胰腺癌是第七常见的恶性肿瘤,在中国,也是导致癌症相关死亡的第六位因素[1]。其5年生存率仅有5%~10%,在确诊胰腺癌后,患者的中位生存时间约为5~6个月[2-3]。实际上,绝大多数胰腺癌患者都出现了局部进展,甚至是远处转移(80%~85%),只有极少数患者是可以手术切除的(15%~20%)[4-5]。胰腺癌的不良预后原因众多,例如,系统免疫炎症指数可能是胰腺癌患者预后不良的独立危险因素[6],早期阶段的检测率低,具有远处转移的高风险,以及化疗的效果较差等[7],手术仅在诊断为早期胰腺癌的15%~20%的患者中被认为是可行的[8],由于胰腺癌患者往往到了晚期,才开始出现少量症状,因而,开发能够早期诊断胰腺癌的工具是有重大意义的[9]。血清碳水化合物抗原19-9(CA19-9)是目前用作评估胰腺癌临床治疗疗效的标志物,尽管它低灵敏度和低特异性,但它仍然是胰腺癌中唯一获得美国食品药品监督管理局批准的标志物,其他抗原(例如CEA和CA125)作为早期标记完全无效,但一些肿瘤学家仍将其用作治疗反应性的标记[10]。因此,寻找更为有效的胰腺癌诊断分子标志物,依旧是个值得深入探讨的课题。
microRNA(miRNA)是长度约为18~25个核苷酸的非编码RNA,发挥着调控基因表达和RNA沉默中的功能。异常的miRNA在多种肿瘤及良性疾病中被发现,并且发挥着重要的作用[11]。研究发现,许多miRNA可以在血浆、血清等体液中稳定存在,这也使得研究循环miRNA以检测疾病的进展成为可能[12-13]。由于miRNA可以在体液(例如血清或血浆)中检测到,因此它们已成为潜在的有用的生物标志物,用于风险评估,诊断和预后[14]。例如,Martínez-Hernández等[15]的研究发现血清miR-19b和miR-26b可能用于预测免疫介导的炎症性疾病的发生,Huang等[16]发现循环中的miR-487a,miR-493-5p,miR-501-3p和miR-502-5p是骨肉瘤的新型潜在诊断生物标志物。可见,血清miRNA作为预测疾病的生物标志物的巨大潜力。
决策树是一种用于判别分析的监督式机器学习算法,它易于理解和解释。它允许通过以分层树或规则集的形式生成可理解的知识结构并以图形直观的方式呈现它们,从而从数据中提取知识[17]。决策树也已用于鉴定癌症中的生物标志物,例如,利用miRNA表达数据进行肺癌诊断和亚型分型[18],使用核受体表达定义一组肺癌的预后生物标志物[19]等。本研究旨在通过分析GEO(Gene Expression Omnibus)数据库中血清miRNA的测序数据,将决策树的方法应用于胰腺癌的预测中,确定胰腺癌的生物标志物。
1 资料与方法
1.1 数据下载
