乳腺癌是全球女性最常见的恶性肿瘤,其发病率位居中国女性恶性肿瘤首位[1]。但乳腺癌往往起病隐匿,早期缺乏特异性表现,临床主要通过乳腺彩超和钼靶进行初步筛查,进而借助病理细胞学检查明确诊断,但这些方法往往导致患者错过早期诊治的重要时机[2]。微小RNA(miRNA)是一种由18~24个核苷酸组成的非编码蛋白RNA小分子[3-4],通过对靶基因的翻译抑制或切割降解来调控基因的表达,其与多种肿瘤的发生发展有关,并有研究发现某些miRNA的异常表达与乳腺癌的不良预后有关[5-6]。通过检测多种miRNA在乳腺癌细胞株中表达的相关研究显示,miR-196a-5p呈显著高表达[7-8],而miR-339-5p表达显著下调[9]。因此,两者的生物学功能可能对乳腺癌诊断有着重要临床意义,本研究联合检测乳腺癌患者血清miR-196a-5p和miR-339-5p表达水平,观察其在乳腺癌早期诊断中的临床价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
选择2016年1月—2017年6月在我院就诊的乳腺外科诊治的乳腺癌患者107例(乳腺癌组),年龄35~79岁,平均(51.28±9.65)岁;根据TNM分期标准:I期34例,II期37例,III期21例,IV期15例;病理为浸润性导管癌72例,黏液腺癌7例,导管内癌8例,小叶癌8例,髓样癌12例。纳入标准:均被病理确诊乳腺癌,女性;术前无放化疗和内分泌治疗;均接受乳腺癌的手术治疗;所有患者临床病理资料完整;无其他肿瘤病史。选择同期在我院诊断为乳腺良性疾病的患者60例(乳腺良性疾病组),年龄35~79岁,平均(52.19±10.58)岁;其中乳腺病33例,乳腺导管内乳头状瘤11例,乳腺不典型增生7例和乳腺纤维瘤9例。选择同期在我院行健康体检者35 例(健康对照组),年龄35~79岁,平均(51.76±9.75)岁。所有的患者均知情同意,并签署知情同意书和经医院伦理委员会审核通过。3组在年龄等基线资料具有可比性。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 血液标本留取 患者各组入院后和乳腺癌手术后1 周抽取肘静脉血10 mL。采用离心机将血液离心,离心半径15 cm,离心速度3000 r/min,离心15 min,抽取上清液放置在除酶管内,放置在-70 ℃冰箱中保存。
1.2.2 qRT-PCR 总RNA 抽取:采用受试者血清400 µL,采用TRIzol 试剂盒进行提取血清总RNA,反转录引物有上海化生有限公司合成,miR-196a-5p 上游引物序列:5'-CGCGCGTAGGTAGTTCATGTT-3',下游引物序列:5'-CAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3';miR-339-5p 上游引物序列为:5'-GGGTCCCTGTCCTCCCCA-3',下游引物序列5'-TGCGTGTCGTGGAGTC-3'。U6 的上游引物为:5'-GAGGCACAGCGGAACG-3',下游引物:5'-CTACCACATAGTCCAGG-3'。miRNA 的检测:选择反转录酶1 µL,RNA5 µL和3 µL 引物,在15 µL 的反应体系中,采用美国ABITaqMan PreAmp Master Mix 进行扩增,扩增条件为:在16 ℃ 30 min,42 ℃反应30 min 和85 ℃反应5 min。取反转录配制20 µL 反应体系,放置在荧光定量仪中进行反应,反应条件为:95 ℃预变性为15 min,94 ℃变性15 s,55 ℃退火30 s,70 ℃延伸30 s,连续40 个循环。每个样品检测3 次,以2-ΔΔCt 表示。
1.2.3 观察指标 比较各组血清miR-196a-5p、miR-339-5p 和乳腺癌特异性标志物CA15-3 水平,三者诊断乳腺癌的效能,以及血清miR-196a-5p和miR-339-5p 表达水平与临床病理特征的关系。
1.3 统计学处理
