- Key points, challenges, and considerations in managing endoleaks during endovascular aneurysm repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Application and efficacy analysis of selective sac embolization via the iliac approach in the management of endoleaks during EVAR
- Expression and mechanistic role of macrophage-enriched lncRNA CCL3-AS1 in carotid plaque instability
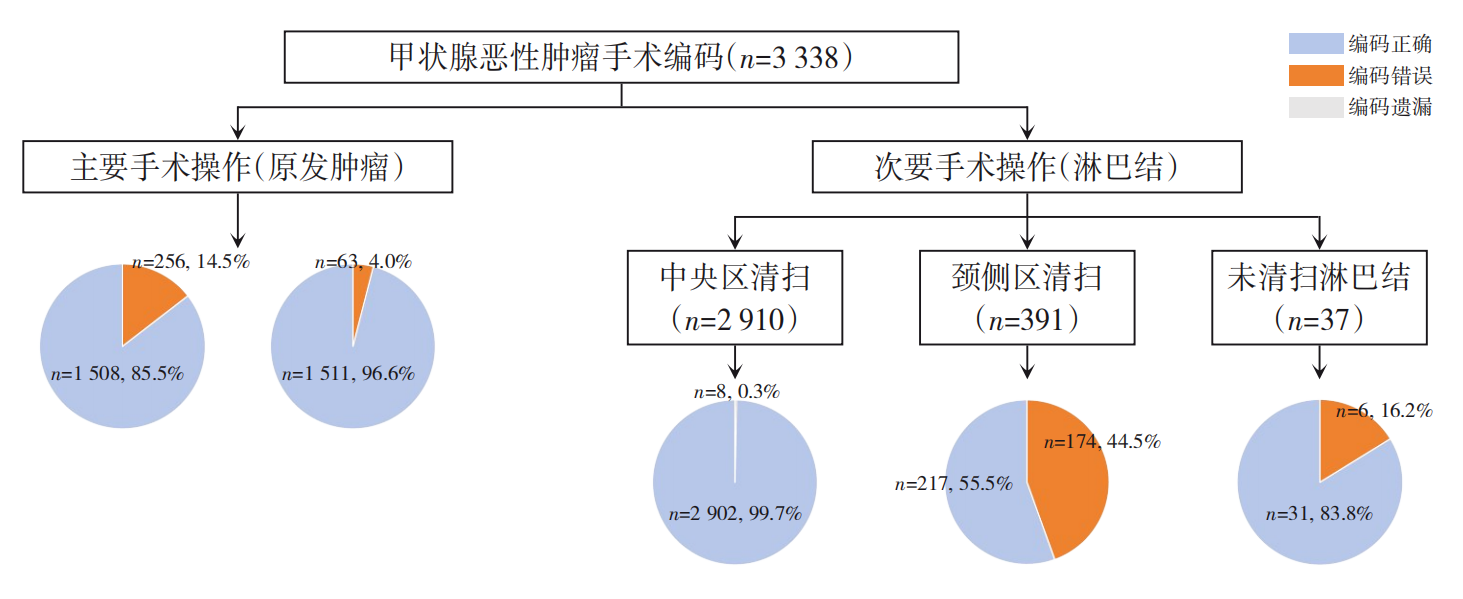
- Assessment of the quality of diagnosis and surgical procedure coding for thyroid cancer on the front page of medical records in a single center
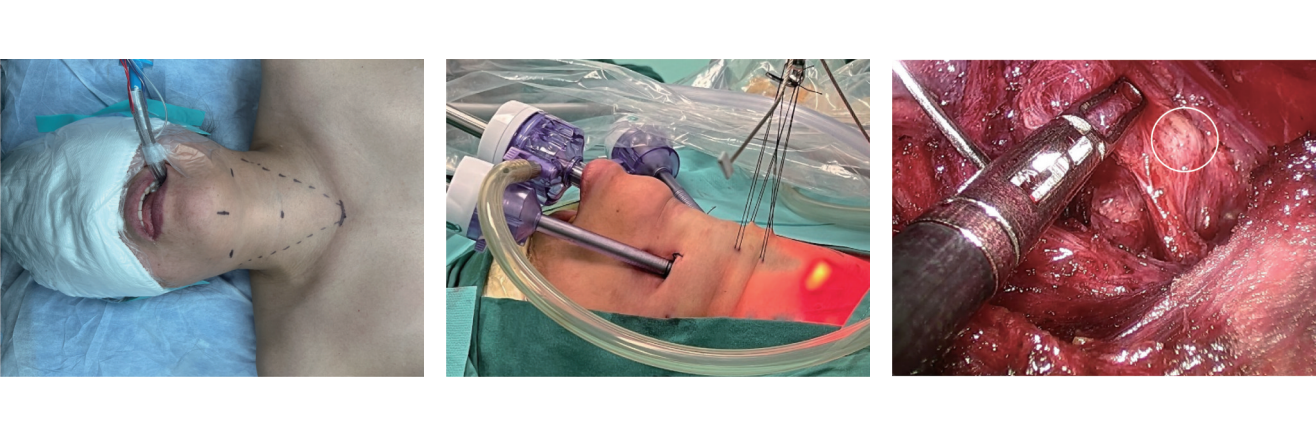
- Seven-step method for robot-assisted endoscopic thyroidectomy (BABA approach)
- Key factors affecting complications and operative time in endoscopic thyroidectomy via oral vestibule and submandibular approach
- Capability building and practical pathways for an excellent assistant in robotic thyroidectomy
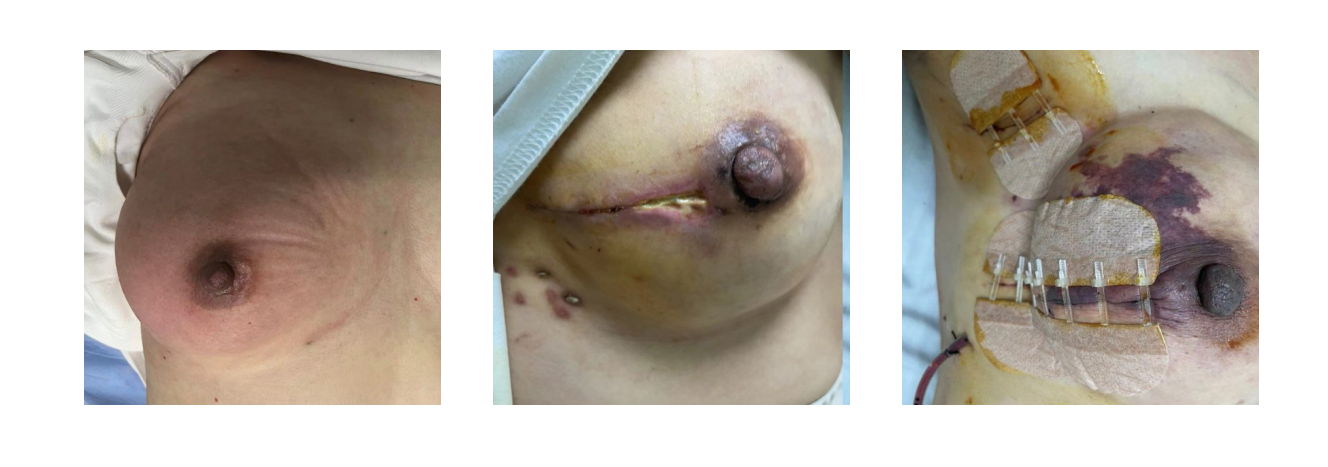
- Risk factors for postoperative complications in patients undergoing implant-based breast reconstruction after mastectomy
- Comparison of pedicled lateral thoracic artery perforator flap and mammoplasty in oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery for early-stage breast cancer
- Chinese expert consensus on robotic-assisted hiatal hernia repair with anti-reflux surgery in adults (2024 Edition)
- Laparoscopic standardized seven-step surgical operative guidelines for hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux disease (2025 edition)
- Application of the "necktie technique" in laparoscopic esophageal hiatal hernia repair and fundoplication surgery
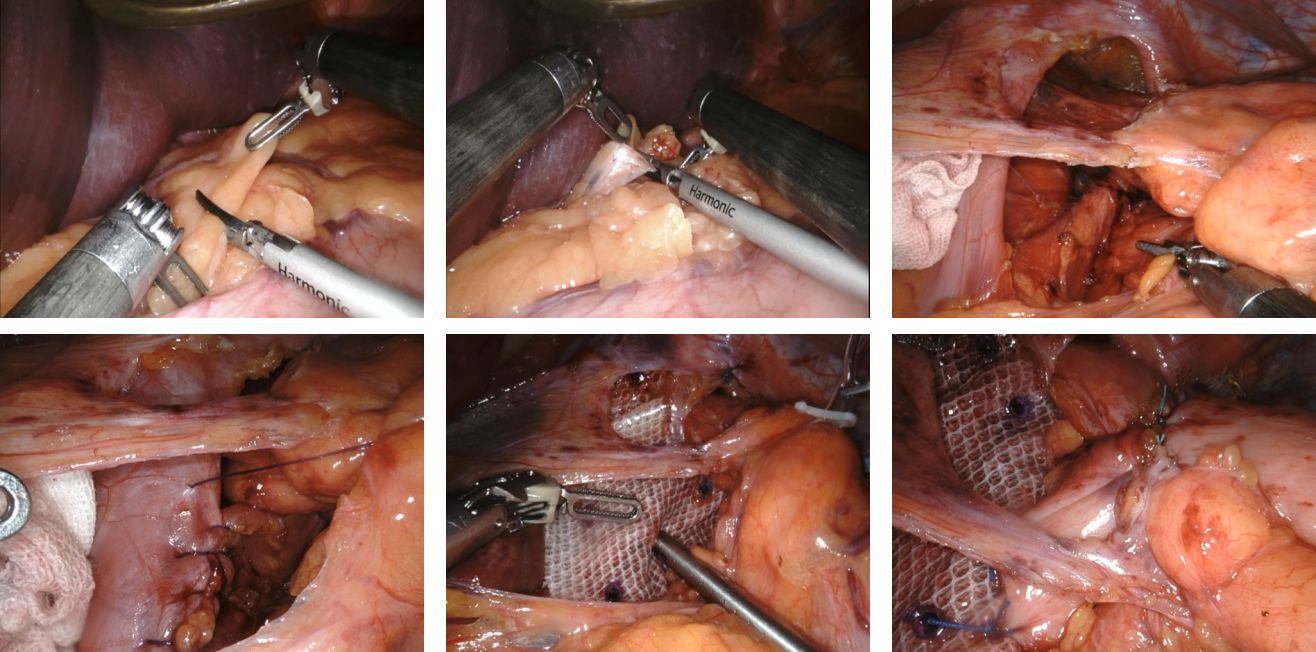
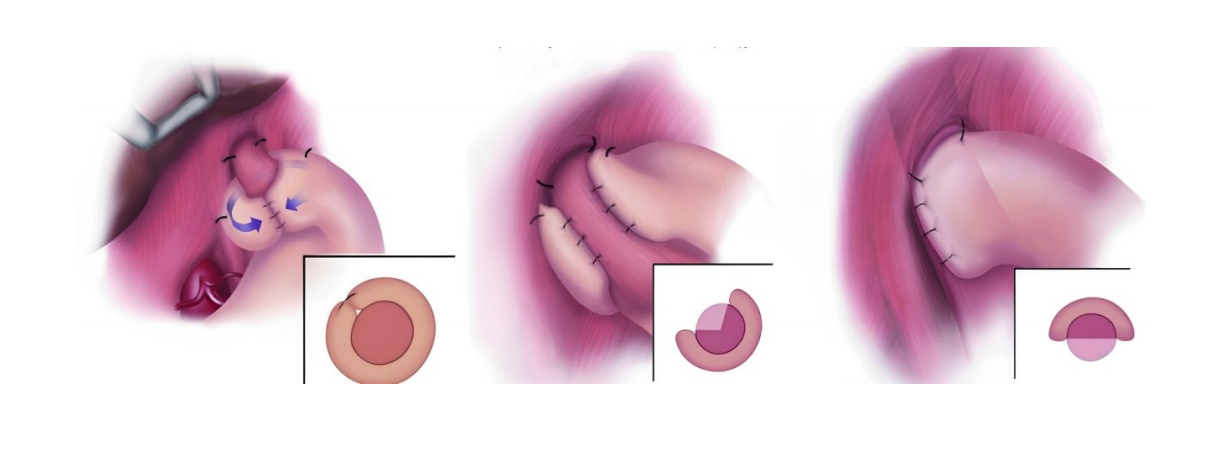