这项研究中我们比较了来自GEO数据库的胰腺癌患者和健康对照人群的血清miRNA表达谱。其中纳入研究的数据集包括:GSE113486,包含40例胰腺癌患者血清miRNA样本,和100例非肿瘤对照样本;GSE85589包含19例健康对照和88例胰腺癌患者血清样本。GEOquery R包用于下载临床信息及表达谱。
1.2 去除批次效应
由于本研究下载的表达谱数据是经过预先处理及标准化的,这里无需进一步处理,但由于GSE113486及GSE85589非同批次测序结果,这里需要进一步去除批次效应,以利进一步研究。批次效应是指表示测序样本在不同的批次处理和测量时引入的与生物状态不相关的系统性的技术偏差。本研究采用sva R包的ComBat函数移除批次效应,并使用主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)评估批次效应移除前后的差异。
1.3 关键miRNA 的初步筛选
LASSO(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator)回归是拟合高维广义线性模型的一种流行的变量选择方法,通过构造惩罚函数以减少变量数并有效避免过度拟合,可以得到更精细的模型。为了筛选出用于鉴别肿瘤与非肿瘤样本的关键miRNA,本研究通过R软件中的glmnet软件包,使用LASSO回归分析筛选重要的miRNA。
1.4 决策树的构建及评价
R语言中的set.seed函数及sample函数可用于生成随机数并用于随机抽样分组,本研究基于以上两个函数,通过随机抽样,将247例样本,随机分为训练集(60%)和测试集(40%),LASSO回归分析筛选的关键miRNA用于训练集中决策树的构建。本研究使用rpart R包实现决策树算法,rpart函数用于决策树的生成,选择交叉验证误差最小的树即最优的树。predict函数用于测试集中观测点的分类,使用ROC曲线分析评价决策树的预测效果,InformationValue R包的plotROC函数用于ROC曲线绘制。
1.5 关键miRNA 的组间差异
为了对比正常血清样本和胰腺癌血清样本中关键miRNA的表达差异,本研究利用Wilcoxon检验对比了关键miRNA分别在GSE113486 及GSE85589数据集中正常与肿瘤样本的表达差异,以及在全部样本中正常与肿瘤样本的表达差异。
1.6 关键miRNA 的功能注释
为进一步了解关键miRNA所涉及的功能,本研究利用miRDB、miRTarBsae及TargetScan3种数据库,预测miRNA的靶向mRNA。其中,在3 种数据库中均有预测到的靶向mRNA将被用于富集分析,注释关键miRNA可能涉及的功能,clusterProfiler R包用于富集分析(enrichment analysis)[20]。
2 结果
2.1 去除批次效应
去除批次效应前,首先利用主成分分析评估两数据集之前的批次效应,分析结果如图1 A所示,两数据集呈现分别聚类,差异明显。经过ComBat函数移除批次效应后的主成分分析结果如图1B,两数据集之间表达量没有出现分别聚类。