采用SPSS15.0统计分析软件对数据进行分析,呈正态分布的计量资料采用均数±标准差(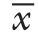 ±s)进行表示,多组独立因素的计量资料采用方差分析,两组独立因素的计量资料采用t检验。采用Logistic二元回归分析得出血清mi R-196 a-5p和miR-339-5p联合变量,绘制出受试者曲线(ROC)评价诊断乳腺癌的效能。采用MedCalc软件计算截断值。检验水准,α=0.05。
±s)进行表示,多组独立因素的计量资料采用方差分析,两组独立因素的计量资料采用t检验。采用Logistic二元回归分析得出血清mi R-196 a-5p和miR-339-5p联合变量,绘制出受试者曲线(ROC)评价诊断乳腺癌的效能。采用MedCalc软件计算截断值。检验水准,α=0.05。
2 结果
2.1 各组血清miR-196a-5p、miR-339-5p 和CA15-3水平比较
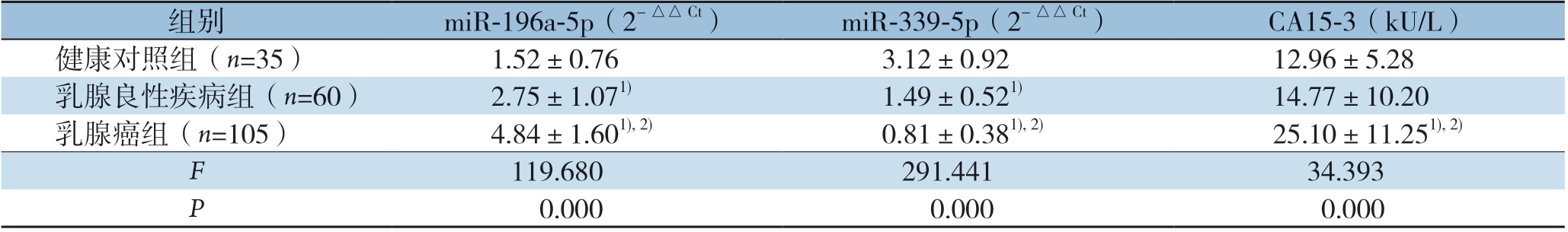
乳腺癌组血清miR-196a-5p表达水平明显高于乳腺良性疾病组和健康对照组(P<0.01),乳腺良性疾病组明显高于健康对照组(P<0.01);乳腺癌组血清miR-339-5p表达水平明显低于乳腺良性疾病组和健康对照组(P<0.01),乳腺良性疾病组明显低于健康对照组(P<0.01);乳腺癌患者血清CA15-3水平明显高于乳腺良性疾病组和健康对照组(P<0.01),而乳腺良性疾病组和健康对照组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(表1)。
表1 各组血清miR-196a-5p、miR-339-5p 和CA15-3 水平比较(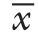 ±s)
±s)
Table 1 Comparison of the serum levels of miR-196a-5p,miR-339-5p and CA15-3 among groups(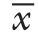 ±s)
±s)
注:1)与健康对照组比较,P<0.01;2)与乳腺良性疾病组比较,P<0.01
Note:1)P<0.01 vs.healthy control group;2)P<0.01 vs.benign breast disease group
组别miR-196a-5p(2-△△Ct) miR-339-5p(2-△△Ct)CA15-3(kU/L)健康对照组(n=35)1.52±0.763.12±0.9212.96±5.28乳腺良性疾病组(n=60)2.75±1.071)1.49±0.521)14.77±10.20乳腺癌组(n=105)4.84±1.601),2)0.81±0.381),2)25.10±11.251),2)F 119.680291.44134.393 P 0.0000.0000.000
2.2 血清miR-196a-5p和miR-339-5p表达水平在诊断乳腺癌的效能
血清miR-196a-5p和miR-339-5p表达的诊断乳腺癌的效能明显优于血清CA15-3(Z=2.543,P<0.05;Z=2.190,P<0.05),而血清miR-196a-5p表达与miR-339-5 p 之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),将miR-196a-5p和miR-339-5p指标进行二元Logistic回归得方程y=1.09×xmiR-196a-5p-3.61×xmiR-339-5p+0.66,联合检测(miR-196a-5p+miR-339-5p)的灵敏度为91.6%,特异度为88.3%,其AUC为0.937,明显高于单个指标表达(miR-196a-5p:Z=3.044,P<0.01;miR-339-5p,Z=3.020,P<0.01)(表2)(图1)。
表2 血清miR-196a-5p、miR-339-5p 和CA15-3 对诊断乳腺癌的诊断效能
Table 2 Diagnostic efficiencies of serum miR-196a-5p,miR-339-5p and CA15-3 for breast cancer
