胰腺癌是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,其发病率逐年增加[1]。胰腺癌是一种生存率极低的高度侵袭性恶性肿瘤,预后极差,总体5年生存率低于5%[2]。由于胰腺癌患者缺乏特异性症状,使得早期诊断困难,通常诊断时已经处于发生局部浸润和远处转移的疾病晚期,从而延误了手术切除时机[3-6]。化疗改善了许多癌症的预后,但其对胰腺癌的治疗效果非常有限,正是由于胰腺癌对化疗药物具有高度的抗性[7]。目前胰腺癌的发病机制仍不清楚,因此迫切需要确定胰腺癌的治疗靶点、预后标记物和新的治疗策略,以对胰腺癌患者的生存提供有意义的影响。
YEATS域含蛋白质4(YEATS domaincontaining protein 4,YEATS4)是一种高度保守的核蛋白,属于YEATS家族结构域蛋白,最初在人脑胶质瘤中被发现[8]。而YEATS结构域由5种YEATS家族结构域蛋白YAF、ENL、AF9、TAF14、SAS5首字母命名[9]。相关报道证实ENL的YEATS结构域通过识别结合组蛋白H3尾部的乙酰化修饰增强白血病相关基因的表达,导致急性白血病发生[10]。目前,YEATS4已被发现参与了致癌过程。YEATS4基因扩增于非小细胞肺癌,抑制p53通路促进肺癌细胞增殖并抑制细胞凋亡[11]。据报道[12],YEATS4作为一种转录调控因子,与卵巢癌细胞的耐药性密切相关。此外,敲低YEATS4蛋白表达可抑制结直肠癌细胞增殖并诱导细胞凋亡[13]。然而,YEATS4在胰腺癌中的功能尚不清楚。本研究利用组织芯片技术及免疫组化方法检测YEATS4在80例胰腺癌组织及相应癌旁组织的表达,分析YEATS4在胰腺癌中的表达与临床病理特征及预后的关系。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料来源
YEATS4抗体购自于台湾Abnova公司,收集了2011年3月—2017年8月于江苏大学附属医院行手术切除以及经病理确诊的80例胰腺导管细胞癌(pancreatic ductal carcinoma,PDAC)患者的临床资料及组织样本。本研究已经通过伦理委员会批准及患者本人知情同意。所有患者术前均未接受任何治疗,样本包括胰腺癌组织及相应癌旁组织。其中男42例,女38例;年龄36~83岁,中位年龄为68岁。
1.2 构建组织芯片
选取80例胰腺癌患者的组织标本,每例标本包含2个位点(胰腺癌组织及相应癌旁组织),共计160个位点,制作我们所需要的组织芯片微阵列。同时充分记录了患者的临床病理信息,包括患者的性别、年龄、肿瘤部位、病理分级、肿瘤分期、淋巴结转移、神经转移、脉管侵犯和随访数据(截至2018年5月)。
