胆管癌(cholangiocarcinoma,CCA)起源于肝脏或胆道内的上皮细胞。英美发达国家发病率呈下降趋势,但全球发病率持续增加,大多数CCA患者诊断时处于晚期,对常见化疗药物易产生耐药性而导致预后不佳[1-2]。CCA发病与寄生虫感染、原发性胆道硬化和胆道畸形等危险因素相关[3]。CCA的发生是个涉及遗传改变和环境因素相互作用的复杂过程[4],多种致癌或抑癌基因的突变被认为参与CCA发生和进展[5]。长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)是一类长度超过200 nt的RNA分子,其异常表达与包括癌症在内的多种疾病密切相关[6-8]。lncRNA CBR3-AS1(也称PlncRNA1)最早发现其在前列腺癌组织中上调并调节细胞增殖和凋亡[9]。然而,lncRNA CBR3-AS1在CCA中的功能尚未完全阐明。本研究旨在探讨CCA患者癌组织中lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达状态及其与预后的关系,并探讨其对CCA细胞增殖和侵袭的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 组织标本收集
本研究收集华中科技大学同济医学院附属武汉中心医院肝胆胰外科于2012年1月—2014年1月期间手术切除的CCA患者组织标本58例。纳入标准:⑴ 患者经病理诊断为原发性CCA;⑵ 除CCA外不存在其他部位原发性恶性肿瘤;⑶ 术前患者未经过任何放化疗或生物治疗;⑷ 具有完整的病例和随访资料。排除标准:不符合上述标准者。本研究经过医院伦理委员会批准同意。
1.2 临床资料收集和随访
收集患者临床资料和随访信息。患者总生存时间为手术后出院第1天到死亡时间或随访截止时间。通过电话或门诊随访,每3个月随访1次,行肝脏彩超、腹部CT及肿瘤标志物检查,随访内容包括患者复发及死亡情况,随访截止至2019年1月,最长随访时间6年,共2例失访。
1.3 实验材料和试剂
CCA细胞系(RBE和QBC939)和正常人胆管上皮细胞系(HIBE)购自日本生物样本保存库。lncRNA CBR3-AS1过表达质粒、阴性对照质粒及lncRNA CBR3-AS1敲降质粒均由上海吉玛生物科技有限公司合成。MTT试剂盒、DMEM培养基、胰蛋白酶和胎牛血清均购于美国Gibco公司,RIPA细胞裂解液及BCA试剂盒购于北京碧云天公司,TRIzol提取试剂、一步法cDNA逆转录试剂盒及SYBR Green real-time PCR MasterMix购于美国Invitrogen 公司,ABI-7500平台。LipofectamineTM 3000 购买自美国Invitrogen公司,qPCR引物由上海生工公司设计并合成。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 细胞培养、转染及分组 所有细胞系在5%CO2、37 ℃条件下培养,培养基为DMEM培养基,取对数期生长良好的细胞行下一步实验。
1.4.2 组织及细胞分组 将CCA细胞系RBE在六孔板上长至汇合80%以上时,按LipofectamineTM3000说明书分别转染lncRNA CBR3-AS1过表达质粒(过表达组)、阴性对照质粒(对照组)及lncRNA CBR3-AS1沉默表达质粒(沉默组)。
