肝脏肿瘤目前临床上治疗以手术为主[1-3],肝硬化是一种或多种病因反复作用形成的以肝实质弥漫性纤维化、假小叶和再生结节形成为特征的慢性进行性肝病。肝硬化患者的肝储备功能和再生能力均下降,因此在肝脏肿瘤合并肝硬化患者在行肝切除时,由于切除范围不精确,术后可导致肝功能不全、术后并发症的发生,严重时可危及生命[4]。因此术前精准评估患者病情以及术中精确切除范围,对行肝切除术的肝硬化患者的预后至关重要。精准肝胆外科的目标是根治性切除病灶,最大限度地保留功能性肝脏,并尽可能减少手术损伤[5]。患者可以获得最佳康复疗效[6]。有研究指出对于结构功能非常复杂的肝脏病变的个体定量评估、肝脏肿瘤范围的界定、合并肝肝硬化的时安全肝脏切除量的准确把握,需要肝脏三维重建技术的有力支持[7-8],三维重建不仅可以精确的提供术前肝脏的解剖结构,包括肿瘤的大小、位置、与肝内重要管道的关系,还能预先精确了解手术后剩余肝脏的功能性体积[9]。而吲哚菁绿(ICG)清除试验能反应肝脏摄取、处理和排泄ICG的全过程,可有效评价肝储备功能[10],目前临床上用于量化评估肝储备功能的主要指标有Child-Pugh评分和ICG排泄试验,Child-Pugh评分较为粗略,血液指标不够灵敏,腹腔积液和肝性脑病两个指标相对主观[11]。有研究[12]指出对同为Child-Pugh A级的肝硬化患者肝储备功能及能耐受肝切除体积的个体差异却很大,需要更精确的定量评估,这个群体患者肝切除后总体病死率为3%~8%。2019年版《肝硬化患者肝切除术后肝功能不全的预防与治疗专家共识》[11]指出对于肝硬化患者,其耐受的肝实质切除可进一步依据ICG 15 min滞留率(ICG-R15)结果做出精确判断。
目前临床上尚无三维可视化技术(3DVT)联合ICG在肝肿瘤合并肝硬化患者手术中应用的相关报道。笔者团队根据2019年版《肝硬化患者肝切除术后肝功能不全的预防与治疗专家共识》[11]制定的安全肝切除标准,从2019年5月开始运用3DVT联合ICG应用于肝肿瘤合并肝硬化的手术中,取得了良好的临床疗效。通过回顾性分析行3DVT联合ICG处理与行3DVT联合传统Child-Pugh分级处理的肝肿瘤合并肝硬化手术患者的临床资料,探讨3DVT联合ICG在肝肿瘤合并肝硬化患者手术中的应用价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
回顾性分析2019年5月—2020年3月行3DVT联合ICG处理的肝肿瘤合并肝硬化手术患者57例患者资料(观察组),将2018年1月—2019年4月行3DVT联合传统Child-Pugh分级处理的肝肿瘤合并肝硬化手术患者62例的临床资料作为历史对照(对照组)。119例患者均有我科高年资且具有丰富开腹和腹腔镜肝切除术经验的外科医师完成,手术学习曲线对本研究两组比较产生的影响较小。研究过程符合我院医学伦理规定(伦理号:ZYYECKYJ[2020]046)。
1.2 纳入标准与排除标准
病例纳入标准:⑴ 术前影像资料提示肝脏肿瘤并伴有肝硬化,且术后病理也证实肝硬化及肿瘤;⑵ 术前肝功能Child-Pugh分级标准为A级,或B级经过治疗后变为A级;⑶年龄≥18岁;⑷ 临床病例资料完整;⑸ 均行手术治疗。病例排除标准:⑴ 具有严重的心肺等基础疾病不能耐受手术者;⑵ 肿瘤晚期,肝外多发转移,无法手术切除者;⑶ 病例资料不完整。
1.3 3DVT 术前评估规划
收集上腹部增强CT或MRI的三期图像数据,将数据导入三维可视化软件系统(IPS_V2.0.7.1,著作权号:2013SR088244),将图像进行图像分割和三维重建,进行肝分段、组织分类、计算功能肝体积、肿瘤占位体积、剩余肝体积等,并根据3DVT制定个体化手术方案及术前规划[13],数据收集过程、三维重建质控体系的建立及研究方法参照指南(2019版)[14]。
1.4 干预措施
1.4.1 观察组 采用3DVT 联合ICG 对患者进行术前精确评估后,根据指南[11](2019 版)安全肝切除决策进行进一步确定手术方案。第一步,根据ICG-R15 及体系初步确定切除范围:即对于肝功能Child-Pugh A级患者行肝切除术时,如术前检测,ICG-R15<10%,切除病灶后预留肝脏体积应该不少于40% 的标准肝体积(standard liver volume,SLV);ICG-R15 为10%~20%,则预留肝体积不少 于60% 的SLV;ICG-R15 为21%~30%,预留肝体积不少于80% SLV。ICG-R15 为30%~40%,则行肝实质切除率(切除肝实质体积展全部功能性肝体积的比例)少于5% 的微量肝切除。若ICG-R15>40%,则只能行局部肿瘤剜除术(图1)。第二步,将影像资料导入三维系统后精确计算切除病灶面积和切面(图2)。第三步,术中根据术前的精准规划,精准切除病灶(图3)。