1.3 免疫组织化学法检测YEATS4的表达
胰腺癌组织和正常胰腺组织经10%的福尔马林固定脱水,常规石蜡包埋后,4 μm连续石蜡切片。采用ABC法进行免疫组织化学的检测,苏木精复染核。IgG代替YEATS4做一抗,检测YEATS4的特异性。阳性定位于胰腺癌细胞胞核,细颗粒状。
1.4 结果判定
两位病理医师在对临床数据不知情的情况下,对染色结果进行评分。染色强度分为:0,无染色;1+,淡黄;2+,黄色;和3+,棕黄。阳性肿瘤细胞的比例分为3个水平:0分(<10%),1分(20%~24%),2分(25%~50%),3分(>50%)。染色指数(SI)计算为染色强度评分与阳性评分的乘积。 最佳截断值被确定如下:SI得分> 3为阳性表达;SI得分≤3为阴性表达[14]。
1.5 统计学处理
采用统计学软件SPSS进行统计分析,通过χ2检验分析YEATS4表达与临床病理特征之间的关系。Kaplan-Meier法计算生存率,并且绘制生存曲线。运用Log-rank检验,取α=0.05为检验水准,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 临床病理特征
本组80例胰腺癌患者详细临床数据资料。男性52.5%(42例),女性47.5%(38例);中位年龄68(36~83)岁;低分化者26.25%(21例),中分化者48.75%(39例),高分化者25%(20例);TNM分期为I/II期者46.25%(37例),III/IV期者53.75%(43例);有神经转移者50例,无神经转移者30例;有淋巴结转移者40例,无淋巴结转移者 40例;有脉管侵犯者33例,无脉管侵犯者47例。
2.2 YEATS4蛋白在胰腺癌组织及胰腺癌旁组织的表达
YEATS4蛋白在胰腺癌组织及胰腺癌旁组织的表达主要在细胞核。YEATS4在胰腺癌组织中的表达明显高于与其对应癌旁组织中的表达(P<0.05)(图1)。胰腺癌组织中YEATS4阳性表达者45例(56.25%),在癌旁组织中阳性表达者为21例(26.25%),胰腺癌组织高表达率高于在胰腺癌旁组织,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
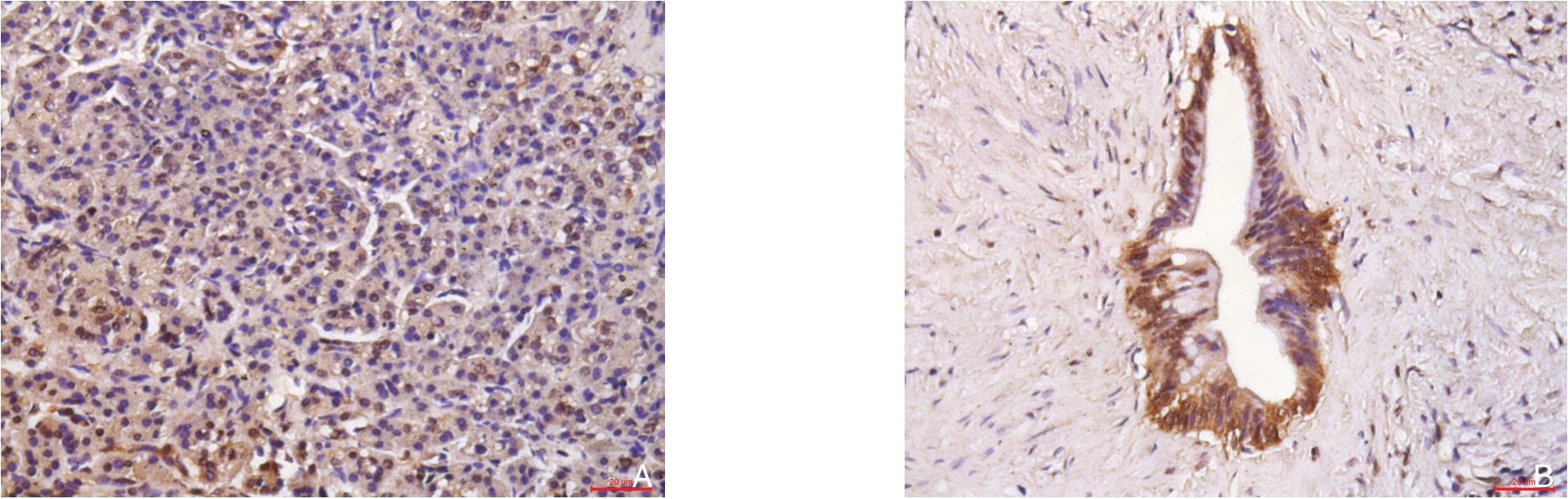
图1 免疫组化法检测YEATS4蛋白表达(×200)
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical staining for YEATS4 protein expression (×200)
A:癌旁组织;B:胰腺癌组织
A: Cancer adjacent tissue; B: Pancreatic cancer tissue