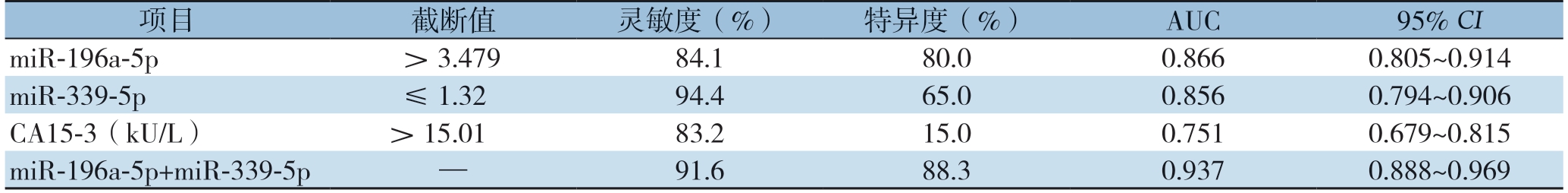
项目196a-5p截断值灵敏度(%)特异度(%)AUC95% CI miR->3.47984.180.00.8660.805~0.914 miR-339-5p≤1.3294.465.00.8560.794~0.906CA15-3(kU/L)>15.0183.215.00.7510.679~0.815 miR-196a-5p+miR-339-5p—91.688.30.9370.888~0.969
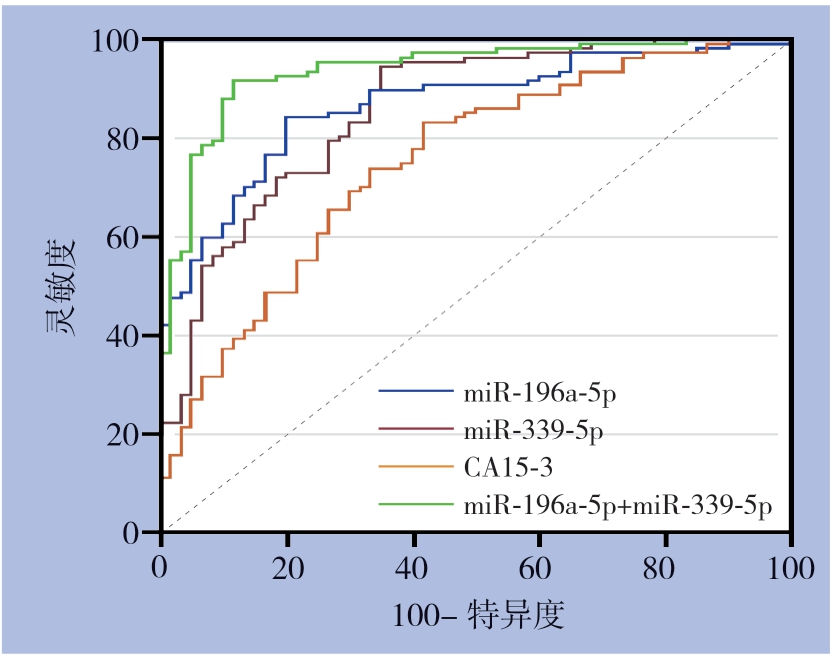
图1 血清miR-196a-5p、miR-339-5p 和CA15-3 在诊断乳腺癌的灵敏度和特异度
Figure 1 The sensitivities and specificities of serum miR-196a-5p,miR-339-5p and CA15-3 in diagnosis of breast cancer
2.3 乳腺癌患者术前miR-196a-5p 和miR-339-5p 表达的关系与术后的变化
乳腺癌患者术前血清miR-196a-5p表达与miR-339-5p呈负相关(r=-0.764,P<0.01),手术后乳腺癌患者血清miR-196a-5p和miR-339-5p表达分为1.86±0.85和2.59±0.86,血清miR-196a-5p表达水平较手术前明显降低(P<0.01),而miR-339-5p表达较术前明显升高(P<0.01)。
2.4 乳腺癌患者血清miR-196a-5p 和miR-339-5p 表达与临床病理因素的关系
乳腺乳腺癌患者血清miR-196a-5p和miR-339-5p表达水平与肿瘤直径、淋巴结转移和TNM分期具明显有关(均P<0.01),而与年龄,绝经否,组织学分级,ER,PR和HER-2无明显关系(均P>0.05)(表3)。
表3 乳腺癌患者血清miR-196a-5p 和miR-339-5p 水平与临床病理因素的关系( ±s)
±s)
Table 3 Relations of serum levels of miR-196a-5p and miR-339-5p in breast cancer patients with clinicopathologic factors( ±s)
±s)

因素年龄(岁例数(n)miR-196a-5ptPmiR-339-5ptP)<50674.84±1.630.0530.9580.81±0.380.0950.924≥50404.83±1.570.82±0.37绝经与否是454.83±1.560.0610.9510.82±0.360.0270.979否624.84±1.640.81±0.39肿瘤直径(cm)>2576.01±1.0513.1360.0000.53±0.2014.8150.000≤2503.49±0.911.14±0.23组织学分级I295.02±1.490.77±0.35II374.66±1.740.4260.6540.85±0.410.3910.678III414.86±1.570.81±0.37
表3 乳腺癌患者血清miR-196a-5p 和miR-339-5p 水平与临床病理因素的关系(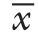 ±s)(续)
±s)(续)
Table 3 Relations of serum levels of miR-196a-5p and miR-339-5p in breast cancer patients with clinicopathologic factors(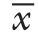 ±s)(continued)
±s)(continued)