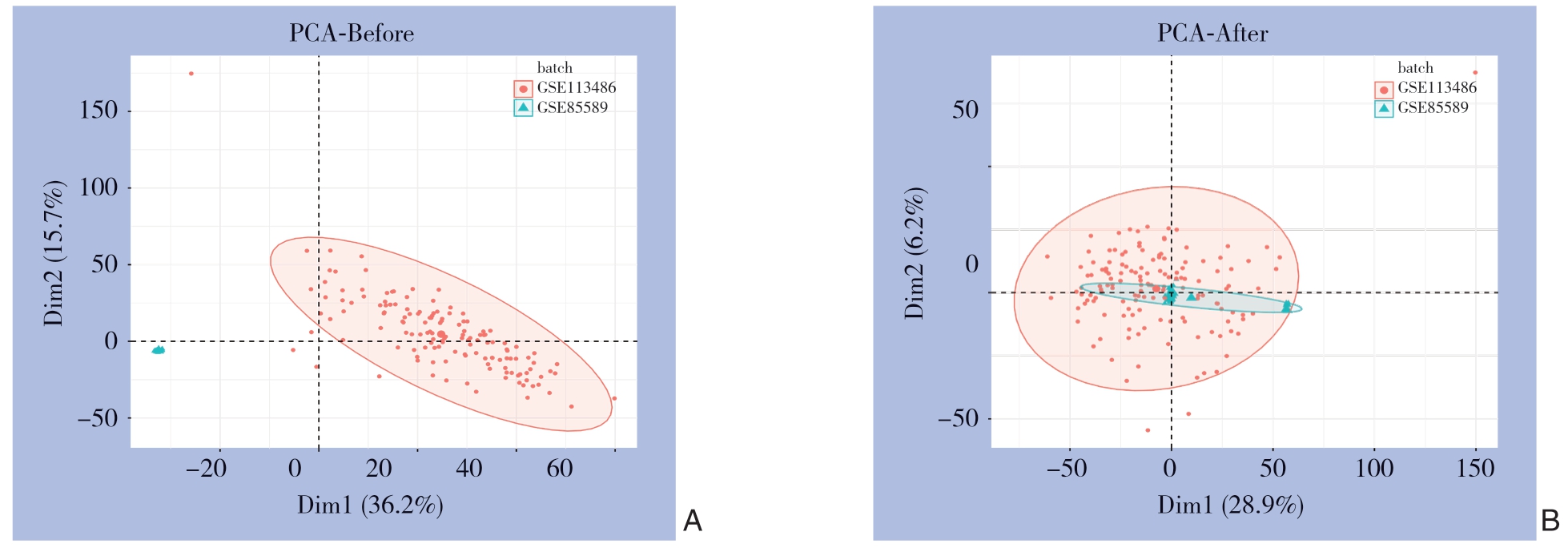
图1 PCA 图 A:批次效应校正前PCA;B:批次效应校正后PCA
Figure 1 PCA plots A:PCA before batch effect adjustment;B:PCA after batch effect adjustment
2.2 关键miRNA 的筛选
去除批次效应后,纳入研究的有247例样本(119例健康对照和128例胰腺癌),共2526个miRNA。对2526个miRNA进行LASSO回归分析,采用10倍交叉验证,结果显示最佳的λ=0.0272212(图2),其对应变量为33,即33个miRNA具有鉴别肿瘤样本及正常样本的潜力。
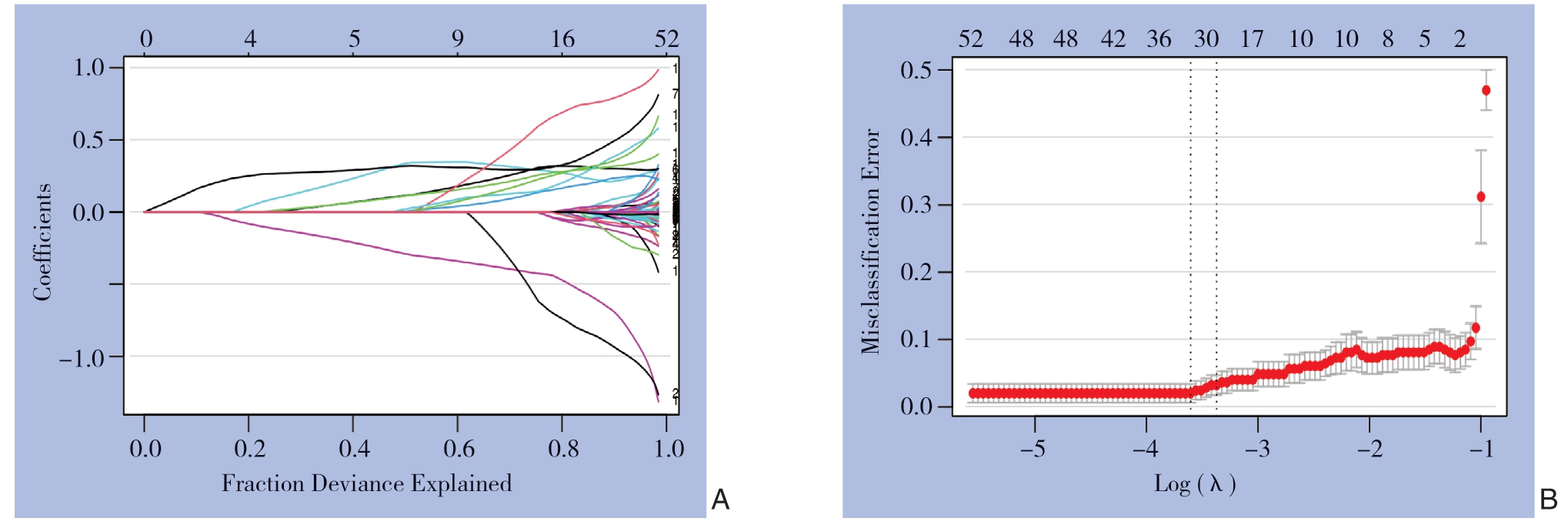
图2 关键miRNA 的筛选 A:LASSO 筛选变量动态过程图;B:交叉验证参数λ 的选择过程图
Figure 2 Screening process of the hub miRNAs A:Dynamic process variable screening by LASSO;B:Dynamic process of selection of cross validation parameter λ
2.3 决策树的构建及评价
为了通过血清miRNA中关键miRNA表达区分肿瘤与正常患者,本研究纳入LASSO回归筛选出的33个关键miRNA,构建决策树并验证决策树的预测效果。研究中将247例样本按6:4的比例进行随机分组,分为训练集(71例正常,77例肿瘤)和测试集(48例正常,51例肿瘤)。将rpart算法应用于训练集,获得了一个简单的决策树模型,模型包含两个miRNA,分别是miR-4532和miR-4668-5p(图3)。

图3 决策树模型
Figure 3 The decision tree model
使用测试数据集(占总数据的40%)来测量分类树的性能。然后通过曲线下的面积来评价该分类器的判别力。结果如图4,在训练集中ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.9481,测试集中AUC为0.9024。即由miR-4532和miR-4668-5p构成的决策树在训练集及测试集中均表现出良好的区分肿瘤与正常样本的能力。
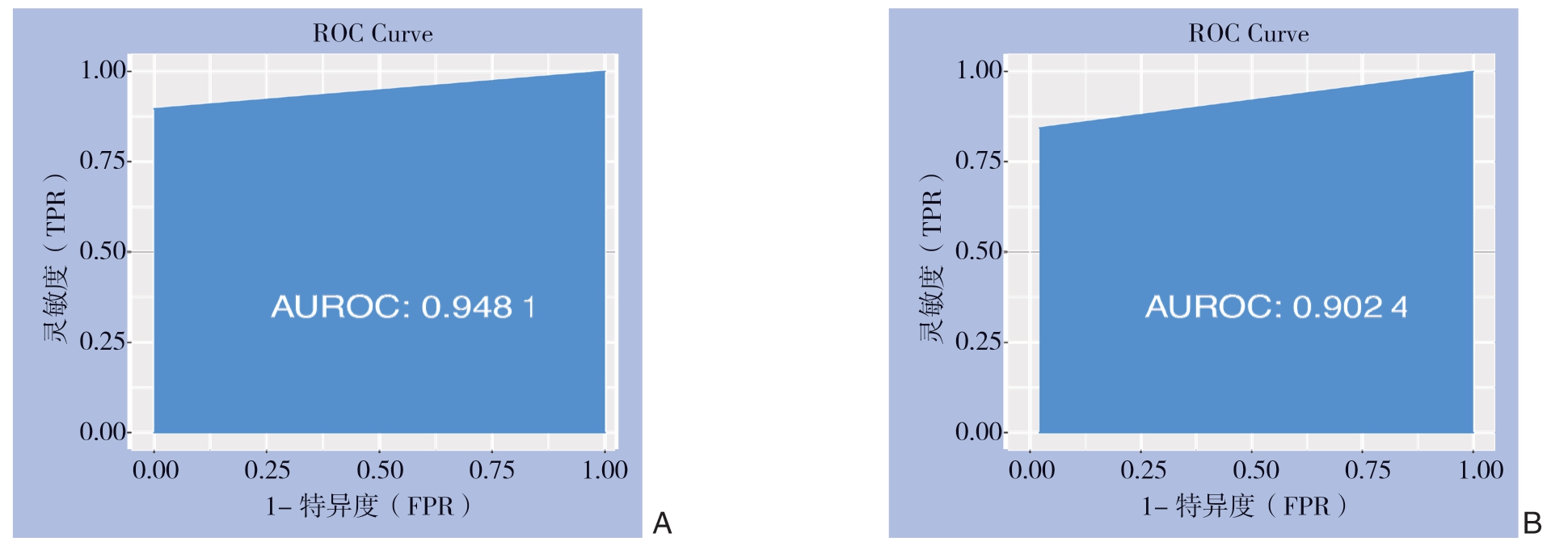
图4 ROC 曲线 A:训练集ROC 曲线;B:测试集ROC 曲线
Figure 4 ROC curves A:ROC curve for training set;B:ROC curve for validation set
