肝细胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC,简称肝癌)是最常见的原发性肝癌,是全球第六大常见癌症,也是导致癌症相关死亡的第三大原因[1]。近年来随着经济水平的发展,人们生活方式的改变,每年约有84万例肝癌新发病例和78万例肝癌相关死亡病例,其中我国约占50%[2-3]。尽管肝癌的治疗技术与手段日新月异,但晚期肝癌的治疗选择仍非常有限。因此开发肝癌早期诊断标志物与探寻新的治疗靶标分子迫在眉睫。
G蛋白信号调节蛋白2(G-protein-signaling modulator 2,GPSM2),也称LGN,是一种可以调节G蛋白活性的蛋白,在有丝分裂中发挥重要作用[4-6]。GPSM2的异常表达与多种癌症的发生发展有关。既往研究发现沉默GPSM2通过诱导Snail表达促进非小细胞肺癌转移[7]。而在乳腺癌细胞中,GPSM2通过PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1结合激酶(PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1 binding kinase,PBK)影响癌细胞的分化,在侵袭性乳腺癌细胞核中检测到GPSM2表达,则提示患者不良预后[8-9]。在胰腺癌中过表达GPSM2促进肿瘤细胞迁移能力[10]。由此可见,GPSM2在人类恶性肿瘤发生发展中发挥重要作用。本研究旨在分析GPSM2在肝癌及癌旁组织中的表达差异及其与患者临床病理特征和生存率的相关性,通过体外试验验证GPSM2对肝癌细胞增殖和糖酵解的影响,并初步探索其潜在分子机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 临床标本
80例肝癌及对应的癌旁(距离肿瘤边缘2 cm)非肿瘤组织来源于2017年1月—2018年12月我院手术切除并病理确诊的标本。所有组织标本离体后液氮快速冷冻,然后长期保存在-80 ℃冰箱。所有患者均签署了书面知情同意书。本研究由西安交通大学第一附属医院医学伦理委员会批准。
1.2 主要材料
肝癌细胞系Huh7购于中国科学院上海生命科学研究院细胞资源中心,由本实验室保存。Dulbecco的改良Eagle培养基(Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium,DMEM)(Hyclone),胰酶及胎牛血清(Gibco),双抗(Hyclone),X-tremeGENE siRNA Transfection Reagent(Roche),GPSM2抗体(Proteintech),RIPA裂解液、BCA蛋白定量试剂盒、5×蛋白示踪缓冲液(中辉赫彩),TRIzol(Life technologies),SYBR Premix Ex Taq™ II Kit (Takara),己糖激酶-2(hexokinase 2,HK2)、肝脏磷酸果糖激酶(phosphofructokinase, liver type,PFKL)、丙酮酸激酶M2(pyruvate kinase M2,PKM2)抗体(Cell Signaling Technology), 缺氧诱导因子1α(Hypoxia inducible factor-1α,HIF-1α)抗体 (Abcam),聚偏二氟乙烯(Polyvinylidene fluoride,PVDF) 膜、增强化学发光(enhanced chemiluminescent,ECL) 试剂(Millipore),GPSM2、β-肌动蛋白(β-actin)引物(擎科),葡萄糖消耗检测试剂盒、乳酸生成检测试剂盒(Abcam),细胞计数试剂盒-8(Cell Counting Kit-8,CCK-8) (Dojindo)。