2.3 YEATS4的表达与临床病理特征之间的关系
分析结果显示,YEATS4蛋白表达与胰腺癌患者的性别、TMN分期、神经转移、淋巴结转移及脉管侵犯均有明显关系(均P<0.05)(表1)。
表1 YEATS4蛋白表达与患者临床病理特征的关系[n(%)]
Table 1 Relationship between YEATS4 protein expression and clinicopathologic features of patients [n (%)]

参数阳性(n=45)阴性(n=35)χ2P性别 男19(42.2)23(65.7)4.3570.037 女26(57.8)12(34.3)年龄(岁) ≥6531(68.9)22(62.9)0.3200.571 <6514(31.1)13(37.1)肿瘤部位 胰头32(71.1)29(82.9)1.5000.221 胰体尾13(28.9)6(17.1)分化程度 高分化11(24.4)9(25.7) 中分化23(51.2)16(45.7)0.2580.879 低分化11(24.4)10(28.6)TNM分期 I/II11(24.4)26(74.3)19.6730.000 III/IV34(75.6)9(25.7)神经转移 有34(756)16(45.7)7.4800.006 无11(24.4)19(54.3)淋巴结转移 有31(68.9)9(25.7)14.6790.000 无14(31.1)26(74.3)脉管侵犯 有23(51.1)10(28.6)4.1270.042 无22(48.9)25(71.4)
2.4 YEATS4的表达与预后的关系
经Kaplan-Meier生存分析及Log-rank检验显示,YEATS4阳性表达组的中位生存时间为15.44个月,阴性表达组的中位生存时间为26.10个月,YEATS4的阳性表达组的预后较阴性表达组差,差异有统计学意义(χ2=7.593,P=0.0059)(图2)。分别分析YEATS4在TMN分期、淋巴结转移、神经转移和脉管侵犯患者中的表达与预后的关系,结果显示,YEATS4阳性表达的胰腺癌患者的不良预后与淋巴结转移、神经转移及肿瘤临床分期相关(图3)。单因素分析提示,YEATS4蛋白表达、TMN分期及淋巴结转移与患者生存预后紧密相关(均P<0.05),多元Cox回归模型分析结果证实,YEATS4蛋白表达可以作为胰腺癌患者预后的独立危险因素(HR=2.1,95% CI=1.1~4.2,P=0.026)(表2)。

图2 YEATS4阳性与阴性胰腺癌患者生存曲线