2.4 关键miRNA 的组间差异
通过W i l c o x o n 检验对比了关键miRNA在胰腺癌血清样本和正常血清样本中的差异,结果表明,两组样本差异有统计学意义 (P<0.05)(图5)。

图5 关键miRNA 胰腺癌血清样本和正常血清样本中差异
Figure 5 Differences of the hub miRNAs in pancreatic and normal serum samples
2.5 富集分析
利用3 种数据库分别预测m i R-4532 和miR-4668-5p的靶向mRNA,结果显示,miR-4532在3种数据库中均预测到的mRNA有6个,miR-4668-5p在3种数据库中均预测到的mRNA有73个。利用clusterProfiler R包进行GO(Gene Ontology)富集分析,及KEGG(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes)通路富集。GO富集主要包括细胞组分(cellular component,CC)、分子功能(molecular function,MF)、生物过程(biological process,BP)。结果如图6所示,关键miRNA的靶基因可能与转录调节复合物,核染色质,转录阻遏物复合体,巨核细胞分化的调控,黏着剂组装,细胞-底物连接组织,巨核细胞分化,黏着斑组装的负调节等功能有关。其KEGG结果表明,关键miRNA的靶基因主要富集于癌症中的转录失调,FoxO信号通路,黏附连接,胰腺癌,乙型肝炎,肝细胞癌,TGF-β信号通路,MAPK信号通路等信号通路中。

图6 GO 及KEGG 分析
Figure 6 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis
3 讨论
miRNA参与了发育和各种生理过程,其失调可能会导致多种疾病的进展[21]。有研究表明,miRNA可以反映病理过程,因而被认为可以用于诊断及鉴别不同的肿瘤类型,甚至是良性疾病的识别。例如,血清miRNA对用于高度准确和特异性地筛查肉瘤[22],Zou等[23]研究发现5 种血清miRNA可用作为鼻咽癌的潜在生物标志物,Zarecki等[24]发现血清miRNA作为骨质疏松性椎体骨折的新型生物标志物等。
使用来自健康个体,胰腺癌和胰腺炎患者的胰腺组织的活检样品进行的比较miRNA表达谱差异的研究,清楚地表明了与正常细胞相比,各种miRNA在癌细胞中的差异表达,预示了miRNA在胰腺癌诊断,预后和抗癌治疗中的潜在作用[25]。Hong等[26]研究发现与邻近的正常胰腺组织相比,胰腺癌组织中共发现了158个miRNA差异表达,例如miR-200,miR-96和miR-217。在胰腺癌患者中,除了胰腺细胞和组织中miRNA的异常表达外,在全身循环中也观察到miRNA失调。