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 细胞培养 人肝癌细胞Huh7培养于含1%双抗、10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基中,并放置于5%CO2、37℃培养箱或1%O2、37℃培养箱中。取生长状态良好且处于对数期的Huh7细胞用于实验。
1.3.2 细胞转染 将处于生长对数期的Huh7细胞计数,以2×106个细胞/孔种于六孔板,待细胞贴壁且细胞融合度约30%~50%后,按照X-tremeGENE siRNA Transfection Reagent的 使用 说 明 书,取X-tremeGENE siRNA Transfection Reagent(μL)与siRNA(μg)比 值 为10:2,使用不含血清的DMEM稀释X-tremeGENE siRNA Transfection Reagent和 siRNA复合物进行转染。siRNA购于百奥迈科生物技术有限公司。GPSM2 siRNA:正义链5'-AGU UCA AGU UGG AAC UGA AdTdT-3',反 义 链5'-UUC AGU UCC AAC UUG AAC UdTdT-3'。对 照siRNA:正 义 链5'-UGC UGA CUC CAA AGC UCU GdTdT-3',反 义 链5'-CAG AGC UUU GGA GUC AGC AdTdT-3'。
1.3.3 Western blot 用RIPA缓冲液在4℃条件下充分裂解细胞,提取总蛋白质。用BCA法定量蛋白浓度,取适量总蛋白加入5×上样缓冲液后95℃煮沸5 min变性蛋白。将变性的蛋白质在10%SDS聚丙烯酰胺凝胶上进行电泳后转移到PVDF膜上。将膜用10%脱脂牛奶在室温封闭2 h后,膜与一抗(GPSM2:1:500;β-actin:1:1 000;HK2:1:1 000;PKM2:1:2 000;PFKL:1:1 000;HIF-1α:1:1 000)4℃孵育过夜,将膜与二抗(1:1 000)室温孵育2 h,用ECL发光液显影,最后应用Amersham™ Imager 680凝胶成像仪拍照。
1.3.4 RNA提取及qRT-PCR 将TRIzol加入细胞中或者破碎的组织中以提取总RNA,用nanodrop测定RNA浓度后,取1 μg总RNA按PrimeScript RT试剂盒说明书将RNA反转录为cDNA。取3 μL cDNA按照SYBR Premix Ex Taq™ II Kit说明书加入引物进行qRT-PCR。反转录及qRT-PCR在BIO-RAD CFX96上进行。GPSM2正向:5'-AGG CAG CCG TGG ATT TTT ATG A-3';反向:5'-CAC CAC TTT TAT CCC CAA CCT CTC-3'。β-actin正向:5'-GGA CTT CGA GCA AGA GAT GG-3'反向:5'-AGC ACT GTG TTG GCG TAC AG-3'。
1.3.5 肝癌组织中GPSM2表达的预后意义 在GEPIA(http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/detail.php)网站平台分析TCGA数据库中GPSM2 mRNA表达与肝癌患者总体生存率和无病生存率的相关性。
