4676-x.
[16]靳小建,卢榜裕,蔡小勇,等.完全内镜双侧腋窝同侧乳晕径路甲状腺手术的临床应用[J].中国普通外科杂志,2013,22(11):1441-1445.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2013.11.014.Jin XJ,Lu BY,Cai XY,et al.Clinical application of total endoscopic thyroidectomy via bilateral axillary and ipsilateral breast approach[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2013,22(11):1441-1445.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2013.11.014.
[17]刘祖军,靳小建,蔡小勇,等.完全内镜双侧乳晕同侧腋窝径路甲状腺切除术的临床应用[J].中国普通外科杂志,2018,27(5):642-646.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.05.018.Liu ZJ,Jin XJ,Cai XY,et al.Clinical use of total endoscopic bilateral nipple-areola and ipsilateral axillary route thyroidectomy[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2018,27(5):642-646.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.05.018.
[18]Barczyński M,Randolph GW,Cernea CR,et al.External branch of the superior laryngeal nerve monitoring during thyroid and parathyroid surgery:International Neural Monitoring Study Group standards guideline statement[J].Laryngoscope,2013,123(Suppl 4):S1-14.doi:10.1002/lary.24301.
[19]Patnaik U,Nilakantan A,Shrivastava T.Anatomical variations of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve in relation to the inferior constrictor muscle:cadaveric dissection study[J].J Laryngol Otol,2012,126(9):907-912.doi:10.1017/S0022215112001454.
[20]Uludag M,Aygun N,Kartal K,et al.Contribution of intraoperative neural monitoring to preservation of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve:a randomized prospective clinical trial[J].Langenbecks Arch Surg,2017,402(6):965-976.doi:10.1007/s00423-016-1544-7.
[21]Glover AR,Norlén O,Gundara JS,et al.Use of the Nerve Integrity Monitor during Thyroid Surgery Aids Identi fication of the External Branch of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve[J].Ann Surg Oncol,2015,22(6):1768-1773.doi:10.1245/s10434-014-4142-3.
[22]Hurtado-López LM,Díaz-Hernández PI,Basurto-Kuba E,et al.Efficacy of Intraoperative Neuro-Monitoring to Localize the External Branch of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve[J].Thyroid,2016,26(1):174-178.doi:10.1089/thy.2015.0190.
[23]Selvan B,Babu S,Paul MJ,et al.Mapping the compound muscle action potentials of cricothyroid muscle using electromyography in thyroid operations:a novel method to clinically type the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve[J].Ann Surg,2009,250(2):293-300.doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b17342.