例如,一些研究报告了miR-18a,miR-21,miR-22,miR-24,miR-25,miR-99a,miR-155,miR-185,miR-191,miR-196a在胰腺癌血液中的差异表达[27],miR-486-5p通过作用于体内多种信号通路参与胰腺腺癌的发生发展[28],胰腺癌细胞中miR-519d减低,且对于胰腺癌细胞增殖和侵袭能力有所增强[29]。
在本研究中,通过LASSO回归发现了33个具有鉴定胰腺癌肿瘤潜力的血清miRNA,并通过机器学习的方法构建了决策树,用于区分胰腺癌肿瘤患者和正常对照,其中miR-4532和miR-4668-5p这两个血清miRNA被认为是有效观测点。同样的,在本研究的训练集和测试集中,该决策树表现出了良好的预测效果,即AUC值分别为0.9481和0.9024,miR-4532和miR-4668-5p在肿瘤和正常样本中也表现出了明显差异,即肿瘤样本血清中表达相对较高。实际上,已经有研究表明hsamiR-4532在肿瘤中发挥重要作用,hsa-miR-4532下调癌症中的高甲基化可能促进乳腺癌细胞中的阿霉素抗性[30],携带hsa-miR-4532的急性髓样白血病细胞衍生的外泌体可以通过激活LDOC1依赖性STAT3信号通路抑制正常的造血干细胞的造血作用等[31]。也有研究表明miR-4668-3p参与结直肠癌的细胞增殖,迁移,侵袭和上皮细胞-间充质转化过程[32],miR-4668-5p在预测舒尼替尼治疗转移性肾细胞癌反应方面具有预测潜力[33]。
决策树在医学上的应用已经颇为广泛,例如,用于肝癌肝切除手术方式选择的决策树[34],基于MRI的决策树用于黄疸型婴儿的胆道闭锁诊断中[35]。随着基因组学的发展和二代测序的成本降低,越来越多的测序可供我们进一步研究,将基因组学数据和决策树结合起来,将是一个很好的思路,用于癌症研究。Sherafatian等[18]基于数据库中miRNA表达数据构建决策树进行肺癌诊断和亚型分型。本研究发现miR-4532和miR-4668-5p在胰腺癌患者的血清中相对表达较高,并通过构建决策树,用于区分正常血清样本和胰腺癌患者血清样本。这将有益于胰腺癌患者的早期诊断,甚至有可能通过进一步研究,取代传统的诊断方法,为胰腺癌的诊断提供一个简单准确的策略。同时,miR-4532和miR-4668-5p的预测作用也显示出了其在胰腺癌进程中的重要作用,有可能作为潜在的治疗靶点,值得进一步研究。
[1]Bray F,Ferlay J,Soerjomataram I,et al.Global cancer statistics 2018:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(6):394-424.doi:10.3322/caac.21492.