因素巴结转移例数(n)miR-196a-5ptPmiR-339-5ptP淋有553.54±0.9213.3340.0000.51±0.2014.7190.000无526.07±1.041.13±0.23TNM 分期I343.12±0.881.25±0.19II374.69±0.43106.7420.0000.81±0.10268.5730.000III~IV366.61±0.870.40±0.16ER阳性644.85±1.650.0690.9450.81±0.380.1260.900阴性434.82±1.520.82±0.37PR阳性664.82±1.630.1410.8880.82±0.380.9620.911阴性414.86±1.570.81±0.37HER-2阳性324.98±1.430.6200.5370.78±0.330.6500.517阴性754.77±1.680.83±0.39
3 讨论
miRNA是一类进化上保守的小分子非编码RNA,成熟miRNA通过与mRNA的3'非翻译区(UTR)结合诱导其降解、翻译抑制或从翻译机制中截留靶向mRNA来调控基因的表达[10]。研究[11-12]表明,特定的miRNA在不同的肿瘤中出现明显的上调或下调,可能作为肿瘤预测标志物和潜在的治疗靶点,具有显著的临床价值。miRNA表达具有组织特异性,其表达差异可以区分不同分化类型的肿瘤,也可以区分正常组织和肿瘤组织,临床诊断中可以帮助寻找肿瘤原发病灶[13-14]。现在其已作为某些特定肿瘤的分子诊断学依据,而且其在肿瘤治疗和预后中的作用也受到极大的关注[15-16]。
miR-196a是2004年发现的HOX家族基因转录而来,在细胞分化的调节过程中扮演着重要角色,与肿瘤的发生发展存在重要联系。现有研究显示miR-196a在多种肿瘤表现出类似致癌基因的生物学特性,且降低miR-196a的表达具有明显抑制肿瘤增殖、转移侵袭、促进凋亡甚至有逆转耐药的作用[12,17]。王艳等[9]研究通过miRNA芯片技术检测847种miRNA在不同侵袭力乳腺癌细胞株中的表达,获得与乳腺癌侵袭相关的miRNA表达谱,miR-339-5p表达显著改变,具有类似抑癌基因的生物学特性,并发现miR-339-5p转染到乳腺癌中能够明显抑制乳腺癌的增殖和转移[18],两者可能成为乳腺癌诊断的重要肿瘤预测标志物。
在一项食管癌的研究证实miR-196a出现高表达,并且发现miR-196a能够促进肿瘤细胞的增殖和迁移,对与预测肿瘤预后和早期诊断方面具有较高的临床价值[19]。在对胃癌的研究中发现出现miR-196a高表达,并且与肿瘤大小和肿瘤分期呈正相关,与患者的生存期呈负相关[20-21]。miR-196a在结肠癌组织或者细胞系中呈高表达,而高表达的miR-196a可以激活Akt信号通路促进结肠癌的侵袭和迁移能力,并且增强细胞对化疗药物的耐药[22]。本组研究显示乳腺癌组患者血清miR-196a-5p表达水平明显优于乳腺良性疾病组和健康对照组,并且术后血清miR-196a-5p水平出现明显降低,说明血清miR-196a-5p表达来源于乳腺癌细胞。miR-196a-5p在乳腺癌的表达水平研究较少,有研究发现通过转染miR-196a-2到乳腺癌细胞内,会起到类似致癌基因的作用,并认为miR-196a-2可以作为乳腺癌的新型标记物[23]。本组研究还发现血清miR-196a-5p表达水平肿瘤直径,分期和淋巴结是否转移具有显相关性,并且发现血清miR-196a-5p表达量超过3.479(2-ΔΔCt),其诊断乳腺癌的灵敏度为84.1%,特异度80.0%,AUC为0.866具有较高的诊断效能,可能作为诊断乳腺癌的敏感指标。
有研究[24-26]发现miR-339-5p表达在胃癌、结肠癌、肺癌和食管癌等实体肿瘤中出现明显的表达异常。在一项胃癌的细胞株研究发现miR-339-5p出现明显的低表达,高侵袭性的细胞株表达更低[27]。且在结肠癌中得到同样的结论[28],将miR-339-5p转染到结肠癌细胞中,其侵袭和增殖能力明显降低,形成肿瘤的能力明显降低。本组研究显示乳腺癌组血清miR-339-5p表达水平明显低于良性乳腺疾病组和健康对照组,并且发现乳腺癌术后血清miR-339-5p表达水平出现明显提高,说明乳腺癌与miR-339-5p表达水平具有一定的联系,与Zheng等[29]报道的结论接近,将miR-339-5p基因转染到乳腺癌细胞,发现在裸鼠体内成瘤的时间明显延长,充分说明miR-339-5p基因有类似抑癌基因的特性。