1.3.6 CCK-8实验 将转染的细胞以1×103个/100 μL培养基加入96孔板中,在含5%CO2、37℃培养箱培育24、48、72 h后,加入CCK-8试剂10 μL/孔,37℃孵育2 h,酶标仪测量450 nm处的吸光度。
1.3.7 葡萄糖消耗与乳酸生成实验 葡萄糖消耗实验:将转染的细胞以2×104个/孔种在6 孔板中,待细胞贴壁后,每孔加入2 mL 无血清培养使细胞饥饿过夜。使用PBS 洗3次后,加入2-脱氧葡萄糖。按照葡萄糖消耗检测试剂盒说明书制备样品,并测量样品在412 nm 的吸光度。乳酸生成实验:将转染的细胞以3×104个/ 孔种在6 孔板中,待细胞贴壁后,每孔加入2 mL 无血清培养,收集24 h后的细胞培养基,离心除去细胞碎片,按照乳酸生成检测试剂盒的说明书加入反应液,检测样品在450 nm处的吸光度。
1.3.8 缺氧模型的建立 将处于生长对数期的Huh7 细胞计数,以5×106个细胞种于皿中,培养基为DMEM 高糖培养基加入10% 胎牛血清和1%双抗,将细胞放入常氧培养箱,待细胞贴壁后放入缺氧培养箱,48 h后取出进行后续实验。
1.4 统计学处理
实验结果采用GraphPad Prism 8.0软件进行分析,两组计量资料采用非参数Wilcoxon符号秩检验,均数比较采用独立样本t检验,各组间比较采用方差分析,P<0.05差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 GPSM2 在肝癌和癌旁非肿瘤组织中的表达
提取80例肝癌组织和癌旁非肿瘤组织总RNA进行qRT-PCR分析,结果显示肝癌组织中GPSM2m RNA表达相较于癌旁非肿瘤组织明显升高(P<0.0001)(图1)。另外,随机选取20例肝癌组织与对应癌旁组织进行Western blot检测,结果提示GPSM2蛋白水平在肝癌组织中也明显高于癌旁组织(P<0.0001)(图2)。

图1 GPSM2 mRNA 在肝癌及癌旁非肿瘤组织中的表达
Figure1 The expression of GPSM2 mRNA in HCC and adjacent non-tumor tissues

图2 GPSM2 蛋白在肝癌及癌旁非肿瘤组织中的表达
Figure2 The GPSM2 protein levels in HCC and adjacent non-tumor tissues
2.2 肝癌组织中GPSM2 mRNA表达与临床病理特征的关系
根据肝癌组织中GPSM2 mRNA表达中位数(5.48)把所有病例分为低表达组(<5.48,n=40)和高表达组(≥5.48,n=40)。如表1所示,GPSM2 mRNA表达与肝癌患者肿瘤大小(P=0.003)、Edmondson-Steiner分级(P=0.025)和TNM分期(P=0.045)有关,而与年龄、性别、HBV感染、血清AFP水平、肿瘤数、血管侵犯无关(均P>0.05)。
2.3 肝癌组织中GPSM2 mRNA表达与患者生存率的关系
在GEPIA(http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/detail.php)网站平台基于TCGA数据分析肝癌组织中GPSM2 mRNA表达与患者预后的相关性,结果显示GPSM2 mRNA高表达的肝癌患者总生存率和无病生存率均明显低于GPSM2 mRNA低表达肝癌患者(均P<0.0001)(图3)。
表1 GPSM2 mRNA 表达与肝癌患者临床病理特征的关系[n=40,n(%)]
Table1 Relations of GPSM2 mRNA expression with clinicopathologic features of HCC patients [n=40,n (%)]