[2][No authors listed].Erratum:Global cancer statistics 2018:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2020,70(4):313.doi:10.3322/caac.21609.
[3]Rawla P,Sunkara T,Gaduputi V.Epidemiology of Pancreatic Cancer:Global Trends,Etiology and Risk Factors[J].World J Oncol,2019,10(1):10-27.doi:10.14740/wjon1166.
[4]Ryan DP,Hong TS,Bardeesy N.Pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J].N Engl J Med,2014,371(11):1039-1049.doi:10.1056/NEJMra1404198.
[5]Kleeff J,Korc M,Apte M,et al.Pancreatic cancer[J].Nat Rev Dis Primers,2016,2:16022.doi:10.1038/nrdp.2016.22.
[6]周发权,陈师,孙红玉,等.系统免疫炎症指数与胰 腺癌患者预后关系的系统评价和Meta分析[J].中国普通外科杂志,2020,29(9):1076-1083.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.09.007.
Zhou FQ,Chen S,Sun HY,et al.Prognostic value of the systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with pancreatic cancer:a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2020,29(9):1076-1083.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.09.007.
[7]Lan B,Zeng S,Grützmann R,et al.The Role of Exosomes in Pancreatic Cancer[J].Int J Mol Sci,2019,20(18):4332.doi:10.3390/ijms20184332.
[8]Wray CJ,Ahmad SA,Matthews JB,et al.Surgery for pancreatic cancer:recent controversies and current practice[J].Gastroenterology,2005,128(6):1626-1641.doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2005.03.035.
[9]Singhi AD,Koay EJ,Chari ST,et al.Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer:Opportunities and Challenges[J].Gastroenterology,2019,156(7):2024-2040.doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.259.
[10]Ballehaninna UK,Chamberlain RS.Serum CA 19-9 as a Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer-A Comprehensive Review[J].Indian J Surg Oncol,2011,2(2):88-100.doi:10.1007/s13193-011-0042-1.
[11]Acunzo M,Romano G,Wernicke D,et al.MicroRNA and cancer--a brief overview[J].Adv Biol Regul,2015,57:1-9.doi:10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.013.
[12]Weber JA,Baxter DH,Zhang S,et al.The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids[J].Clin Chem,2010,56(11):1733-1741.doi:10.1373/clinchem.2010.147405.
[13]Chen M,Calin GA,Meng QH.Circulating microRNAs as Promising Tumor Biomarkers[J].Adv Clin Chem,2014,67:189-214.doi:10.1016/bs.acc.2014.09.007.
[14]Keller A,Leidinger P,Bauer A,et al.Toward the blood-borne miRNome of human diseases[J].Nat Methods,2011,8(10):841-843.doi:10.1038/nmeth.1682.
[15]Martínez-Hernández R,Fuente H,Lamana A,et al.Utility of circulating serum miRNA profiles to evaluate the potential risk and severity of immune-mediated inflammatory disorders[J].J Autoimmun,2020,111:102472.doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102472.
[16]Huang C,Wang Q,Ma S,et al.A four serum-miRNA panel serves as a potential diagnostic biomarker of osteosarcoma[J].Int J Clin Oncol,2019,24(8):976-982.doi:10.1007/s10147-019-01433-x.
[17]Safavian SR,Landgrebe D.A survey of decision tree classifier methodology[J].IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern,21(3):660-674.doi:10.1109/21.97458.
[18]Sherafatian M,Arjmand F.Decision tree-based classifiers for lung cancer diagnosis and subtyping using TCGA miRNA expression data[J].Oncol Lett,2019,18(2):2125-2131.doi:10.3892/ol.2019.10462.