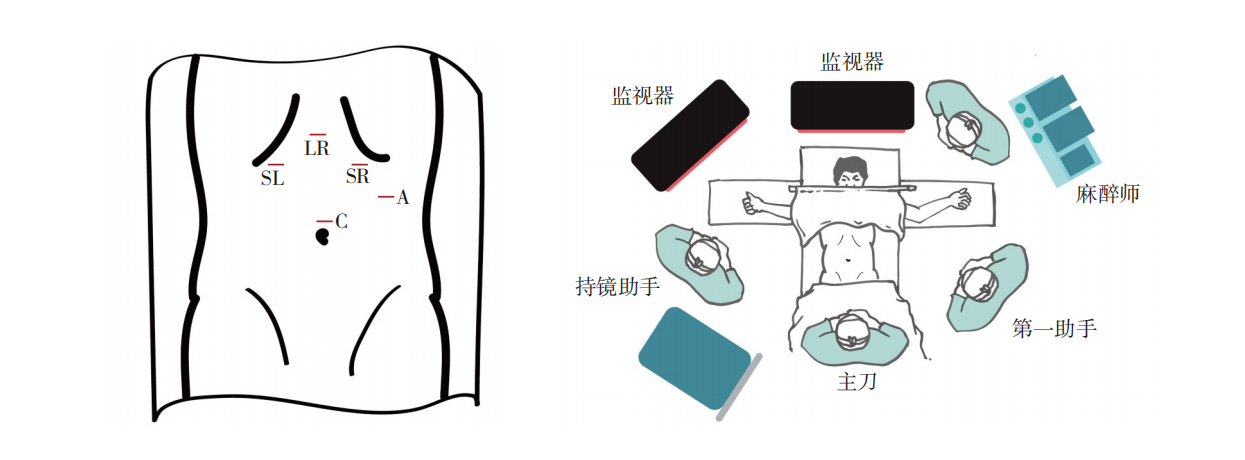
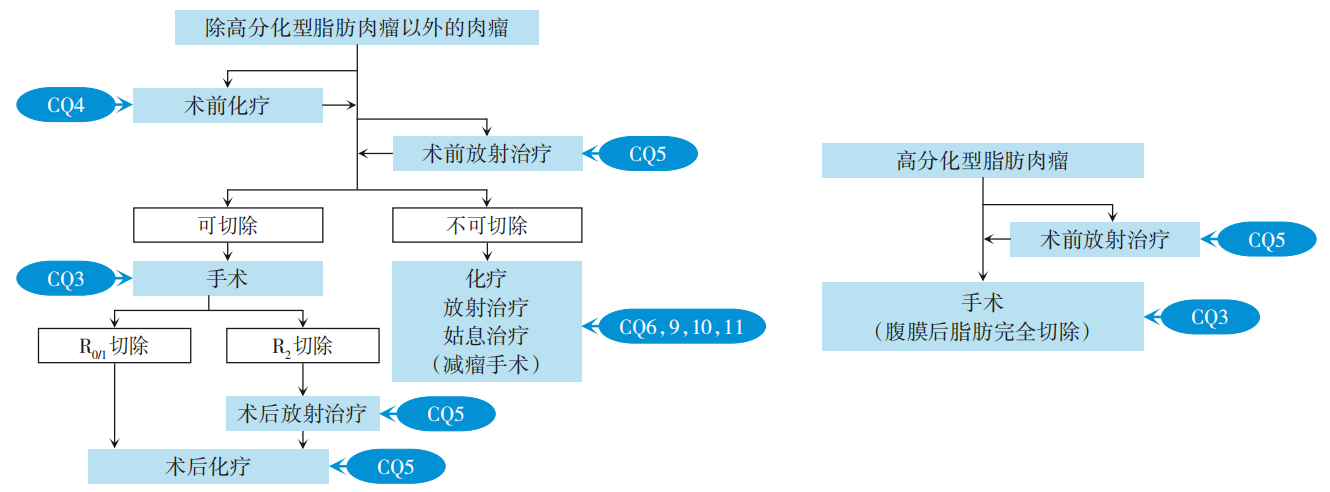
- Interpretation of the Japanese Clinical practice guidelines for the management of retroperitoneal sarcoma and clinical advances
- Causes and prevention strategies of surgical complications in laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair with mesh and fundoplication: a single-center analysis of 432 cases
- In situ laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy via the left-sided combined middle approach: a report of 4 cases
- Cross-sectional analysis and prospective prediction of pancreatic cancer disease burden based on the GBD database
- Current Issue
- Published Ahead-of-Print
- Virtual Issues
- Previous Issues
-
2025,34(6):1083-1096, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250291
Abstract:
Venous malformation (VM) is the most common type of congenital vascular anomaly, characterized by a lifelong progressive course that poses significant threats to patients' physical and mental health. In terms of treatment, the innovative application of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) to VM has emerged as a reliable therapeutic option, demonstrating definitive clinical efficacy while offering advantages such as safety, minimal invasiveness, shorter hospital stays, and lower cost. Nevertheless, there is still no authoritative guideline or consensus, either from domestic or international sources, that provides standardized recommendations for RFA in the treatment of VM. To fill this void, the Emergency Medicine Branch of the Chinese Medical Association and the Interventional Physicians Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association convened a multidisciplinary panel of experts from various