1.4.2 对照组 采用3DVT 联合Child-Pugh分级对患者进行术前评估:将术前肝功能评分为Child-Pugh A级,或经治疗后评分为Child-Pugh A级的肝硬化合并肿瘤的患者纳入手术;将这些患者的影像资料导入三维系统后明确肿瘤位置和周围组织关系;规划解剖性肝切除手术方案;对肿瘤均进行解剖性肝切除。

图1 ICG试验过程 A:ICG静脉注入;B:ICG-R15结果
Figure1 ICG testing process A:Venous injection of ICG;B:Results of ICG-R15

图2 3DVT辅助肝切除模型 A:高亮下可以清楚的看到重建后的三维图像中肿瘤与周围动脉、静脉、肾脏、肾上腺、胆道系统的空间结构关系;B:系统规划切面、输入身高与体质量后明确肿瘤占位体积和切除后的肝脏剩余体积,可以精准切除肝脏肿瘤
Figure2 3DVT-assisted liver resection model A:Clear presence of the space relations of the liver tumor with the adjacent arteries,veins,kidney,adrenal gland and biliary system after three dimensional reconstruction under highlight;B:Precise resection of the liver tumor after determination of the occupying volume of the tumor and residual liver volume by systematic planning of the cut surface and input of body height and weight

图3 手术标本(精准切除病灶切除,包膜完整,手术损伤降到最低)
Figure3 Surgical specimen (precise resection of the lesion as evidenced by intact capsule and minimized surgical trauma)
1.5 出院标准
⑴ 一般情况良好:患者能正常进食,排气排便正常;⑵ 无发热、口服NSAIDs类止痛药可以缓解疼痛,切口愈合良好,无感染;⑶ 白细胞、转氨酶[门冬氨酸氨基转氨酶(aspartate transaminase,AST)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(alanine transaminase,ALT)]、总胆红素(total bilirubin,TBIL)等临床指标基本正常。
1.6 观察指标
两组基线资料的对比分析,两组术中资料包括手术时间、出血量、失血量统计分析,两组术后资料包括术后炎症指标、肝功能、术后住院时间、术后并发症。炎症指标包括T N F-α、IL-2、IL-6;肝功能结果包括ALT、AST、TBIL。根据Clavien-Dindo并发症分级[15],并发症的分级内容:I级包括切口感染、肺部感染(无抗生素治疗);II级包括胸腔积液(未穿刺引流)、肺部感染(抗生素治疗),III级包括胸腔积液(穿刺引流)、腹腔脓肿、胆瘘;IV级包括腹腔出血、肝衰竭、多器官功能不全;V级为死亡。国际肝脏外科学组(ISGLS)根据肝切除5 d后国际标准化比值(international normalized ratio,INR)、高胆红素等检验指标,并结合肝脏功能、肾脏功能、呼吸功能以及是否需要特殊评估和特殊临床治疗,将肝硬化患者肝切除术后肝功能不全严重程度分为A、B、C 3个等级。A级:凝血正常(INR<1.5),无神经症状,尿量正常[>0.5 mE/(kg·h)],尿素氮(BUN)<150 mg/dL,无尿毒症,动脉血氧饱和度>90%,临床上不需要特殊处理;B级:已出现凝血功能不佳(INR 1.5~<2.0),开始出现神经系统症状(如嗜睡和困惑),尿量不足[≤0.5 mE/(kg·h)],BUN<150 mg/dL,无尿毒症;C级:凝血功能不佳(INR≥2.0),出现严重神经症状和(或)肝性脑病,利尿剂无法处置的肾功能衰竭.BUN≥150 mg/dL[16]。
1.7 统计学处理
采用SPSS 25.0版本统计学软件进行分析,对于符合正态分布的计量资料两组之间采用独立样本t检验,同组前后比较采用配对t检验,用均数±标准差表示(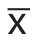 ±s),对于不符合正态分布的计量资料采用Wilcoxon秩和检验;对于计数资料采用χ2检验和Fisher精确检验。
±s),对于不符合正态分布的计量资料采用Wilcoxon秩和检验;对于计数资料采用χ2检验和Fisher精确检验。
2 结 果
2.1 两组基线资料比较分析
两组的一般资料包括年龄、性别、饮酒史、肝炎病史、酗酒史、肿瘤位置、肿瘤直径等,差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05)(表1)。