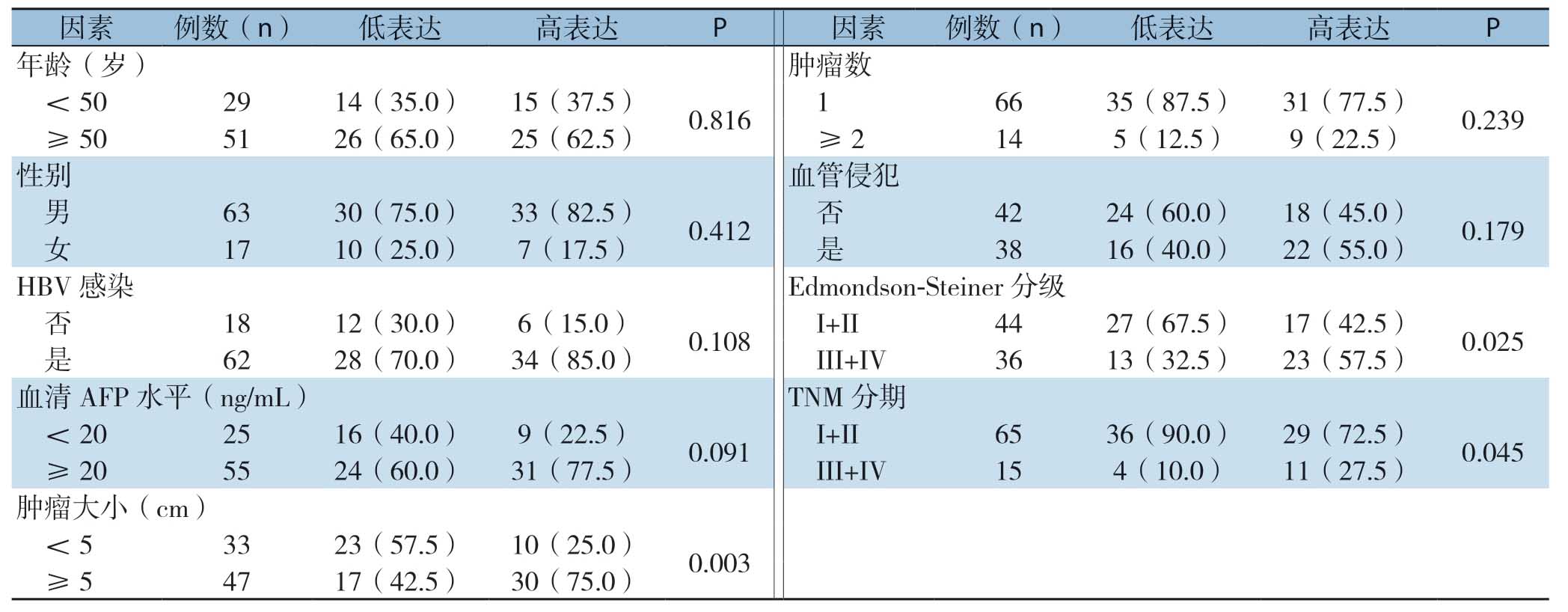
因素例数(n) 低表达 高表达 P 因素例数(n) 低表达 高表达 P年龄(岁) 肿瘤数<50 29 14(35.0) 15(37.5) 0.816 1 66 35(87.5) 31(77.5) 0.239≥50 51 26(65.0) 25(62.5) ≥2 14 5(12.5) 9(22.5)性别 血管侵犯男63 30(75.0) 33(82.5) 0.412 否 42 24(60.0) 18(45.0) 0.179女17 10(25.0) 7(17.5) 是 38 16(40.0) 22(55.0)HBV 感染 Edmondson-Steiner分级否18 12(30.0) 6(15.0) 0.108 I+II 44 27(67.5) 17(42.5) 0.025是62 28(70.0) 34(85.0) III+IV 36 13(32.5) 23(57.5)血清AFP 水平(ng/mL) TNM分期<20 25 16(40.0) 9(22.5) 0.091 I+II 65 36(90.0) 29(72.5) 0.045≥20 55 24(60.0) 31(77.5) III+IV 15 4(10.0) 11(27.5)肿瘤大小(cm)<5 33 23(57.5) 10(25.0) 0.003≥5 47 17(42.5) 30(75.0)

图3 GPSM2 mRNA 高表达与低表达肝癌患者生存分析 A:总生存率曲线;B:无病生存率曲线
Figure3 Survival analysis of HCC patients with high or low expression of GPSM2 mRNA A:Overall survival curves;B:Disease-free survival curves
2.4 干扰GPSM2 对肝癌细胞增殖和糖酵解的影响
在Huh7细胞中瞬时转染GPSM2 siRNA和对照组siRNA,转染48 h后Western blot检测发现干扰组GPSM2蛋白水平明显降低(P<0.05)(图4)。应用CCK-8检测细胞增殖能力变化,结果显示干扰GPSM2明显抑制Huh7细胞增殖能力(P<0.05)(图5)。另外,检测结果发现干扰GPSM2明显抑制Huh7细胞葡萄糖消耗和乳酸生成(P<0.05)(图6)。
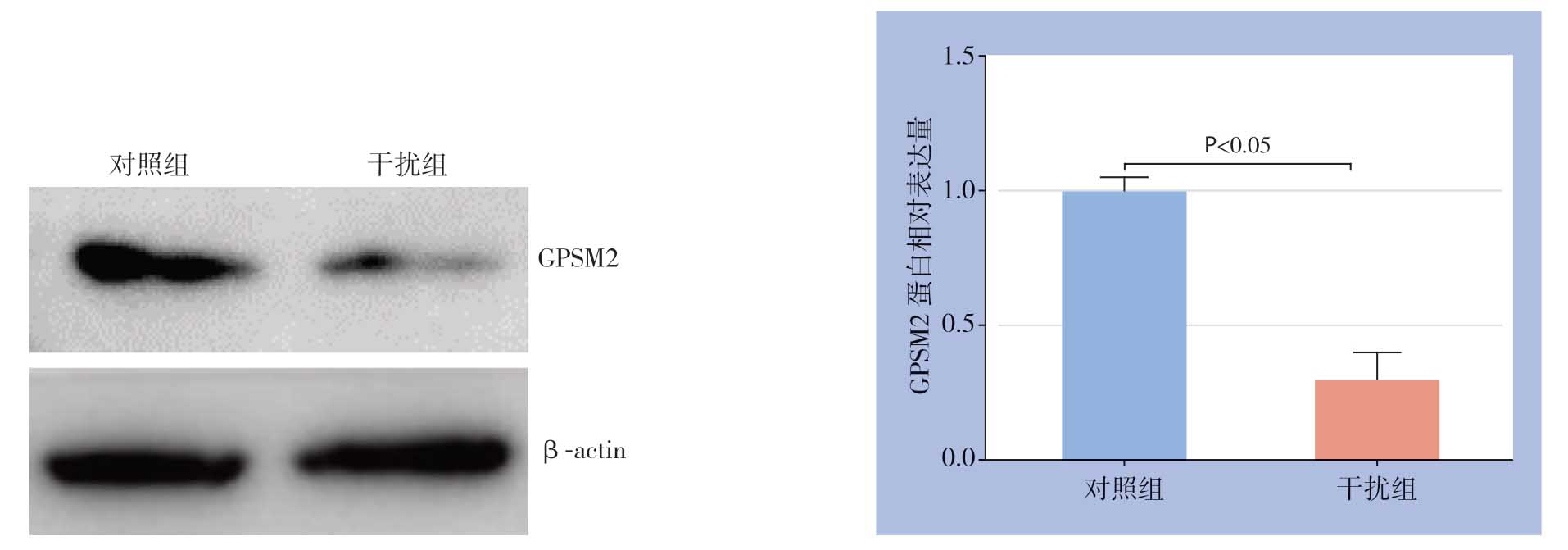
图4 GPSM2 siRNA 在Huh7 细胞中的干扰效果
Figure4 The knockdown efficiency of GPSM2 siRNA in Huh7 cells
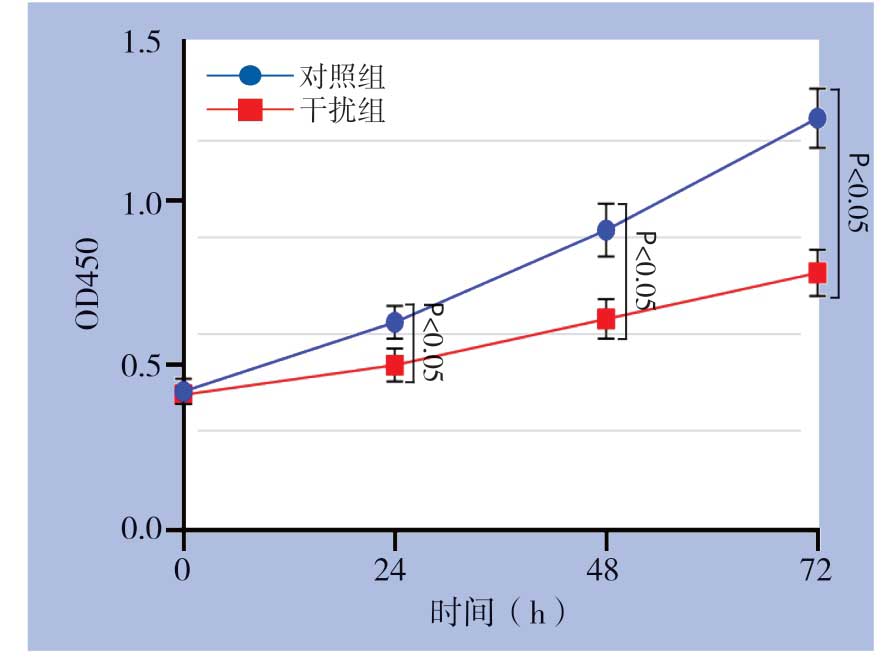
图5 干扰GPSM2 对Huh7 细胞增殖能力的影响
Figure5 Effect of GPSM2 silencing on the proliferation of Huh7 cells

图6 干扰GPSM2 对Huh7 细胞葡萄糖消耗和乳酸生成的影响
Figure6 Effects of GPSM2 silencing on the glucose consumption and lactate production of Huh7 cells
2.5 干扰GPSM2 对肝癌细胞中糖酵解关键限速酶蛋白水平的影响

图7 干扰GPSM2 对Huh7 细胞中HK2、PFKL 和PKM2 蛋白表达的影响