fields that include vascular tumor surgery, vascular surgery, plastic surgery, interventional radiology, diagnostic imaging, emergency medicine, general surgery, and internal medicine. Drawing upon both domestic and international research, the panel reviewed and discussed recent advances and the clinical significance of RFA in VM treatment. As a result, they developed and refined the Expert consensus on radiofrequency ablation treatment for venous malformation (2025 version). This consensus includes 20 expert recommendations covering indications, ablation strategies, perioperative management, and approaches to the prevention and management of related complications. The aim is to enhance clinicians' understanding and practical skills in the standardized application of RFA for VM, thereby ensuring its safety and effectiveness in clinical practice.
-
ZHAO Yu, ZHAO Jichun, ZHANG Lan, HUANG Jianhua, GUO Pingfan, WANG Tao, LI Yongjun, WANG Haiyang, CHEN Quan,
2025,34(6):1097-1108, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250096
Abstract:
The incidence of chronic venous disease (CVD) is significantly higher in the elderly population compared to non-elderly individuals, with more severe disease manifestations. Additionally, elderly CVD patients often have comorbid conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, making the evaluation process more complex and increasing treatment difficulty. Currently, there are no established recommendations in China for the diagnosis and treatment of CVD in individuals aged 60 and above. Against this backdrop, the Peripheral Vascular Disease Management Branch of the Chinese Geriatric Society has developed the Chinese Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Venous