表1 术前一般资料比较
Table1 Comparison of the general data

资料 观察组(n=57)对照组(n=62) t/χ2 P年龄(岁,images/BZ_83_475_811_508_856.png±s) 50.9±1.7 51.5±1.6 0.262 0.793性别[n(%)]男30(52.6) 33(53.2) 0.004 0.948女27(47.4) 29(46.8)肝炎乙肝 53(92.9) 55(88.7)丙肝 3 (5.3) 5 (8.1) 0.399 0.527无1 (1.8) 2 (3.2)长期酗酒史有10(17.5) 13(20.9) 0.223 0.637无47(82.5) 49(79.1)肿瘤位置左半肝 32(56.1) 35(56.5) 0.001 0.973右半肝 25(43.9) 27(43.5)肿瘤直径(cm,images/BZ_83_475_811_508_856.png±s) 3.65±0.19 3.71±0.17 0.223 0.824
2.2 两组手术相关指标比较
两组的手术时间比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);观察组的术中出血量、住院时间少于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05)(表2)。
2.3 两组实验室指标比较
两组患者术前各项炎症因子与肝功能指标水平间差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。术后7 d,两组的TNF-α、IL-6水平及AST、ALT、TBIL均较各自术前水平明显降低,而IL-2水平均较各自术前明显升高(均P<0.05);两组间比较,观察组各项炎症因子与肝功能指标的变化均优于对照组(均P<0.05)(表3)。
表2 手术相关指标比较(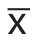 ±s)
±s)
Table2 Comparison of the surgery-related variables (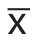 ±s)
±s)

组别 手术时间(h)术中出血量(mL)住院时间(d)观察组(n=57) 5.81±0.16 260.17±8.43 9.73±0.26对照组(n=62) 5.53±0.12 285.81±8.15 12.29±0.85 t 1.418 2.184 6.576 P 0.159 0.031 0.000
表3 炎症因子与肝功能指标比较(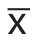 ±s)
±s)
Table3 Comparison of the inflammatory factors and liver function indexes (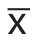 ±s)
±s)

注:1)与术前比较,P<0.05
Note:1) P<0.05 vs.preoperative value
指标 观察组(n=57) 对照组(n=62) P TNF-α(pg/mL)术前 47.4±0.4 48.1±0.5 >0.05术后7 d 9.9±0.21) 15.4±0.71) <0.05 IL-2(pg/mL)术前 49.8±0.3 50.4±0.8 >0.05术后7 d 121.5±0.81) 106.8±1.81) <0.05 IL-6(pg/mL)术前 121.5±1.2 122.6±1.8 >0.05术后7 d 47.2±1.11) 60.7±0.91) <0.05 ALT(U/L)术前 56.2±1.1 57.1±0.9 >0.05术后7 d 39.6±1.21) 46.7±1.01) <0.05 AST(U/L)术前 40.5±0.9 41.2±1.1 >0.05术后7 d 33.9±1.01) 37.4±1.31) <0.05 TBIL(μmol/L)术前 18.4±0.8 18.9±0.9 >0.05术后7 d 13.6±0.41) 16.1±0.71) <0.05
2.4 两组肝功能不全及并发症发生率比较
两组术后各级肝功能不全的发生率比较,差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05),观察组术后肝功能不全总发生率明显低于对照组(P=0.028)(表4);两组I、II、III级并发症的发生率差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05),但观察组术后总并发症发生率明显低于对照组(P=0.045)(表5)。两组术后均无患者发生死亡及肝功能衰竭等严重的并发症发生。
表4 术后肝功能不全分级比较[n(%)]