1.4.3 细胞活力检测 使用3-(4,5-二甲基噻唑-2-基)-2,5-二苯基四唑溴化物(MTT)细胞增殖/活力测定试剂盒根据说明书检测细胞活力。测量并记录570 nm波长下每孔的吸光度A570 nm,细胞活力计算公式=(A570 nm样本/A570 nm对照)×100%。
1.4.4 细胞侵袭测定 使用具有8 mm聚碳酸酯核孔过滤器Transwell室行侵袭测定。将转染细胞种植到用40 μL Matrigel预涂覆上室中,用200 μL无血清培养基孵育,且下室用600 μL含FBS的培养基填充。多聚甲醛用于细胞固定,0.1%结晶紫用于染色,37 ℃孵育24 h后计数黏附在下表面的细胞数目。
1.4.5 实 时 定 量PCR(qRT-PCR) 使 用TRIzol从肿瘤标本或细胞系中提取总RNA,并使用SuperScriptIII逆转录酶试剂盒反转录成cDNA。用SYBR Premix Ex Taq TM II试 剂 盒 在ABI-7500平台上进行PCR扩增,GAPDH为内参。lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达采用以下引物测定:lncRNA CBR3-AS1引物序列,正向:5'-CAG TGG GGA ACT CTG ACT CG-3', 反 向5'-GTG CCT GGT GCT CTC TTA CC-3'。GAPDH引物序列,正向:5'-GTC AAC GGA TTT GGT CTG TAT T-3',反向:5'-AGT CTT CTG GGT GGC AGT GAT-3'。采用2-ΔΔCt法定量,计算lncRNA CBR3-AS1相对表达量。
1.5 统计学处理
数据以平均值±标准差(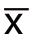 ±s)表示,使用SPSS 20.0行统计分析。t检验用于比较两组间差异,使用Kaplan-Meier法和对数秩检验统计生存率差异,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±s)表示,使用SPSS 20.0行统计分析。t检验用于比较两组间差异,使用Kaplan-Meier法和对数秩检验统计生存率差异,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 lncRNA CBR3-AS1在CCA组织与细胞系中的表达
lncRNA CBR3-AS1在CCA组织中表达量明显高于癌旁组织[(8.2±1.4)vs.(1.3±0.4),P<0.01](图1A);CCA细胞系RBE和QBC939中CBR3-AS1平均表达水明显高于正常胆管上皮细胞系HIBE(均P<0.01)(图1B)。
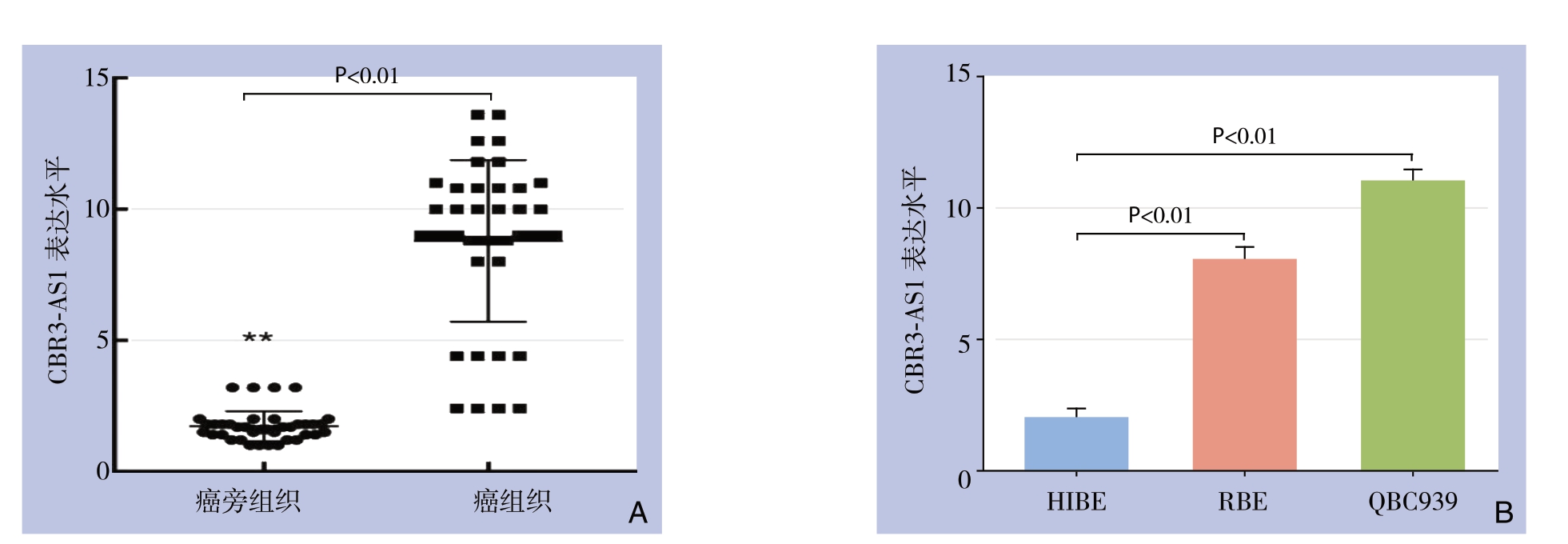
图1 qRT-PCR检测lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达
Figure1 Expressions of lncRNA CBR3-AS1 determined by qRT-PCR
A:CCA组织与癌旁资质的表达;B:CCA细胞系与正常胆管上皮细胞系
A:CCA and adjacent tissues; B:CCA cell lines and normal biliary epithelial cells
2.2 lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达与CCA患者临床病理特征的关系