Figure 2 Survival curves of pancreatic cancer patients with positive and negative YEATS4 expression
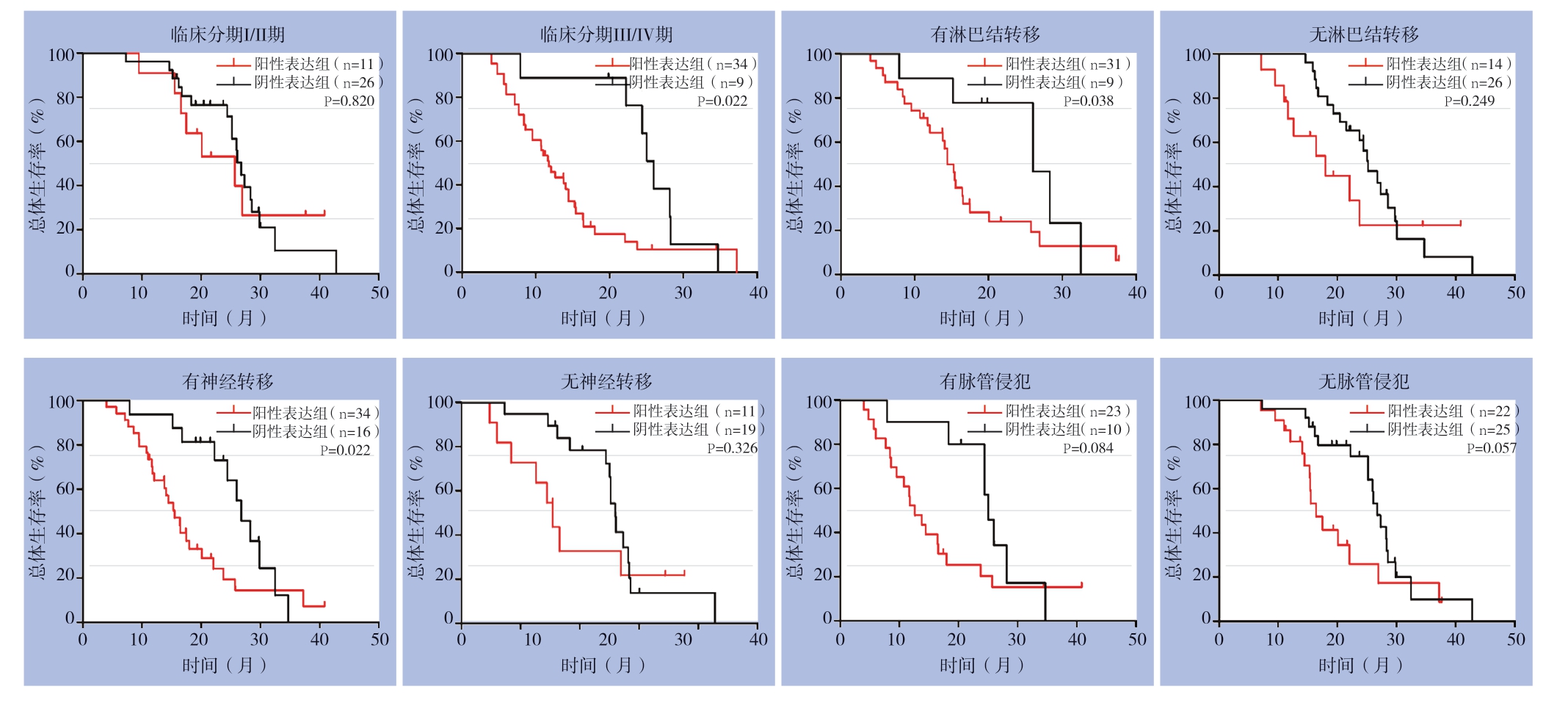
图3 不同临床病理因素胰腺癌患者中YEATS4表达与生存率的关系
Figure 3 Relationship between YEATS4 and prognosis in pancreatic cancer patients with different clinicopathologic features
表2 胰腺癌患者预后因素分析
Table 2 Analysis of prognostic factors for pancreatic cancer patients
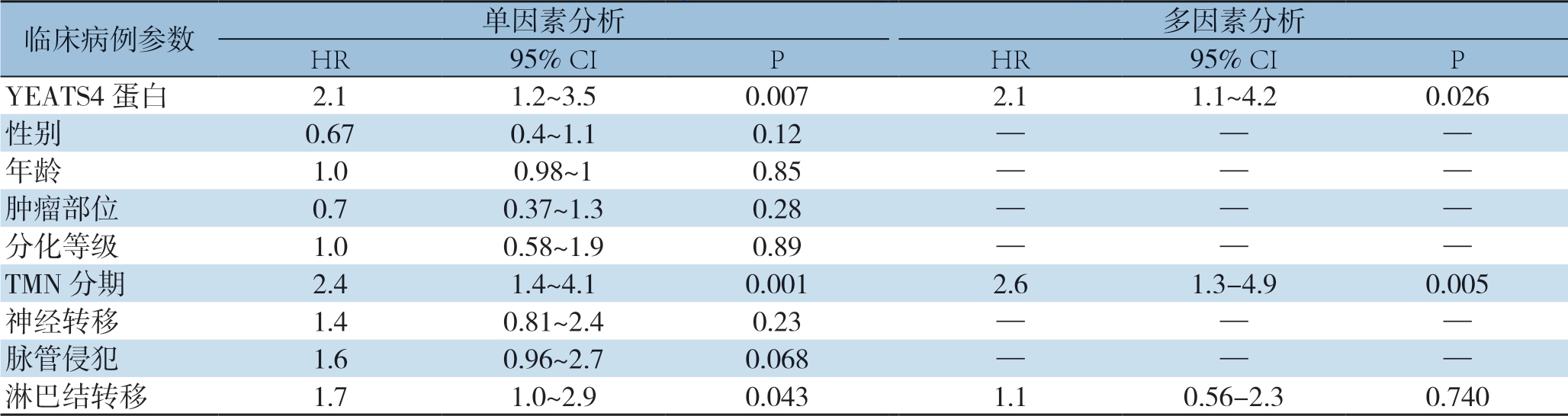
临床病例参数单因素分析多因素分析HR95% CIPHR95% CIP YEATS4蛋白2.11.2~3.50.0072.11.1~4.20.026性别0.670.4~1.10.12——年龄1.00.98~10.85——肿瘤部位0.70.37~1.30.28——分化等级1.00.58~1.90.89——TMN分期2.41.4~4.10.0012.61.3-4.90.005神经转移1.40.81~2.40.23——脉管侵犯1.60.96~2.70.068——淋巴结转移1.71.0~2.90.0431.10.56-2.30.740
3 讨 论
YEATS4位于人类染色体区域12q13-15,其蛋白含有227个氨基酸,分子量为26.7 kD。YEATS4在C-末端具有带负电荷的α-螺旋结构,这是真核转录因子激活域的典型特征,也是蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用区域[8]。N端结构域是由YEATS蛋白家族中高度保守的tf2f结构域组成[15]。Ding等[16]报道YEATS4可以作为转录共激活剂用于AP-2β以增强其DNA结合活性。先前研究指出YEATS4与人类MLLT1和MLLT3蛋白具有高度的序列同源性,表明编码的蛋白可能代表某种转录因子,可以通过 C末端激活域与髓细胞-淋巴细胞白血病(myeloid-lymphoid leukemia,MLL)编码蛋白AF10相互作用,参与白血病的发生和发展[17]。YEATS4通过与一般转录因子TFIIF相互作用,在RNA转录过程中起着重要作用[18]。最近研究[19]表明,YEATS4是一个关键的RNA干扰(RNA interference,RNAi)组分,可使细胞核中RNAi过程正常进行。以上研究表明YEATS4在RNA转录过程中的重要性,参与了细胞增殖、分化和致癌等过程。