Table4 Comparison of the different grades of postoperative liver dysfunction [n (%)]

组别 A级 B级 C级 总数观察组(n=57) 6(10.5) 1(1.8) 0(0.0) 7(12.3)对照组(n=62) 17(27.4) 2(3.2) 2(3.2) 21(33.9)χ2 3.715 0.249 1.811 4.835 P 0.054 0.618 0.178 0.028
表5 术后并发症比较[n(%)]
Table5 Comparison of the postoperative complications [n (%)]

组别 I级 II级 III级 IV级V级 总数观察组(n=57) 2(3.0) 6(10.6) 1(1.8) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 9(15.4)对照组(n=62) 6(9.7) 16(25.8) 1(1.6) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 23(37.1)χ2 1.580 3.196 0.003 — — 4.007 P 0.209 0.074 0.953 — — 0.045
3 讨 论
3DVT在导入二维的影像资料后,通过系统对图像进行处理和三维重建,可以精确的计算残肝体积,其平均误差范围<30 mL[17],这样可以在保证切缘安全的基础上避免过多的肝组织切除,精准的构建了肿瘤与周围组织,管道系统的空间关系,有利于术中进行精准肝肿瘤切除,减少术中的损伤[18]。有研究指出,对于肝肿瘤患者,术前进行3DVT,有利于制定最优的手术方案,进行术中的精准肝切除是避免术后严重并发症的关键[19-22]。
肝硬化患者在发展到肝硬化失代偿期之前即肝功能处于代偿阶段,常规肝功能检查常常无明显异常或者轻微异常,但是事实上肝脏内部有功能性的肝细胞已经出现损伤性减少。而ICG-R15则是最常用来评估剩余功能性肝细胞数量的多少,即肝脏有效储备功能的指标。Child-Pugh评分是对肝功能进行分级的工具,主要针对肝脏的合成、肝细胞损伤以及代谢功能的评估,同样分级为Child-Pugh的肝硬化患者,但是肝功能的储备状态可能有比较大的差异,有研究[23]统计了Child-Pugh A级的肝病患者,结果显示ICG-R15的变化范围为12.4%~54.1%,说明有一部分的患者肝功能储备已经重度受损。赖瑞敏等[24]认为ICG-R15在反应肝硬化患者肝储备功能方面较终末期肝病模型(MELD)评分和Child-Pugh评分更敏感。因此可以表明Child-Pugh A级代偿期患者实际的肝内有功能性的肝细胞存在差异,及肝储备功能有差异,使得肝脏疾病的转归也存在差异。由此可见,ICG清除试验是更为敏感的检测方法,可以作为预测肝硬化患者预后的可靠指标[25-26]。ICG清除试验已纳入肝切除围手术期管理专家共识(2017版)[27]和原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2017版)[28]中,有助于优化术前的手术方案和确定安全的肝手术切除量,有利于降低术后并发症的发生。
本研究通过两组对比发现3DVT 联合ICG取得了良好的效果,与对照组对比,由于术前的精准评估,对肝储备功能更敏感的检测,避免了不必要的手术损伤,从而减少了术中出血量。且术中手术时间比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),但由于技术熟练的肝胆外科医师按照操作指南对患者进行更精细的操作,术后住院时间明显缩短(9.73±0.26)d;与对照组对比,治疗后观察组的TNF-α、IL-6含量低于对照组,IL-2含量高于对照组,证实了观察组的操作对患者肝功能更有效的保护,与朱云峰等[29]、张雄杰等[30]研究结果一致。与对照组的常规Child评分比较,观察组筛选出Child评分适合肝切除而经吲哚箐绿实验后不能行肝切除的患者,或者本应该行解剖性肝切除但经吲哚箐绿实验改为行局部肿瘤切除的患者,由此导致两组手术方式的不同,并经过此改变降低了术后患者并发症的发生率,改善了肝功能,减少了不必要的损伤,本研究发现观察组术后7 d的ALT、AST、TBIL指标均低于对照组,与罗树宾等[31]研究结果一致。本研究观察组与对照组比较,肝功能不全发生率、术后并发症发生率均低于对照组。由于ICG清除试验与Child-Pugh评分相比,在反应肝硬化患者肝储备功能方面更为敏感,有利于早期判断肝功能不全,指导手术方案的选择,可以提高疗效,对患者的预后有巨大的应用价值。
综上,3DVT 联合ICG 能为术者提供精准的三维立体手术视野和肿瘤的精确的空间定位,提供了患者精准的肝功能储备状态,在治疗肝肿瘤并肝硬化的优势非常明显,疗效满意。这一切都得益于精准肝脏手术理念的贯彻,相信随着社会的发展,精准肝脏手术理念会得到越来越多术者的认可和推广。但是本研究为单中心病例对照研究,患者预后疗效并未进行长期观察,所得的结论有一定的局限性,希望后续的研究能进行多中心的RCT研究进行深入探讨。