根据lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达相对水平中位值,将58例CCA患者分为lncRNA CBR3-AS1高表达组30例和lncRNA CBR3-AS1低表达组28例。统计分析结果显示,lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达与年龄、肿瘤部位、血管浸润、分化状态、HBV感染和血清肿瘤标志物CEA和CA19-9均无明显关系(均P>0.05),与淋巴结转移(P=0.030)、TNM分期(P=0.007)和术后复发(P=0.001)明显有关(表1)。
表1 lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达与CCA患者临床病理参数之间的关系[n(%)]
Table1 The relations of lncRNA CBR3-AS1 expression with the clinicopathologic characteristics of cholangiocarcinoma patients [n (%)]

参数 n 高表达(n=30) 低表达(n=28) P性别 男 25 14(46.7) 11(39.3) 0.570 女 33 16(53.3) 17(60.7)年龄(岁) <60 31 18(60.0) 13(46.4) 0.300 ≥60 27 12(40.0) 15(53.6)肿瘤部位 肝内 11 4(13.3) 7(25.0)0.481 肝门 24 14(46.7) 10(35.7) 远端 23 12(40.0) 11(39.3)淋巴结转移 有 25 17(56.7) 8(28.6) 0.030 无 33 13(43.3) 20(71.4)血管浸润 阳性 17 11(36.7) 6(21.4) 0.202 阴性 41 19(63.3) 22(78.6)分化程度 高/中 20 10(33.3) 10(35.7) 0.848 低 38 20(66.7) 18(64.3)TNM分期 I~II 33 12(40.0) 21(75.0) 0.007 III~IV 25 18(60.0) 7(25.0)HBV感染 阳性 26 13(43.3) 13(46.4) 0.812 阴性 32 17(56.7) 15(53.6)血浆CEA(ng/mL) >5 38 21(70.0) 17(60.7) 0.457 ≤5 20 9(30.0) 11(39.3)血浆CA19-9(μL/mL) >37 36 22(73.3) 14(50.0) 0.067 ≤37 22 8(26.7) 14(50.0)术后复发 有 42 27(90.0) 15(53.6) 0.001 无 16 3(10.0) 13(46.4)
2.3 lncRNA CBR3-AS1高表达与CCA患者预后的关系
Kaplan-Meier生存分析示,lncRNA CBR3-AS1高表达组CCA患者总生存率明显低于lncRNA CBR3-AS1低表达组CCA患者(P=0.004)(图2)。
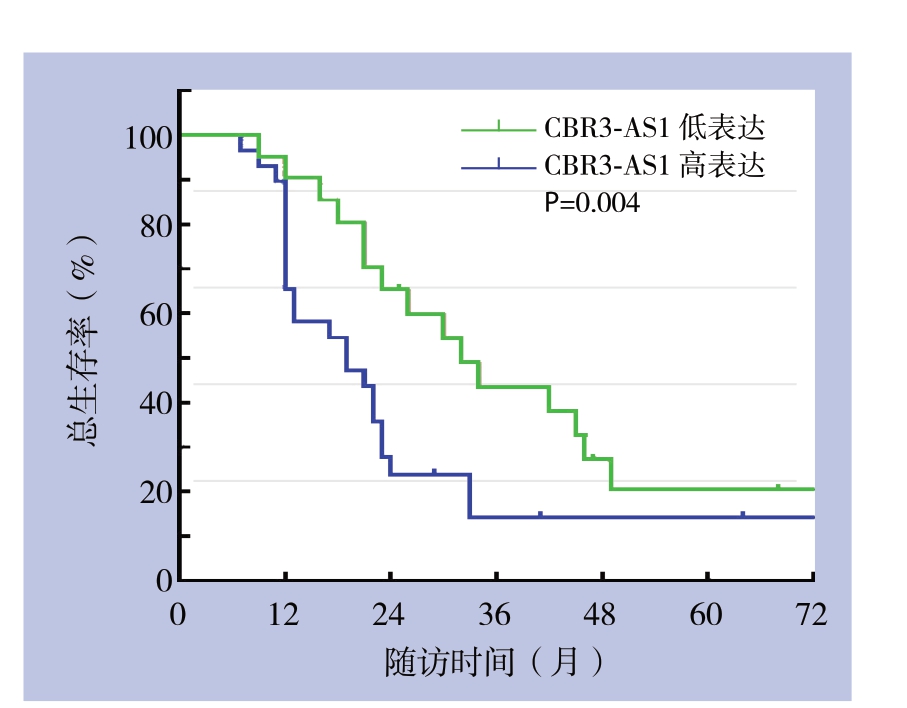
图2 不同lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达水平CCA患者的生存曲线
Figure2 The survival curves of CCA patients with different lncRNA CBR3-AS1 expression levels
2.4 影响CCA患者总生存率的危险因素分析