[19]Jeong Y,Xie Y,Xiao G,et al.Nuclear receptor expression defines a set of prognostic biomarkers for lung cancer[J].PLoS Med,2010,7(12):e1000378.doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000378.
[20]Yu G,Wang LG,Han Y,et al.clusterProfiler:an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters[J].OMICS,2012,16(5):284-287.doi:10.1089/omi.2011.0118.
[21]Hammond SM.An overview of microRNAs[J].Adv Drug Deliv Rev,2015,87:3-14.doi:10.1016/j.addr.2015.05.001.
[22]Jin Z,Liu S,Zhu P,et al.A novel serum miRNA-pair classifier for diagnosis of sarcoma[J].PLoS One,2020,15(7):e0236097.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0236097.
[23]Zou X,Zhu D,Zhang H,et al.MicroRNA expression profiling analysis in serum for nasopharyngeal carcinoma diagnosis[J].Gene,2020,727:144243.doi:10.1016/j.gene.2019.144243.
[24]Zarecki P,Hackl M,Grillari J,et al.Serum microRNAs as novel biomarkers for osteoporotic vertebral fractures[J].Bone,2020,130:115105.doi:10.1016/j.bone.2019.115105.
[25]Rawat M,Kadian K,Gupta Y,et al.MicroRNA in Pancreatic Cancer:From Biology to Therapeutic Potential[J].Genes (Basel),2019,10(10):752.doi:10.3390/genes10100752.
[26]Hong TH,Park IY.MicroRNA expression profiling of diagnostic needle aspirates from surgical pancreatic cancer specimens[J].Ann Surg Treat Res,2014,87(6):290-297.doi:10.4174/astr.2014.87.6.290.
[27]Morimura R,Komatsu S,Ichikawa D,et al.Novel diagnostic value of circulating miR-18a in plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer[J].Br J Cancer,2011,105(11):1733-1740.doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.453.
[28]任天宇,周新童,党胜春.miR-486-5p的靶基因预测 及其在胰腺腺癌中作用的生物信息学分析[J].中国普通外科杂志,2020,29(6):715-722.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.06.012.
Ren TY,Zhou XT,Dang SC.Prediction of target gene of miR-486-5p and bioinformatics analysis of their roles in pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2020,
29(6):715-722.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.06.012.
[29]梁治坤,程凡天,胡走肖,等.miR-519d在胰腺癌 细胞中的表达及其作用[J].中国普通外科杂志,2018,27(9):1142-1147.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.09.009.
Liang ZK,Cheng FT,Hu ZX,et al.Expression and action of miR-519d in pancreatic cancer cells[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2018,27(9):1142-1147.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2018.09.009.
[30]Feng F,Zhu X,Wang C,et al.Downregulation of hypermethylated in cancer-1 by miR-4532 promotes adriamycin resistance in breast cancer cells[J].Cancer Cell Int,2018,18:127.doi:10.1186/s12935-018-0616-x.
[31]Zhao C,Du F,Zhao Y,et al.Acute myeloid leukemia cells secrete microRNA-4532-containing exosomes to mediate normal hematopoiesis in hematopoietic stem cells by activating the LDOC1-dependent STAT3 signaling pathway[J].Stem Cell Res Ther,2019,10(1):384.doi:10.1186/s13287-019-1475-7.
[32]Li H,Guo S,Zhang M,et al.Long non-coding RNA AGAP2-AS1 accelerates cell proliferation,migration,invasion and the EMT process in colorectal cancer via regulating the miR-4,668-3p/SRSF1 axis[J].J Gene Med,2020,22(11):e3250.doi:10.1002/jgm.3250.
[33]Kováčová J,Juracek J,Poprach A,et al.Abstract 1800:miR-376b and miR-4668 predict therapeutic response to sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma[C]//Atlanta:AACR Annual Meeting,2019.doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2019-1800.
[34]Garonzik-Wang JM,Majella Doyle MB.Decision Tree for Liver Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J].JAMA Surg,2016,151(9):853-854.doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2016.1149.
[35]Kim YH,Kim MJ,Shin HJ,et al.MRI-based decision tree model for diagnosis of biliary atresia[J].Eur Radiol,2018,28(8):3422-3431.doi:10.1007/s00330-018-5327-0.