[1]Siegel RL,Miller KD,Jemal A.Cancer statistics,2019[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2019,69(1):7-34.doi:10.3322/caac.21551.
[2]Bray F,Ferlay J,Soerjomataram I,et al.Global cancer statistics 2018:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(6):394-424.doi:10.3322/caac.21492.
[3]Yang P,Qiu J,Li J,et al.Nomograms for Pre- and Postoperative Prediction of Long-term Survival for Patients Who Underwent Hepatectomy for Multiple Hepatocellular Carcinomas[J].Ann Surg,2016,263(4):778-786.doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000001339.
[4]Pugh RN,Murray-Lyon IM,Dawson JL,et al.Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices[J].Br J Surg,1973,60(8):646-649.doi:10.1002/bjs.1800600817.
[5]Rahbafi NN,Garden OJ,Padbury R,et al.Posthepatectomy liver failure:a definition and grading by the International Study Group of Liver Surgery(ISGLS)[J].Surgery,2011,149(5):713-724.doi:10.1016/j.surg.2010.10.001.
[6]荚卫东,陈浩,葛勇胜,等.三维可视化技术在巨块型肝细胞癌精准肝切除中的应用价值[J].中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志,2018,7(1):35-39.doi:10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2018.01.010.
Jia WD,Chen H,Ge YS,et al.Application value of threedimensional visualization technique in precise hepatectomy for massive hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Chinese Journal of Hepatic Surgery,2018,7(1):35-39.doi:10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2018.01.010.
[7]王碧菠,陈博,李星辰,等.3D打印距骨部件修复重建距骨病损的生物力学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(3):306-310.doi:10.7507/1002-1892.201705068.
Wang BB,Chen B,Li XC,et al.Biomechanical study on repair and reconstruction of talar lesion by three-dimensional printed talar components[J].Chinese Journal of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery,2018,32(3):306-310.doi:10.7507/1002-1892.201705068.
[8]Yao R,Xu G,Mao SS,et al.Three-dimensional printing:review of application in medicine and hepatic surgery[J].Cancer Biol Med,2016,13(4):443-451.doi:10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2016.0075.