Figure7 Effects of GPSM2 silencing on HK2,PFKL,and PKM2 protein expressions in Huh7 cells
糖酵解过程受到3个关键限速酶调控,包括HK2、PFKL和PKM2。应用Western blot检测干扰GPSM2对Huh7细胞中HK2、PFKL和PKM2蛋白水平的影响。结果发现干扰GPSM2明显减少HK2蛋白水平(P<0.05),而不影响PFKL和PKM2蛋白水平(图7)。
2.6 缺氧诱导肝癌细胞中GPSM2表达
缺氧微环境是肝癌细胞糖酵解的关键驱动因素,故进一步研究缺氧是否诱导肝癌细胞中GPSM2表达。将Huh7细胞在缺氧培养箱中培养48 h后,Western blot检测HIF-1α和GPSM2蛋白水平。结果显示缺氧导致Huh7细胞中HIF-1α蛋白明显蓄积,同时缺氧导致GPSM2蛋白水平明显上调(P<0.05)(图8)。
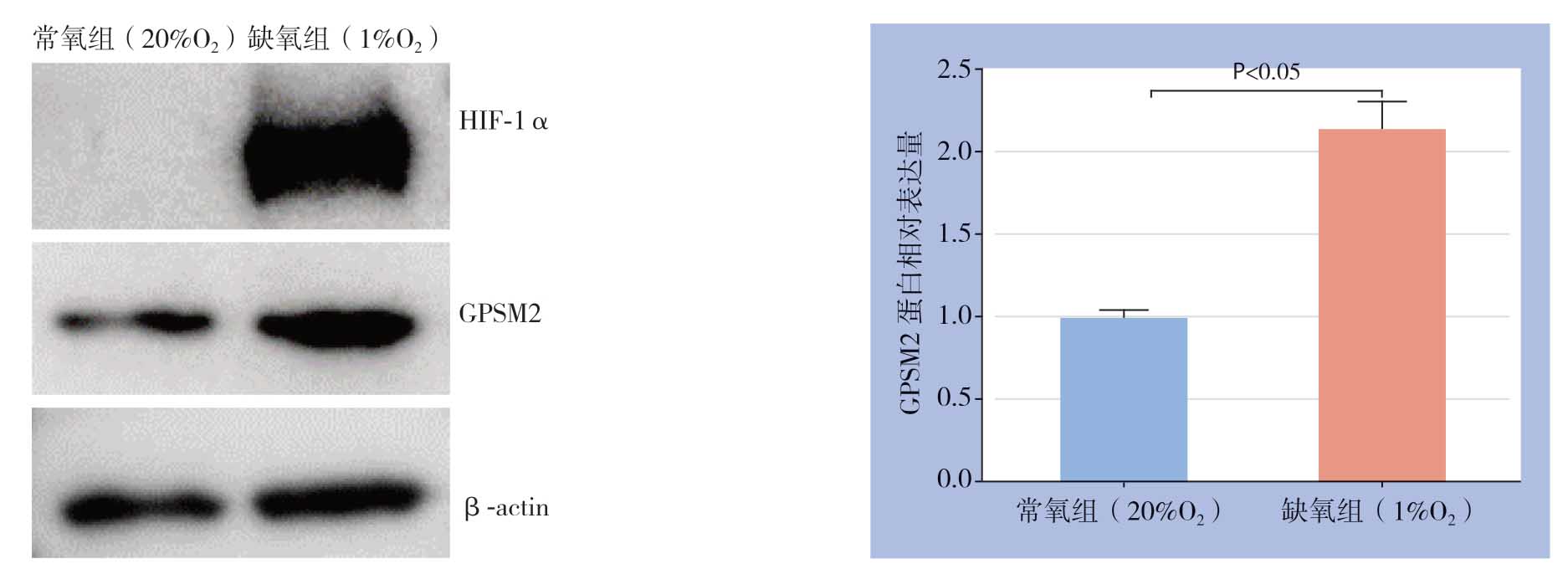
图8 缺氧对Huh7 细胞中HIF-1α 和GPSM2 蛋白表达的影响
Figure8 Effects of hypoxia on HIF-1α and GPSM2 protein expression in Huh7 cells
3 讨 论
肝癌是世界范围内最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,每年中国有超过30万人死于肝癌,约占全世界肝癌相关死亡人数的一半[11]。肝癌生长、转移及免疫逃逸的分子机制复杂,是目前研究的热点及难点[12-14]。深入研究参与肝癌恶性进展的关键分子及调控网络,对探寻抗肝癌的新生物学靶点及靶向治疗方案、提高肝癌治疗效果及改善患者的预后具有重要意义。
缺氧是包括肝癌在内的许多实体肿瘤的常见特征,与肿瘤进展及不良预后密切相关[15-17]。HIF-1是由α亚基和β亚基组成的异二聚体[18]。在缺氧条件下,稳定了HIF-1α亚基,从而在核中与HIF-1β组成稳定的HIF-1转录复合体,进而结合到目的基因启动子区域缺氧反应元件(hypoxiaresponse element,HRE),诱发基因转录[18]。HIF-1靶基因参与了肝癌的许多细胞过程,包括糖酵解、增殖、干性、耐药性、免疫逃逸、血管生成和转移[19-20]。越来越多的癌基因被证实是HIF-1的靶基因,在肝癌的进展中发挥重要作用。本课题组既往研究发现,在肝癌中缺氧诱导的HIF-1通过与血管扩张刺激磷蛋白(vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein,VASP) 启动子区域的HRE结合,在转录水平上调控VASP的表达,继而VASP通过激活Akt和ERK通路促进肝癌侵袭和转移[21]。缺氧诱导的TUFT1通过激活Ca2+/PI3K/Akt通路促进肝癌生长和转移[22]。Fibulin-5通过下调基质金属蛋白酶7(matrix metalloproteinase 7,MMP-7)表达抑制肝癌细胞迁移和侵袭[23]。本研究证实在缺氧条件下肝癌细胞中GPSM2蛋白表达显著升高。在肝癌临床样本中,GPSM2 mRNA和蛋白表达均显著高于对应癌旁非肿瘤组织,临床数据分析提示GPSM2 mRNA高表达与肝癌患者恶性临床病理特征(肿瘤体积≥5 cm、高Edmondson-Steiner分级和高TNM分期)以及不良预后密切相关。以上结果表明GPSM2在肝癌进展中可能作为癌基因发挥作用,其可能是HIF-1的潜在靶基因。