单因素分析显,示淋巴结转移、血管浸润、TNM分期、术后复发和CBR3-AS1表达是影响总生存率的危险因素(均P<0.01),多因素分析显示,TNM分期(P=0.014)和lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达(P=0.020)是影响CCA患者总生存率的独立危险因素(表2)。
2.5 转染效率检测及lncRNA CBR3-AS1对CCA细胞增殖的影响
转染后,沉默组lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达量明显低于对照组(P<0.01);过表达组lncRNA表达量明显高于对照组(P<0.01)(图3)。转染24、48、72 h后,过表达组细胞增殖活力明显高于对照组;沉默组细胞增殖活力明显低于对照组(图4)。
表2 影响CCA患者总生存率的危险因素分析
Table2 Analysis of risk factors for overall survival of CCA patients
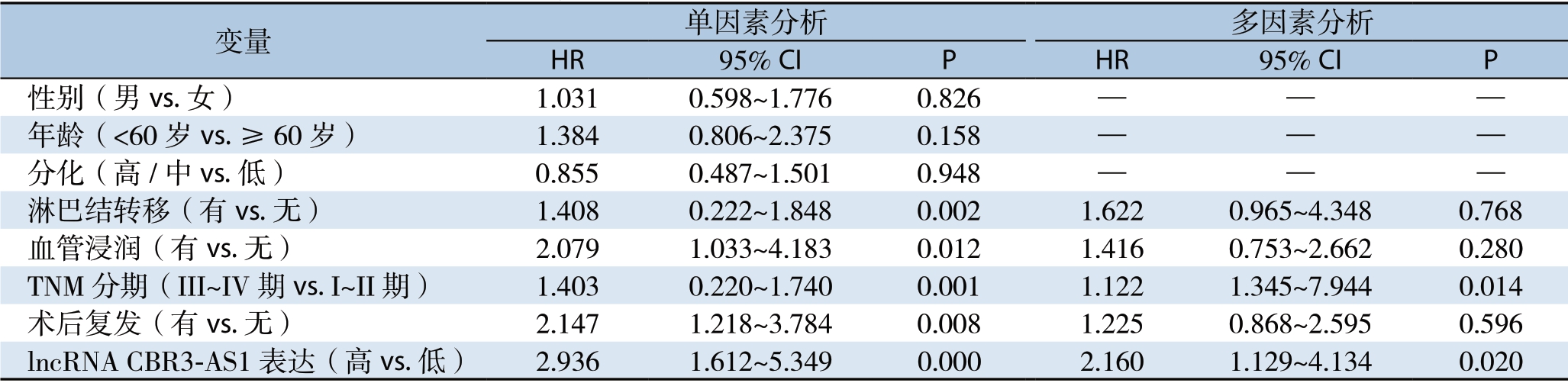
变量 单因素分析 多因素分析HR 95% CI P HR 95% CI P 性别(男vs.女) 1.031 0.598~1.776 0.826 — — —年龄(<60岁vs.≥60岁) 1.384 0.806~2.375 0.158 — — —分化(高/中vs.低) 0.855 0.487~1.501 0.948 — — —淋巴结转移(有vs.无) 1.408 0.222~1.848 0.002 1.622 0.965~4.348 0.768血管浸润(有vs.无) 2.079 1.033~4.183 0.012 1.416 0.753~2.662 0.280 TNM分期(III~IV期vs.I~II期) 1.403 0.220~1.740 0.001 1.122 1.345~7.944 0.014术后复发(有vs.无) 2.147 1.218~3.784 0.008 1.225 0.868~2.595 0.596 lncRNA CBR3-AS1表达(高vs.低) 2.936 1.612~5.349 0.000 2.160 1.129~4.134 0.020

图3 转染效率检测
Figure3 Transfection efficiency measurement

图4 细胞增殖活性检测
Figure4 Cell proliferation assay
2.6 CBR3-AS1在体外调节细胞侵袭
200倍视野下,过表达组侵袭细胞数为(340±23)个,沉默组侵袭细胞数为(115±9)个,对照组侵袭细胞数为(203±17)个;过表达组侵袭细胞数明显多于对照组(P<0.01),沉默组侵袭细胞数明显少于对照组(P<0.01)(图5)。
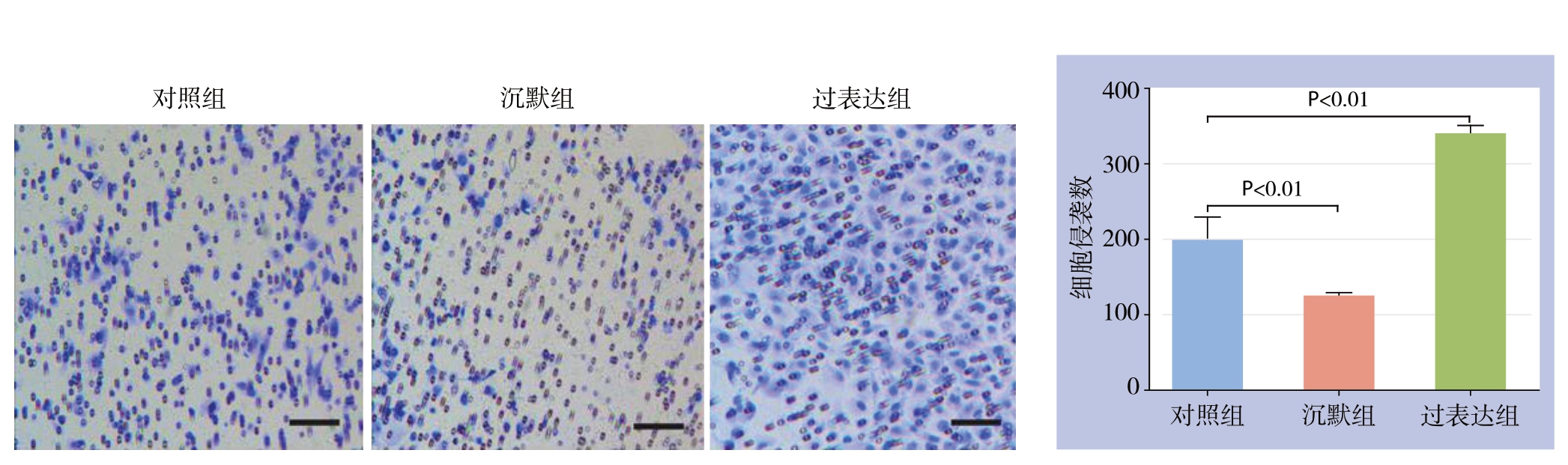
图5 细胞侵袭能力检测(比例尺:100 μm)
Figure5 Determination of the cell invasion ability (scale bar:100 μm)
3 讨 论
CCA是第二常见的原发性肝肿瘤[9]。CCA早期诊断不易,大多数患者诊断时处于晚期而失去最佳手术时机,导致患者5年生存率低至10%,因此,鉴别CCA预后相关分子标志物对改善患者预后至关重要[10]。