[9]Yan QH,Xu DG,Shen YF,et al.Observation of the effect of targeted therapy of 64-slice spiral CT combined with cryoablation for liver cancer[J].World J Gastroenterol,2017,23(22):4080-4089.doi:10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.4080.
[10]张明明,张岭漪.吲哚菁绿清除试验评估肝储备功能的应用价值[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2019,35(8):1878-1881.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.08.052.
Zhang MM,Zhang LY.Value of indocyanine green clearance test in assessing liver reserve function[J].Journal of Clinical Hepatology,2019,35(8):1878-1881.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.08.052.
[11]中国研究型医院学会肝胆胰外科专业委员会.肝硬化患者肝切除术后肝功能不全的预防与治疗专家共识(2019版)[J].中华消化外科杂志,2019,18(4):297-302.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2019.04.001.
Society of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery of Chinese Research Hospital Association.Expert consensus on prevention and treatment of post-hepatectomy liver function insufficiency in patients with liver cirrhosis (2019 edition)[J].Chinese Journal of Digestive Surgery,2019,18(4):297-302.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2019.04.001.
[12]Poon RT,Fan ST.Assessment of hepatic reserve for indication of hepatic resection:how I do it[J].J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg,2005,12(1):31-37.doi:10.1007/s00534-004-0945-0.
[13]Cai W,Fan Y,Hu H,et al.Postoperative liver volume was accurately predicted by a medical image three dimensional visualization system in hepatectomy for liver cancer[J].Surg Oncol,2017,26(2):188-194.doi:10.1016/j.suronc.2017.03.006.
[14]中华医学会数字医学分会,中国医师协会肝癌专业委员会,中国医师协会临床精准医学专业委员会,等.复杂性肝脏肿瘤三维可视化精准诊治指南(2019版)[J].中国实用外科杂志,2019,39(8):766-774.doi:10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.08.02.
Chinese Society of Digital Medicine,Professional Committee of Liver Cancer of Chinese Medical Doctor Association,Professional Committee of Precision Medicine of Chinese Medical Doctor Association,et al.Guidelines for three-dimensional visualization diagnosis and treatment of complex liver tumors(2019 edition)[J].Chinese Journal of Practical Surgery,2019,39(8):766-774.doi:10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.08.02.
[15]Clavien PA,Barkun J,de Oliveira ML,The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications:five-year experience[J].Ann Surg,2009,250(2):187-196.doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b13ca2.
[16]Rahbari NN,Garden OJ,Padbury R,et al.Posthepatectomy liver failure:a definition and grading by the International Study Group of Liver Surgery(ISGLS)[J].Surgery,201l,149(5):713-724.doi:10.1016/j.surg.2010.10.001.
[17]Seo CT,Kang SW,Cho M.Three-dimensional free view reconstruction in axially distributed image sensing[J].Chin Opt Lett,2017,15(8):81102.doi:10.3788/COL201715.81102.
[18]Guan T,Fang C,Mo Z,et al.Long-Term Outcomes of Hepatectomy for Bilateral Hepatolithiasis with Three-Dimensional Reconstruction:A Propensity Score Matching Analysis[J].J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A,2016,26(9):680-688.doi:10.1089/lap.2016.0165.
[19]Li SQ,Huang T,Shen SL,et al.Anatomical versus non-anatomical liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma exceeding Milan criteria[J].Br J Surg,2017,104(1):118-127.doi:10.1002/bjs.10311.
[20]王程,黄强,杨骥.三维可视化技术在肝脏恶性肿瘤手术中应用价值Meta分析[J].中国普通外科杂志,2020,29(1):19-26.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.01.003.
Wang C,Huang Q,Yang J.Meta-analysis of application value of three-dimensional visualization technique in liver cancer surgery[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2020,29(1):19-26.doi:10.7659/ j.issn.1005-6947.2020.01.003.
[21]张化玉.三维可视化技术指导肝段切除联合胆道硬镜在复杂肝胆管结石治疗中的应用[J].中国普通外科杂志,2018,27(6):796-800.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.06.022.