Disease in the Elderly based on domestic and international guidelines, relevant evidence-based medical research, and the physiological and clinical characteristics of the elderly population in China. This consensus aims to provide an important reference for improving the diagnosis and treatment of CVD in elderly patients in China.
-
2025,34(6):1109-1120, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250268
Abstract:
As a type of central venous access device, the totally implantable venous access port (TIVAP) is widely used in patients requiring long-term or intermittent intravenous infusion, chemotherapy, nutritional support, and other treatments. It effectively reduces the need for repeated punctures and offers advantages such as safety and convenience. However, in primary healthcare institutions, there are still inconsistencies in procedures and non-standardized practices in the maintenance and complication management of TIVAP. To enhance the safety and standardization of TIVAP usage and to ensure treatment efficacy, the Colorectal and Anorectal Surgery Branch of the Henan Medical Doctor Association convened a multidisciplinary panel of experts to develop this expert consensus on grassroots technical specifications, integrating domestic and international evidence-based findings and clinical experience. The consensus covers the assessment, maintenance, management, and prevention of complications of TIVAP, and proposes 10 expert recommendations with an emphasis on operational feasibility and suitability for primary care. It aims to provide scientific, standardized, and practical guidance for frontline healthcare workers, reduce the risk of complications, and improve clinical quality and patient safety.