在对抑制乳腺癌的机制研究中发现miR-339-5p可以通过抑制BCL-6水平的表达,从而抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖和迁移[30]。本组研究还发现乳腺癌肿瘤分期越高,淋巴结出现转移,直径越大,血清miR-339-5p表达越低,同时发现≤1.32(2-ΔΔCt)时,其灵敏度为94.4%,特异度为65.0%,AUC为0.856,在诊断乳腺癌具有较高的诊断效能,故血清miR-339-5p可能为诊断乳腺癌的诊断指标。
本组研究发现血清miR-196a-5p表达水平与miR-339-5p表达呈负相关,并且发现血清miR-196a-5p和miR-339-5p表达水平在诊断乳腺癌的诊断效能均高于CA15-3,联合检测miR-196a-5p和miR-339-5p能够明显提高对乳腺癌的诊断效能,其灵敏度达到91.6%,特异度为88.3%,AUC明显高于单个指标,说明两指标之间存在某种互补性,故联合检测能够提高乳腺癌诊断效能,但其具体作用机制尚需进一步实验证实。综上所述,联合miR-196a-5p和miR-339-5p基因检测有助于对乳腺癌的诊断。
[1]赫捷,陈万青,李霓,等.中国女性乳腺癌筛查与早诊早治指南(2021,北京)[J].中国肿瘤,2021,30(3):161–191.doi:10.11735/j.issn.1004–0242.2021.03.A001.He J,Chen WQ,Li N,et al.China Guideline for the Screening and Early Detection of Female Breast Cancer(2021,Beijing)[J].China Cancer,2021,30(3):161–191.doi:10.11735/j.issn.1004–0242.2021.03.A001.
[2]黎立喜,马飞.乳腺癌筛查和早期诊断的血液生物学标志物[J].国际肿瘤学杂志,2021,48(2):109–112.doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn371439–20200629–00021.
Li LX,Ma F.Blood biomarkers for breast cancer screening and early diagnosis[J].Journal of International Oncology,2021,48(2):109–112.doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn371439–20200629–00021.
[3]张帆,李泽东,彭禹,等.基于血清miRNA表达数据的胰腺癌诊断决策树构建[J].中国普通外科杂志,2021,30(2):211–218.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005–6947.2021.02.010.
Zhang F,Li ZD,Peng Y,et al.Construction of decision tree for diagnosis of pancreatic cancer based on serum miRNA expression data[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2021,30(2):211–218.doi:10.7659/j.issn.1005–6947.2021.02.010.
[4]杨浚沨,王龙强,李海,等.乳腺癌循环miRNA生物标志物的筛选及验证[J].中国普通外科杂志,2015,24(5):696–700.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005–6947.2015.05.016.