Zhang HY.Application value of 3-D visualization guidance combined with rigid choledochoscope in treatment of complicated hepatic bile duct stones[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2018,27(6):796-800.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.06.022.
[22]白军军,李航,孙宝震,等.数字化三维重建技 术在肝癌精准肝切除术中的应用[J].中国普通外科杂志,2018,27(7):826-833.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.07.005.
Bai JJ,Li H,Sun BZ,et al.Application of digital 3D reconstruction technique in precise hepatectomy for liver cancer[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2018,27(7):826-833.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.07.005.
[23]康玮玮,周莉,刘旭华,等.肝硬化患者吲哚菁绿清除试验的临床评价[J].中华消化外科杂志,2009,8(4):300-301.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2009.04.019.
Kang WW,Zhou L,Liu XH,et al.Clinical evaluation of indocyanine green clearance test in patients with liver cirrhosis[J].Chinese Journal of Digestive Surgery,2009,8(4):300-301.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2009.04.019.
[24]赖瑞敏,王明芳,朱月永.吲哚菁绿清除试验对乙型肝炎肝硬化患者肝脏储备功能的评估价值[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2016,32(9):1739-1742.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.09.021.
Lai RM,Wang MF,Zhu YY.Value of indocyanine green test in evaluating liver reserve function in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis[J].Journal of Clinical Hepatology,2016,32(9):1739-1742.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.09.021.
[25]Lisotti A,Azzaroli F,Buonfiglioli F,et al.Indocyanine green retention test as a noninvasive marker of portal hypertension and esophageal varices in compensated liver cirrhosis[J].Hepatology,2014,59(2):643-650.doi:10.1002/hep.26700.
[26]Cheng XP,Zhao J,Chen Y,et al.Comparison of the ability of the PDD-ICG clearance test,CTP,MELD,and MELD-Na to predict short-term and medium-term mortality in patients with decompensated hepatitis B cirrhosis[J].Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2016,28(4):444-448.doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000000538.
[27]中华医学会外科学分会肝脏外科学组.肝切除术围手术期管理专家共识(2017年版)[J].中国实用外科杂志,2017,37(5):525-530.doi:10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2017.05.17.
Liver Surgery Group,Society of Surgery,Chinese medical Association.Expert consensus on perioperative management of liver resection (2017 edition)[J].Chinese Journal of Practical Surgery,2017,37(5):525-530.doi:10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2017.05.17.
[28]中华人民共和国卫生和计划生育委员会医政医管局.原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2017年版)[J].中华消化外科杂志,2017,16(7):635-647.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2017.07.001.
Bureau of Medical Administration and Medical Authority,National Health and Family Planning Commission.Standardization of diagnosis and treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (2017 edition) [J].Chinese Journal of Digestive Surgery,2017,16(7):635-647.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2017.07.001.
[29]朱云峰,李建生,马金良,等.三维重建技术在肝门部胆管癌术前评估中的价值[J].中国普通外科杂志,2016,25(2):175-180.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2016.02.003.
Zhu YF,Li JS,Ma JL,et al.Value of three- dimensional reconstruction in preoperative assessment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2016,25(2):175-180.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2016.02.003
[30]张雄杰,张能平.三维重建联合腹腔镜行肝精准切除治疗原发性肝癌疗效[J].中国现代普通外科进展,2019,22(10):781-784.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-9905.2019.10.007.
Zhang XJ,Zhang NP.Clinical observation of Three-dimensional Reconstruction combined with Laparoscopic precise hepatectomy in the treatment of Primary Hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Chinese Journal of Current Advances in General Surgery,2019,22(10):781-784.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-9905.2019.10.007.
[31]罗树宾,毛家玺,刘聪,等.三维可视化技术在肝癌肝切除术前评估中的应用[J].中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志,2020,9(2):131-136.doi:10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2020.02.009.
Luo SB,Mao JX,Liu C,et al.Application of three-dimensional visualization in preoperative evaluation of hepatectomy for liver cancer[J].Chinese Journal of Hepatic Surgery,2020,9(2):131-136.doi:10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2020.02.009.