-
2025,34(6):1121-1129, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250257
Abstract:
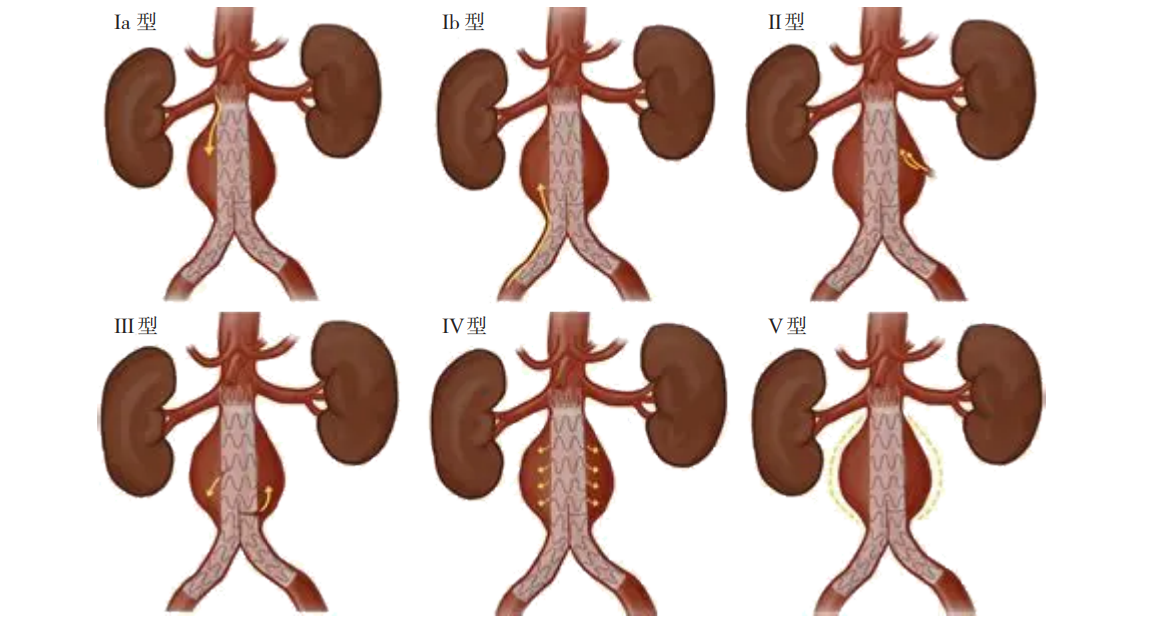
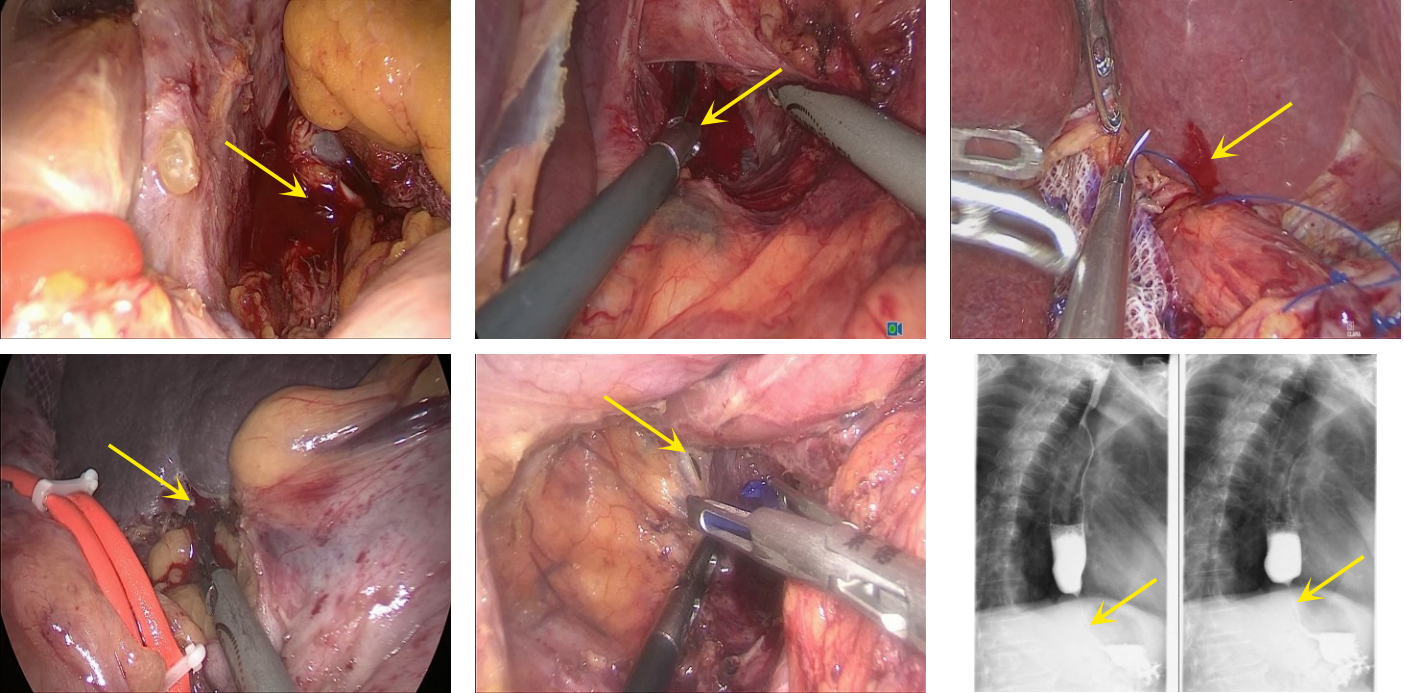
Endoleak is a major cause of poor long-term outcomes and reintervention after endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) for abdominal aortic aneurysms. The prevention and management of endoleaks are critical to improving the safety and efficacy of EVAR procedures. This article aims to summarize the key challenges and strategies in managing various types of endoleaks during EVAR, providing guidance to reduce the incidence of postoperative endoleaks.