Yang JF,Wang LQ,Li H,et al.Screening and verification of circulating miRNA biomarkers of breast cancer[J].Chinese Journal of General Surgery,2015,24(5):696–700.doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005–6947.2015.05.016.
[5]Shimomura A,Shiino S,Kawauchi J,et al.Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting breast cancer in the early stage[J].Cancer Sci,2016,107(3):326–334.doi:10.1111/cas.12880.
[6]He Y,Deng F,Yang S,et al.Exosomal microRNA:a novel biomarker for breast cancer[J].Biomark Med,2018,12(2):177–188.doi:10.2217/bmm-2017–0305.
[7]Shahabi A,Naghili B,Ansarin K,et al.miR-140 and miR-196a as Potential Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Patients[J].Asian Pac JCancer Prev,2020,21(7):1913–1918.doi:10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.7.1913.
[8]陈晶,赵璐,宋牧,等.has-mir-125a-5p和has-mir-196a2基因多态性与新疆汉族和维吾尔族乳腺癌的相关性研究[J].重庆医学,2018,47(12):1685–1687.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671–8348.2018.12.030.
Chen J,Zhao L,Song M,et al.Correlation of gene polymorphism of has-mir-125a-5p and has-mir-196a2 with breast cancer in the Han and Uyghur nationalities[J].Chongqing Medicine,2018,47(12):1685–1687.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671–8348.2018.12.030.
[9]王艳.人乳腺癌细胞侵袭相关miRNAs的筛选及hsa-miR-339-5p生物学功能的初步研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2010,doi:10.7666/d.D128766.
Wang Y.The expression of hsa-miR-339–5p in breast cancer and the preliminary study of its biological behavior[D].Hefei:Anhui Medical University,2010,doi:10.7666/d.D128766.
[10]Dong H,Lei J,Ding L,et al.MicroRNA:function,detection,and bioanalysis[J].Chem Rev,2013,113(8):6207–6233.doi:10.1021/cr300362f.
[11]Piasecka D,Braun M,Kordek R,et al.MicroRNAs in regulation of triple-negative breast cancer progression[J].JCancer Res Clin Oncol,2018,144(8):1401–1411.doi:10.1007/s00432–018–2689–2.
[12]高航,赵峰,吴衍,等.微小RNA-9–5p靶向HIC1降低乳腺癌细胞对多柔比星敏感性的研究[J].外科理论与实践,2020,25(3):227–233.doi:10.16139/j.1007–9610.2020.03.011.
Gao H,Zhao F,Wu Y,et al.Study on microRNA-9–5p reducing sensitivity of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin through targeting HIC1[J].Journal of Surgery Concepts &Practice,2020,25(3):227–233.doi:10.16139/j.1007–9610.2020.03.011.
[13]王晓琼,张玲玲,王江洪,等.miRNA在肺癌筛查、诊断、治疗及预后中的应用价值[J].唐山师范学院学报,2017,39(5):65–68.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009–9115.2017.05.019.
Wang XQ,Zhang LL,Wang JH,et al.The Value of Mirna in the Screening,Diagnosis,Treatment and Prognosis of Lung Cancer[J].Journal of Tangshan Teachers College,2017,39(5):65–68.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009–9115.2017.05.019.
[14]高杰,张晓,魏超.差异表达miRNA 在胰腺癌预后判断中的价值[J].癌变·畸变·突变,2019,31(3):173–179.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004–616x.2019.03.001.
Gao J,Zhang X,Wei C,et al.Involvement of differentially expressed miRNA in prognosis of pancreatic cancers[J].Carcinogenesis,Teratogenesis &Mutagenesis,2019,31(3):173–179.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004–616x.2019.03.001.
[15]马跃,高英静,何浪.乳腺癌差异表达miRNA在预后中的意义[J].医学研究杂志,2018,47(1):39–44.doi:10.11969/j.issn.1673–548X.2018.01.011.
Ma Y,Gao YJ,He L.Differential Expression of miRNA i n Breast Cancer and the Significance in Prognosis[J].Journal of Medical Research,2018,47(1):39–44.doi:10.11969/j.issn.1673–548X.2018.01.011.
[16]周琨,陆霁,殷晓星,等.血清miRNA-128a和miRNA-128b表达对胃癌早期诊断和预后的影响[J].复旦学报:医学版,2019,46(6):797–802.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672–8467.2019.06.013.