有氧糖酵解,也称为Warburg效应,是有别于正常细胞而存在于癌细胞中的一种葡萄糖代谢现象,表现为葡萄糖主要被加工成乳酸[24-25]。虽然在ATP生成方面效率较低,但糖酵解可以增加生物合成,抑制细胞凋亡,并产生信号代谢物,以增强癌细胞在艰难条件下的存活[26-29]。在既往的研究中发现GPSM2可以通过激活PI3K/AKT通路促进肝癌生长和转移[30]。本研究进一步研究了GPSM2对肝癌细胞糖酵解的影响。通过siRNA干扰Huh细胞中GPSM2表达,我们发现肝癌细胞增殖、葡萄糖消耗以及乳酸生成均显著减少。进一步研究发现干扰GPSM2可以降低糖酵解限速酶HK2表达,以上结果提示GPSM2可能通过调控HK2影响肝癌细胞糖酵解。既往研究[30]发现,在肝癌细胞中GPSM2激活PI3K/Akt信号通路。而研究已经证实PI3K/Akt信号通路通过调控HK2表达促进肝癌细胞糖酵解[31]。因此,笔者推测GPSM2可能通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路促进HK2表达。
综上所述,本研究的临床数据发现肝癌组织中GPSM 2表达上调并与不良预后相关,GPSM 2可能通过增强HK2表达促进肝癌细胞增殖和糖酵解。另外,本研究证实GPSM2是一个缺氧反应基因,其可能介导缺氧诱导的肝癌细胞糖酵解。
[1]Ferlay J,Soerjomataram I,Dikshit R,et al.Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide:sources,methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012[J].Int J Cancer,2015,136(5):E359-386.doi:10.1002/ijc.29210.
[2]Chen W,Zheng R,Baade PD,et al.Cancer statistics in China,2015[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2016,66(2):115-132.doi:10.3322/caac.21338.
[3]Bray F,Ferlay J,Soerjomataram I,et al.Global cancer statistics 2018:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(6):394-424.doi:10.3322/caac.21492.
[4]Blumer JB,Chandler LJ,Lanier SM.Expression analysis and subcellular distribution of the two G-protein regulators AGS3 and LGN indicate distinct functionality.Localization of LGN to the midbody during cytokinesis[J].J Biol Chem,2002,277(18):15897-15903.doi:10.1074/jbc.M112185200.
[5]Campbell AP,Smrcka AV.Targeting G protein-coupled receptor signalling by blocking G proteins[J].Nat Rev Drug Discov,2018,17(11):789-803.doi:10.1038/nrd.2018.135.