本次研究结合应用了免疫组化技术和临床数据资料分析揭示YEATS4在胰腺癌组织中的异常表达及预后意义。研究结果显示,YEATS4在胰腺癌组织中的表达显著高于正常组织及癌旁组织,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。同时,YEATS4表达与性别、TMN分期、神经转移、淋巴结转移、脉管侵犯有关(P<0.05),而与年龄、肿瘤部位、分化程度无关。这说明胰腺癌的发生是一种渐进逐步发展的过程,YEATS4可能参与了胰腺癌的发展和转移过程。生存分析表明YEATS4蛋白阴性表达组与阳性表达组相比具有生存优势,生存期相对延长。此外,发现在YEATS4高表达的胰腺癌患者中临床分期较晚(III~IV)、有淋巴结转移及神经转移的预后相对较差。单因素及多因素回归分析结果进一步证实了YEATS4蛋白表达可作为胰腺癌患者预后的独立危险因素。
多数研究表明,多种类型肿瘤具有沿神经侵袭的生物学特性,是影响肿瘤患者术后生存质量的重要因素。胰腺癌细胞可直接浸润神经束膜或束膜周围的脉管,侵犯神经,形成新的转移灶,是造成胰腺癌患者严重背痛和术后复发的原因。Ji等[20]发现YEATS4调节细胞核和细胞裂解液中β-链接蛋白(β-catenin)的表达和磷酸化,同时,YEATS4直接调控β-catenin的转录表达并调控β-catenin启动子区的乙酰化。胞质β-catenin的磷酸化/降解过程调节着Wnt经典信号通路,Wnt/β-catenin通路是诱导上皮组织上皮间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)产生的关键信号转导通路[21]。Schmalhofer等[22]证实EMT发生后,肿瘤细胞的侵袭能力将明显增强。由此推测YEATS4可能通过间接调控Wnt/β-catenin通路来诱导胰腺癌上皮EMT的发生,从而引起癌细胞的侵袭和转移,有待后续基础实验的进一步验证。
本次研究应用了组织芯片技术,进一步证实了YEATS4在胰腺癌组织中的高表达与预后价值,将对胰腺癌靶向药物治疗的研发及胰腺癌患者的术后评估提供重要的理论依据和临床指导。
[1]Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, et al. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States[J]. Cancer Res, 2014, 74(11):2913-2921. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0155.