-
ZHANG Lei, XIA Dexiang, LI Rui, GUO Pengcheng, LI Xin, SHU Chang
2025,34(6):1130-1138, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250295
Abstract:
Background and Aims Endovascular repair of aortic arch diseases poses a major challenge in vascular surgery due to the need to both effectively exclude the lesion and preserve perfusion of supra-aortic branch vessels. The Castor branched aortic covered stent, with its integrated design and ability to maintain left subclavian artery (LSA) patency, offers potential advantages. When combined with the chimney technique for the left common carotid artery (LCCA), it may provide a minimally invasive and feasible solution for patients with insufficient proximal landing zones. This study aims to evaluate the preliminary feasibility and safety of this combined approach and provide clinical reference for the endovascular management of complex aortic arch pathologies.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 15 patients with aortic arch diseases who underwent treatment with the Castor branched stent-graft combined with LCCA chimney stenting at the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University between February 2023 and December 2024. Baseline characteristics, surgical procedures, perioperative complications, and follow-up outcomes were analyzed to assess technical success, complication rates, and branch vessel patency.Results Among the 15 patients (11 males, average age 63.8 years), primary diagnoses included aortic dissection (33.4%), aortic arch aneurysm (53.3%), and penetrating aortic ulcer (13.3%). The technical success rate was 100%, with no perioperative deaths or major complications. During the follow-up period (4-26 months, mean 12.9 months), no adverse events such as stroke, paralysis, endoleak, or stent migration occurred. The patency rate of both the LCCA and LSA remained 100%.Conclusion The Castor branched aortic stent-graft combined with LCCA chimney technique appears to be a technically feasible and safe short-term option for treating aortic arch diseases with insufficient proximal landing zones. It may serve as a promising alternative for complex aortic arch repair; however, large-scale, multicenter studies with long-term follow-up are needed to further validate its efficacy and safety.
-
LIU Chen, WEI Yupeng, PANG Liwei, WANG Shiyue, GANG Qingwei, JIANG Han, LUN Yu, ZHANG Jian
2025,34(6):1139-1148, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250059
Abstract:
Background and Aims Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a common arterial dilation disease in vascular surgery, with aneurysm rupture being its most serious complication, often leading to fatal hemorrhage and posing a severe threat to patients' lives. Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR), due to its minimally invasive nature, safety, and rapid recovery, has become the preferred treatment for AAA. However, endoleak, a complication unique to EVAR, remains a major clinical challenge. Persistent endoleak can lead to sustained high pressure within the aneurysm sac, increasing the risk of continued expansion and rupture. It is one of the main causes of the high reintervention rate following EVAR. In particular, the treatment strategy for type Ⅱ endoleaks remains controversial. This study was conducted to evaluate the clinical value of selective sac embolization via the iliac approach combined with standard EVAR in managing intraoperative immediate endoleaks. Methods The clinical data of AAA patients with a risk of endoleak who underwent standard EVAR at the First Hospital of China Medical University between March 2023 and September 2024 were retrospectively collected. Patients were divided into an intervention group ( n=42) and a non-intervention group ( n=32) based on whether selective sac embolization via the iliac approach was performed during operation. General clinical data, preoperative anatomical characteristics of the AAA, surgical details, and postoperative follow-up results were compared between the two groups. Results There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, sex, anatomical features, rupture rate, or off-label use (all P>0.05). The technical success rate during surgery was 100% in both groups. One patient in the intervention group experienced transient sigmoid colon ischemia after operation, which resolved with conservative treatment. The mean follow-up period was (6.49±4.68) months. The proportions of aneurysm sac shrinkage, stability, and enlargement in the intervention group were 40.5%, 57.1%, and 2.4%, respectively, compared to 59.4%, 40.6%, and 0.0% in the non-intervention group, with no statistically significant differences (all P>0.05). The incidence of endoleak during follow-up was also comparable between the two groups ( P>0.05). Conclusion For intraoperative endoleaks during standard EVAR, selective sac embolization via the iliac approach is a technically simple and safe method that provides short-term outcomes comparable to those in patients without intraoperative endoleaks. Its long-term efficacy warrants further investigation through extended follow-up.