全基因组测序技术发展促进了各种非编码RNA(no coding RNA,ncRNA)的发现,其中大量非编码RNA被证实参与癌症发生和发展过程[11],对多种人类癌症具有诊断和预后价值[12]。lncRNA是一种新发现的非编码RNA分子,涉及细胞发育和分化、转录和翻译及代谢调节[13]。越来越多的研究表明lncRNA可作为致癌基因或肿瘤抑制基因参与包括胃癌、肝细胞癌、肺癌、前列腺癌和结肠直肠癌在内的多种肿瘤进展[14-16]。最近研究认为lncRNA也参与CCA发生和进展:如NEAT-1过表达有助于CCA细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移,同时使CCA细胞对化疗药物吉西他滨更敏感[17],CCAT1被证实为CCA患者不良预后标志物[18],而AFAP1-AS1可作为CCA细胞生长和转移启动因子[19]。
lncRNA CBR3-AS1是21号染色体上的蛋白质编码基因,位于羰基还原酶3(CBR3)的反义区域,其可在体外促进乳腺癌细胞增殖和侵袭[20],lncRNA CBR3-AS1在前列腺癌[21]和食道癌[22]的癌组织中过表达且体外调节细胞凋亡和增殖。本研究发现,与相应CCA癌旁组织和正常细胞系比较,lncRNA CBR3-AS1在CCA组织和细胞系中显著上调,lncRNA CBR3-AS1高表达与较差的总生存率相关。单因素和多因素分析显示,lncRNA CBR3-AS1是CCA患者预后不良的独立危险因素。上述结果表明lncRNA CBR3-AS1可能参与CCA肿瘤进展,并可作为潜在预后标志物。近年来研究报道多个lncRNA分子可作为预测CCA不良预后的分子,最新研究报道lncRNA SPRY4-IT1可在CCA中发挥癌基因作用,促进肿瘤发展且与CCA不良预后相关,是新的预后生物标志物[23];而lncRNANEF下调与CCA不良预后相关,并发挥抑癌基因作用[24]。
本研究通过功能丧失和获得实验证明lncRNA CBR3-AS1在CCA肿瘤进展中的功能。lncRNA CBR3-AS1敲降后可显著抑制体外CCA细胞增殖活力;反之,lncRNA CBR3-AS1过表达可显著促进体外CCA细胞增殖。CBR3-AS1过表达可促进CCA细胞侵袭。反之,CBR3-AS1敲降后可抑制CCA细胞侵袭,这与骨肉瘤[25]中的报道类似,在骨肉瘤细胞系中,敲降lncRNA CBR3-AS1可抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖、迁移及侵袭,并诱导凋亡[25]。研究结果提示lncRNA CBR3-AS1作为致癌lncRNA分子在CCA发生和进展中可能起重要作用,这可能解释了CCA lncRNA CBR3-AS1高表达的患者预后差的原因。尽管如此,lncRNA CBR3-AS1靶基因和致癌潜在机制尚值得更进一步研究。
总之,本研究发现lncRNA CBR3-AS1在CCA组织和细胞系中上调表达,与CCA患者不良预后显著相关。lncRNA CBR3-AS1可调节CCA细胞增殖和侵袭,可能是CCA一种新的预后分子标志物和治疗靶点。
[1] Oliveira IS,Kilcoyne A,Everett JM,et al.Cholangiocarcinoma:classification,diagnosis,staging,imaging features,and management[J].Abdom Radiol (NY),2017,42(6):1637-1649.doi:10.1007/s00261-017-1094-7.