[2]Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(1):7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21442.
[3]Regel I, Hausmann S, Benitz S, et al. Pathobiology of pancreatic cancer: implications on therapy[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2016, 16(2):219-227. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2016.1129276.
[4]Sohal DP, Mangu PB, Khorana AA, et al. Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(23):2784-2796. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.67.1412.
[5]Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2017, 67(1):7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21387.
[6]Jin X, Wu Y. Diagnostic utility of clinical and biochemical parameters in pancreatic head malignancy patientswith normal carbohydrate antigen 19-9 levels[J]. Afr Health Sci, 2015, 15(1):123-130. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v15i1.17.
[7]Saung MT, Zheng L. Current Standards of Chemotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer[J]. Clin Ther, 2017, 39(11):2125-2134. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.08.015.
[8]Fischer U, Heckel D, Michel A, et al. Cloning of a novel transcription factor-like gene amplified in human glioma including astrocytoma grade I[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 1997, 6(11):1817-1822.
[9]Le Masson I, Yu DY, Jensen K, et al. Yaf9, a novel NuA4 histone acetyltransferase subunit, is required for the cellular response to spindle stress in yeast [J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2003, 23(17):6086-6102.
[10]Wan L, Wen H, Li Y, et al. ENL links histone acetylation to oncogenic gene expression in acute myeloid leukaemia [J]. Nature, 2017, 543(7644):265-269. doi: 10.1038/nature21687.
[11]Pikor LA, Lockwood WW, Thu KL, et al. YEATS4 is a novel oncogene amplified in non-small cell lung cancer that regulates the p53 pathway[J].Cancer Res, 2013, 73(24):7301-7312. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1897.
[12]Kim YR, Park MS, Eum KH, et al. Transcriptome analysis indicates TFEB1 and YEATS4 as regulatory transcription factors for drug resistance of ovarian cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(31)31030-31038. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5208.
[13]Tao K, Yang J, Hu Y, et al. Knockdown of YEATS4 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2015, 7(3):616-623.
[14]Zheng J, Huang S, Huang Y, et al. Expression and prognosis value of shp2 in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(6):7853-7859. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4675-5.
[15]Schulze JM, Wang AY , Kobor MS. YEATS domain proteins: a diverse family with many links to chromatin modification and transcription[J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2009, 87(1):65-75. doi: 10.1139/O08-111.
[16]Ding X, Fan C, Zhou J, Zhong Y, et al. GAS41 interacts with transcription factor AP-2beta and stimulates AP-2beta-mediated transactivation[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2006, 34(9):2570-2578. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl319.
[17]Debernardi S, Bassini A, Jones LK, et al. The MLL fusion partner AF10 binds GAS41, a protein that interacts with the human SWI/SNF complex[J]. Blood, 2002, 99(1):275-281.
[18]Heisel S, Habel NC, Schuetz N, et al. The YEATS family member GAS41 interacts with the general transcription factor TFIIF[J]. BMC Mol Biol, 2010, 11:53. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-53.
[19]Gandhi SG, Bag I, Sengupta S, et al. Drosophila oncogene Gas41 is an RNA interference modulator that intersects heterochromatin and the small interfering RNA pathway[J]. FEBS J, 2015, 282(1):153-173. doi: 10.1111/febs.13115.
[20]Ji S, Zhang Y, Yang B. YEATS Domain Containing 4 Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation and Mediates Tumor Progression via Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway[J].Oncol Res, 2017, 25 (9):1633-1641. doi: 10.3727/096504017X1487852814415 0.
[21]朱智杰, 阮君山, 李尧, 等. Wnt信号通路诱导肿瘤细胞上皮间质转化的研究进展[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2012, 28(7):904-907. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2012.07.005.Zhu ZJ, Ruan JS, Li Y, et al. Research progress of Wnt signaling pathway induced EMT in tumor cells[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin, 2012, 28(7):904-907. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2012.07.005.
[22]Schmalhofer O, Brabletz S, Brabletz T. E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and ZEB1 in malignant progression ofcancer[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2009, 28(1/2):151-166. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9179-y.