[6]Dunn HA,Orlandi C,Martemyanov KA.Beyond the Ligand:Extracellular and Transcellular G Protein-Coupled Receptor Complexes in Physiology and Pharmacology[J].Pharmacol Rev,2019,71(4):503-519.doi:10.1124/pr.119.018044.
[7]Deng M,Liu B,Zhang Z,et al.Knockdown of G-protein-signaling modulator 2 promotes metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer by inducing the expression of Snail[J].Cancer Sci,2020,111(9):3210-3221.doi:10.1111/cas.14519.
[8]Fukukawa C,Ueda K,Nishidate T,et al.Critical roles of LGN/GPSM2 phosphorylation by PBK/TOPK in cell division of breast cancer cells[J].Genes Chromosomes Cancer,2010,49(10):861-872.doi:10.1002/gcc.20795.
[9]Deng M,Zhang Z,Liu B,et al.Localization of GPSM2 in the Nucleus of Invasive Breast Cancer Cells Indicates a Poor Prognosis[J].Front Oncol,2020,10:227.doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.00227.
[10]魏彪,张建新,崔磊,等.GPSM2过表达对人胰腺癌细胞迁移能力的影响[J].中国普通外科杂志,2017,26(3):311-316.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2017.03.007.
Wei B,Zhang JX,Cui L,et al.Effects of GPSM2 over-expression on migration ability of human pancreatic cancer cells[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2017,26(3):311-316.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2017.03.007.
[11]Grandhi MS,Kim AK,Ronnekleiv-Kelly SM,et al.Hepatocellular carcinoma:From diagnosis to treatment[J].Surg Oncol,2016,25(2):74-85.doi:10.1016/j.suronc.2016.03.002.
[12]陈云茹,丹增措姆,白文东,等.SFPQ在肝细胞癌的表达及其对细胞增殖与细胞周期的影响[J].中国普通外科杂志,2019,28(1):49-57.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2019.01.007.