-
2025,34(6):1149-1156, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240585
Abstract:
Background and Aims Critical limb ischemia (CLI) represents the end stage of lower extremity arterial disease. Infrapopliteal artery lesions, due to their complex anatomical and pathological characteristics, pose significant therapeutic challenges, with patients facing high rates of amputation and mortality. In recent years, endovascular treatment techniques have evolved rapidly; however, controversy remains regarding the optimal treatment strategy. To systematically compare the efficacy of different treatment modalities, this study conducted a network Meta-analysis to comprehensively evaluate balloon angioplasty (BA), bare-metal stents (BMS), drug-coated balloons (DCB), drug-eluting stents (DES), and orbital atherectomy (OA) in the treatment of CLI involving infrapopliteal artery lesions, providing evidence to guide clinical decision-making on optimal endovascular therapy.Methods A comprehensive search of multiple medical databases was performed, and 17 randomized controlled trials with a total of 2 379 patients were included. A network Meta-analysis was conducted. The primary outcomes were 1-year primary patency rate, target lesion revascularization (TLR) rate, and major amputation rate.Results DCB showed the highest efficacy in 1-year primary patency, significantly outperforming DES (OR=4.55, 95% CI=1.14-20.00), BMS (OR=15.77, 95% CI=3.50-71.00), and BA (OR=9.02, 95% CI=2.43-33.47). DCB also demonstrated the lowest 1-year TLR rate, significantly lower than BA (OR=0.40, 95% CI=0.22-0.72). There were no statistically significant differences among treatment methods in terms of the 1-year major amputation rate; however, the cumulative ranking analysis suggested that DES may be the most effective in reducing major amputation risk.Conclusion DCB offers clear advantages in improving primary patency and reducing TLR rates, while DES may be the most effective strategy for reducing the risk of major amputation. DCB and DES should be prioritized in the endovascular treatment of CLI involving infrapopliteal artery lesions.
-
ZHANG Yuanyuan, WANG Yawen, DAI Yangyang, YANG Liu
2025,34(6):1157-1170, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250283
Abstract:
Background and Aims Aortic aneurysm, a major cardiovascular disease with high mortality and disability rates, has emerged as a critical global public health challenge. Elevated body mass index (BMI) has been confirmed as an independent risk factor for aortic aneurysm. However, the long-term trends and heterogeneity of the disease burden attributable to high BMI in China-across sex, age, and region-remain insufficiently studied. This study, based on the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) database, aimed to analyze the changes in the disease burden of high BMI-related aortic aneurysm in China from 1990 to 2021 and compare these trends with those in global and socio-demographic index (SDI)-stratified regions.Methods Data from GBD 2021 were used to extract mortality rates and disability-adjusted life years (DALY) due to aortic aneurysm attributable to high BMI in China from 1990 to 2021. Age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) and age-standardized DALY rate (ASDR) were calculated. Long-term trends were assessed using the estimated annual percentage change (EAPC) and Joinpoint regression models. An autoregressive integrated moving average model was applied to project trends from 2022 to 2036.Results During the study period, deaths and DALY from aortic aneurysms attributable to high BMI in China increased nearly sevenfold. ASMR rose from 1 to 3 per 100 000 population (EAPC=3.91), and ASDR increased from 23 to 74 per 100 000 (EAPC=4.11), both showing a marked upward trend. Males consistently bore a higher burden across all age groups, particularly among those aged ≥65 years. Decomposition analysis revealed that the increased burden in males was mainly driven by epidemiological improvements, while that in females was primarily attributable to population aging. Compared with the United States and global trends, China exhibited a faster increase in high BMI-related aortic aneurysm burden, which is projected to remain elevated over the next 15 years.Conclusion The disease burden of aortic aneurysm attributable to high BMI continues to rise in China, with pronounced differences across sex and age. Targeted weight management, health interventions, and early screening strategies are urgently needed for high-risk populations to curb the upward trend and optimize public health resource allocation.