[2] Esnaola NF,Meyer JE,Karachristos A,et al.Evaluation and management of intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J].Cancer,2016,122(9):1349-1369.doi:10.1002/cncr.29692.
[3] Nutthasirikul N,Hahnvajanawong C,Techasen A,et al.Targeting the Δ133p53 isoform can restore chemosensitivity in 5-fluorouracilresistant cholangiocarcinoma cells[J].Int J Oncol,2015,47(6):2153-2164.doi:10.3892/ijo.2015.3188.
[4] Sachs N,de Ligt J,Kopper O,et al.A Living Biobank of Breast Cancer Organoids Captures Disease Heterogeneity[J].Cell,2018,172(1/2):373-386.doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.010.
[5] Sae-Lao T,Tohtong R,Bates DO,et al.Sulfated Galactans from Red Seaweed Gracilaria fisheri Target EGFR and Inhibit Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Proliferation[J].Am J Chin Med,2017,45(3):615-633.doi:10.1142/S0192415X17500367.
[6] Hanly DJ,Esteller M,Berdasco M.Interplay between long noncoding RNAs and epigenetic machinery:emerging targets in cancer?[J].Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci,2018,373(1748).pii:20170074.doi:10.1098/rstb.2017.0074.
[7] Fang Y,Fullwood MJ.Roles,Functions,and Mechanisms of Long Non-coding RNAs in Cancer[J].Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics,2016,14(1):42-54.doi:10.1016/j.gpb.2015.09.006.
[8] Wang WT,Ye H,Wei PP,et al.LncRNAs H19 and HULC,activated by oxidative stress,promote cell migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma through a ceRNA manner[J].J Hematol Oncol,2016,9(1):117.doi:10.1186/s13045-016-0348-0.