Zhou K,Lu J,Yin XX,et al.Impact of serum miRNA-128a and miRNA-128b expression on early diagnosis and prognosis in patients with gastric cancer[J].Fudan University Journal of Medical Sciences,2019,46(6):797–802.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672–8467.2019.06.013.
[17]姜黎黎,万里,王朝霞.miR-196a在肿瘤研究中的进展[J].现代肿瘤医学,2015,23(16):2389–2392.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672–4992.2015.16.41.
Jiang LL,Wan L,Wang ZX.Progression of miR-196 a in tumor[J].Journal of Modern Oncology,2015,23(16):2389–2392.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672–4992.2015.16.41.
[18]刘雪,吴正升,吴强.乳腺癌细胞中miR-339–5p对BCL-6表达的调节[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2013,29(3):244–246.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001–7399.2013.03.003.
Liu X,Wu ZS,Wu Q.BCL-6 is a target gene of miR-339–5p in breast cancer[J].Chinese Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology,2013,29(3):244–246.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001–7399.2013.03.003.
[19]Ma Y,Wang B,Guo Y,et al.Inhibition of miR-196a affects esophageal cancer cell growth in vitro[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2016,84:22–27.doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.013.
[20]Feng C,She J,Chen X,et al.Exosomal miR-196a-1 promotes gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis by targeting SFRP1[J].Nanomedicine(Lond),2019,14(19):2579–2593.doi:10.2217/nnm-2019–0053.
[21]Li HL,Xie SP,Yang YL,et al.Clinical significance of upregulation of mir-196a-5p in gastric cancer and enriched KEGG pathway analysis of target genes[J].Asian Pac JCancer Prev,2015,16(5):1781–1787.doi:10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.5.1781.
[22]Li S,Zhou J,Wang Z,et al.Long noncoding RNAGAS5 suppresses triple negative breast cancer progression through inhibition of proliferation and invasion by competitively binding miR-196a-5p[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2018,104:451–457.doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.056.
[23]Jedlinski DJ,Gabrovska PN,Weinstein SR,et al.Single nucleotide polymorphism in hsa-mir-196a-2 and breast cancer risk:a case control study[J].Twin Res Hum Genet,2011,14(5):417–421.doi:10.1375/twin.14.5.417.
[24]Li Y,Zhang X,Yang Z,et al.miR-339–5p inhibits metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the epithelial-tomesenchymal transition[J].Oncol Lett,2018,15(2):2508–2514.doi:10.3892/ol.2017.7608.
[25]Huang E,Fu J,Yu Q,et al.CircRNA hsa_circ_0004771 promotes esophageal squamous cell cancer progression via miR-339–5p/CDC25A axis[J].Epigenomics,2020,12(7):587–603.doi:10.2217/epi-2019–0404.
[26]陈杰,郭文超,陈攀,等.干扰lncRNARHPN1-AS1表达通过靶向miR-339–5p对肝癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J].中国医学装备,2021,18(2):142–148.doi:10.3969/J.ISSN.1672–8270.2021.02.036.
Chen J,Guo WC,Chen P,et al.Study on the effect of interfering the expression of lncRNARHPN1-AS1 on proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by targeting miR-339–5p[J].China Medical Equipment,2021,18(2):142–148.doi:10.3969/J.ISSN.1672–8270.2021.02.036.
[27]Chen FR,Sha SM,Wang SH,et al.RP11–81H3.2 promotes gastric cancer progression through miR-339-HNRNPA1 interaction network[J].Cancer Med,2020,9(7):2524–2534.doi:10.1002/cam4.2867.
[28]Zhou C,Lu Y,Li X.miR-339–3p inhibits proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer[J].Oncol Lett,2015,10(5):2842–2848.doi:10.3892/ol.2015.3661.
[29]Zheng L,Zhang Y,Fu Y,et al.Long non-coding RNAMALAT1 regulates BLCAP mRNA expression through binding to miR-339–5p and promotes poor prognosis in breast cancer[J].Biosci Rep,2019,9(2):BSR20181284.doi:10.1042/BSR20181284.
[30]Wu ZS,Wu Q,Wang CQ,et al.MiR-339–5p inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro and may be a potential biomarker for breast cancer prognosis[J].BMCCancer,2010,10:542.doi:10.1186/1471–2407–10–542.