Chen YR,Dan ZCM,Bai WD,et al.Expression of SFPQ in hepatocellular carcinoma and its effect on cell proliferation and cell cycle[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2019,28(1):49-57.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2019.01.007.
[13]丁琭,莫缓椰,鲜瑶,等.肝细胞癌中miR-942-5p的表达及其与患者恶性特征及不良预后的关系[J].中国普通外科杂志,2019,28(7):840-847.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2019.07.010.
Ding L,Mo HY,Xian Y,et al.Expression of microRNA-942-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma and its relations with malignant feature and unfavorable outcomes of the patients[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2019,28(7):840-847.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2019.07.010.
[14]陈世发,赵礼金.肝癌发生发展机制的研究进展及其治疗现状[J].中国普通外科杂志,2018,27(7):910-923.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.07.016.
Chen SF,Zhao LJ.Research progress on mechanisms for occurrence of liver cancer and its treatment status[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2018,27(7):910-923.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.07.016.
[15]Jing X,Yang F,Shao C,et al.Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment[J].Mol Cancer,2019,18(1):157.doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1089-9.
[16]Xia S,Pan Y,Liang Y,et al.The microenvironmental and metabolic aspects of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Ebiomedicine,2020,51:102610.doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.102610.
[17]孟永斌,程彬彬,杜娟,等.缺氧促进肝细胞癌发生发展机制的研究进展[J].中国普通外科杂志,2020,29(1):97-103.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.01.012.
Meng YB,Cheng BB,Du J,et al.Research progress of mechanism for hypoxia promoting the occurrence and development of hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2020,29(1):97-103.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.01.012.
[18]Semenza GL.Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine[J].Cell,2012,148(3):399-408.doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.021.
[19]Xiong XX,Qiu XY,Hu DX,et al.Advances in Hypoxia-Mediated Mechanisms in Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J].Mol Pharmacol,2017,92(3):246-255.doi:10.1124/mol.116.107706.
[20]Méndez-Blanco C,Fondevila F,García-Palomo A,et al.Sorafenib resistance in hepatocarcinoma:role of hypoxia-inducible factors[J].Exp Mol Med,2018,50(10):1-9.doi:10.1038/s12276-018-0159-1.
[21]Liu Z,Wang Y,Dou C,et al.Hypoxia-induced up-regulation of VASP promotes invasiveness and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Theranostics,2018,8 (17):4649-4663.doi:10.7150/thno.26789.
[22]Dou C,Zhou Z,Xu Q,et al.Hypoxia-induced TUFT1 promotes the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the Ca(2+)/PI3K/AKT pathway[J].Oncogene,2019,38(8):1239-1255.doi:10.1038/s41388-018-0505-8.
[23]Tu K,Dou C,Zheng X,et al.Fibulin-5 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by down-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression[J].BMC Cancer,2014,14:938.doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-938.
[24]Hsu PP,Sabatini DM.Cancer cell metabolism:Warburg and beyond[J].Cell,2008,134(5):703-707.doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.021.
[25]DeBerardinis RJ,Chandel NS.Fundamentals of cancer metabolism[J].Sci Adv,2016,2(5):e1600200.doi:10.1126/sciadv.1600200.
[26]Lee N,Kim D.Cancer Metabolism:Fueling More than Just Growth[J].Mol Cells,2016,39(12):847-854.doi:10.14348/molcells.2016.0310.
[27]Hanahan D,Weinberg RA.Hallmarks of cancer:the next generation[J].Cell,2011,144(5):646-674.doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013.
[28]DeBerardinis RJ,Lum JJ,Hatzivassiliou G,et al.The biology of cancer:metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation[J].Cell Metab,2008,7(1):11-20.doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2007.10.002.
[29]黄荣,汪泓,陈保华,等.巨噬细胞移动抑制因子促进有氧糖酵解与直肠癌细胞耐药性的关系[J].中国普通外科杂志,2017,26(10):1265-1271.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2017.10.007.
Huang R,Wang H,Chen BH,et al.Relationship of macrophage migration inhibition factor enhancing aerobic glycolysis to drug resistance of colorectal cancer cells[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2017,26(10):1265-1271.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2017.10.007.
[30]He XQ,Zhang YF,Yu JJ,et al.High expression of G-protein signaling modulator 2 in hepatocellular carcinoma facilitates tumor growth and metastasis by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J].Tumour Biol,2017,39(3):1010428317695971.doi:10.1177/1010428317695971.
[31]Feng J,Li J,Wu L,et al.Emerging roles and the regulation of aerobic glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2020,39(1):126.doi:10.1186/s13046-020-01629-4.