[9] Bergquist A,von Seth E.Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma[J].Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol,2015,29(2):221-232.doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2015.02.003.
[10] Rizvi S,Khan SA,Hallemeier CL,et al.Cholangiocarcinoma - evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies[J].Nat Rev Clin Oncol,2018,15(2):95-111.doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.157.
[11] Tachmazidou I,Süveges D,Min JL,et al.Whole-Genome Sequencing Coupled to Imputation Discovers Genetic Signals for Anthropometric Traits[J].Am J Hum Genet,2017,100(6):865-884.doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.04.014.
[12] Rachagani S,Macha MA,Heimann N,et al.Clinical implications of miRNAs in the pathogenesis,diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer[J].Adv Drug Deliv Rev,2015,81:16-33.doi:10.1016/j.addr.2014.10.020.
[13] Lin A,Li C,Xing Z,et al.The LINK-A lncRNA activates normoxic HIF1α signalling in triple-negative breast cancer[J].Nat Cell Biol,2016,18(2):213-224.doi:10.1038/ncb3295.
[14] Sanchez Calle A,Kawamura Y,Yamamoto Y,et al.Emerging roles of long non coding RNA in cancer[J].Cancer Sci,2018,109(7):2093-2100.doi:10.1111/cas.13642.
[15] 胡走肖,郑小林.长链非编码RNA MIF-AS1在肝癌中表达及其与上皮-间充质转化的关系[J].中国普通外科杂志,2019,28(7):848-856.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2019.07.011.
Hu ZX,Zheng XL.Expression of long non-coding RNA MIF-AS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its association with epithelialmesenchymal transition[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2019,28(7):848-856.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2019.07.011.
[16] 陈伟业,邢宏松,江帆,等.长链非编码RNA HOST2对胰腺癌细胞增殖迁移和侵袭的影响[J].中国普通外科杂志,2019,28(3):285-291.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2019.03.006.
Chen WY,Xing HS,Jiang F,et al.Effects of long non-coding RNA HOST2 on proliferation,migration and invasion in pancreatic cancer cells[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2019,28(3):285-291.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2019.03.006.
[17] Parasramka M,Yan IK,Wang X,et al.BAP1 dependent expression of long non-coding RNA NEAT-1 contributes to sensitivity to gemcitabine in cholangiocarcinoma[J].Mol Cancer,2017,16(1):22.doi:10.1186/s12943-017-0587-x.
[18] Jiang XM,Li ZL,Li JL,et al.LncRNA CCAT1 as the unfavorable prognostic biomarker for cholangiocarcinoma[J].Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2017,21(6):1242-1247.
[19] Lu X,Zhou C,Li R,et al.Long Noncoding RNA AFAP1-AS1 Promoted Tumor Growth and Invasion in Cholangiocarcinoma[J].Cell Physiol Biochem,2017,42(1):222-230.doi:10.1159/000477319.
[20] Xu L,Zhu H,Gao F,et al.Upregulation of the long non-coding RNA CBR3-AS1 predicts tumor prognosis and contributes to breast cancer progression[J].Gene:X,2019,2:100014.doi:/doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.100014.
[21] Fang Z,Xu C,Li Y,et al.A feed-forward regulatory loop between androgen receptor and PlncRNA-1 promotes prostate cancer progression[J].Cancer Lett,2016,374(1):62-74.doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.033.
[22] Wang CM,Wu QQ,Li SQ,et al.Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA PlncRNA-1 promotes esophageal squamous carcinoma cell proliferation and correlates with advanced clinical stage[J].Dig Dis Sci,2014,59(3):591-597.doi:10.1007/s10620-013-2956-7.
[23] Xu Y,Yao Y,Jiang X,et al.SP1-induced upregulation of lncRNA SPRY4-IT1 exerts oncogenic properties by scaffolding EZH2/LSD1/DNMT1 and sponging miR-101-3p in cholangiocarcinoma[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2018,37(1):81.doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0747-x.
[24] Liang Z,Zhu B,Meng D,et al.Down-regulation of lncRNA-NEF indicates poor prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J].Biosci Rep,2019,39(5).pii:BSR20181573.doi:10.1042/BSR20181573.
[25] Zhang Y,Meng W,Cui H.LncRNA CBR3-AS1 predicts unfavorable prognosis and promotes tumorigenesis in osteosarcoma[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2018,102:169-174.doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.081.