-
DING Yunpeng, YIN Xiaoliang, LANG Dehai, HU Songjie
2025,34(6):1171-1177, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250133
Abstract:
Background and Aims Spontaneous isolated superior mesenteric artery dissection (SISMAD) is a relatively common type of visceral artery dissection, typically presenting with acute abdominal pain. In severe cases, it may lead to intestinal ischemia or even necrosis. With the widespread use of imaging techniques such as CT angiography (CTA), the detection rate of SISMAD has significantly increased. However, there is still controversy regarding its optimal treatment strategy, especially in choosing between conservative management and endovascular intervention, as no unified standard currently exists. This study aimed to compare the short- and medium-term outcomes of the two treatment modalities by retrospectively analyzing the clinical data of SISMAD patients treated at our center in order to provide evidence for individualized treatment decisions.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 174 patients diagnosed with SISMAD at Ningbo Second Hospital between January 2018 and December 2023. Among them, 30 patients received conservative treatment, and 144 underwent endovascular intervention (including stent implantation alone or in combination with coil embolization of the false lumen). All patients were diagnosed using CTA or superior mesenteric artery angiography and classified accordingly. Patients were followed up at 1 month and 1 year after treatment to assess clinical symptom relief and radiological outcomes, including dissection remodeling and stent patency.Results In the conservative group, the symptom relief rate was 90.0% at 1 month and 92.8% at 1 year; in the interventional group, the corresponding rates were 99.3% and 98.6%. The difference in symptom relief at 1 month was statistically significant (P=0.016), while the difference at 1 year was not (P>0.05). Subgroup analysis by classification showed that the interventional group generally had higher symptom relief rates than the conservative group across all types. However, none of the differences reached statistical significance (all P>0.05). The conservative group showed poorer symptom control in type Ⅲ patients, including one death. The technical success rate of endovascular treatment was 99.3%, with no cases of stent displacement or occlusion within 1 year. The complete remodeling rate was 86.8%, and the stent patency rate was 100.0%. Some patients had minor mural thrombus formation within the stent without evidence of flow obstruction.Conclusion Endovascular intervention offers a high technical success rate and favorable short- and medium-term efficacy in SISMAD patients, particularly for type Ⅱ and Ⅲ cases with compromised true lumen perfusion. Treatment strategies should be tailored based on the dissection type and the degree of true lumen compression to improve clinical outcomes and reduce associated risks.
-
MA Lin, TIAN Xuan, ZHENG Han, LIU Jianlong, YIN Yuedi, WANG Lingyan, LI Jinyong, LIU Xiao, ZHOU Mi, HUA Run
2025,34(6):1178-1187, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250290
Abstract:
Background and Aims Acute inferior vena cava thrombosis (IVCT) commonly occurs secondary to inferior vena cava filter (VCF) implantation. If not promptly treated, it may lead to serious complications such as bilateral lower limb swelling and pulmonary embolism and can also reduce the likelihood of successful filter retrieval. Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy (PMT) and catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT) are currently the main interventional treatments for IVCT, but comparative studies evaluating their efficacy and safety remain limited. This study was to conduct a prospective randomized controlled trial to compare the clinical efficacy and safety of AngioJet mechanical thrombectomy versus conventional CDT in the treatment of acute IVCT and to explore factors influencing filter retrieval rates, thereby providing evidence-based guidance for clinical decision-making.Methods From January 2022 to December 2024, patients diagnosed with acute IVCT following VCF implantation were prospectively enrolled at the Department of Vascular Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Capital Medical University. Patients were randomly assigned to either the CDT group (n=46) or the PMT group (n=48) according to the interventional procedure used. The two groups were compared in terms of filter retrieval rates, thrombus clearance outcomes, operative time, thrombolytic drug dosage, and incidence of complications. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify factors associated with primary filter retrieval.Results A total of 94 patients were enrolled, with 46 in the CDT group and 48 in the PMT group. Compared to the CDT group, the PMT group demonstrated a significantly higher primary filter retrieval rate (77.1% vs. 43.5%), grade Ⅲ thrombus clearance rate (70.8% vs. 37.0%), and better postoperative thrombus scores. Additionally, the PMT group required lower urokinase doses and shorter thrombolysis duration (all P<0.05). The overall filter retrieval rate and 3-month IVC patency were similar between groups, both exceeding 93%. Regarding safety, the CDT group had a higher incidence of catheter-related infections and medical adhesive-related skin injury, while vagal reflex symptoms were more frequent in the PMT group. Logistic regression analysis identified thrombus clearance rate as an independent factor significantly associated with primary filter retrieval in the PMT group (OR=190.773, P<0.05).Conclusion Compared to CDT, AngioJet mechanical thrombectomy combined with manual aspiration achieves higher thrombus clearance and primary filter retrieval rates in the treatment of acute IVCT while also reducing thrombolysis duration and drug dosage. However, attention should be paid to the increased risk of vagal reflex symptoms. There was no significant difference between the two groups in secondary filter retrieval rates or long-term IVC patency. The choice of intervention should be based on the patient's condition, timing of filter retrieval, and individualized clinical considerations.
-
LIU Qiong, CHEN Haodong, DAI Yuan, DING Xiaofang, LUO Wanghui, TANG Shihui, CHEN Yan
2025,34(6):1188-1195, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250227
Abstract:
Background and Aims Totally implantable venous access port (TIVAP) are widely used for chemotherapy, blood transfusion, and nutritional support in patients with malignancies. Among them, upper arm port (UAP) are increasingly recommended in clinical practice due to their advantages in avoiding thoracic complications and providing more concealed incisions. Currently, two main implantation techniques are used for UAP: the tunnel needle-transverse incision technique and the puncture point-transverse incision technique. This study aims to compare the clinical outcomes of these two techniques in patients with hematological malignancies, focusing on safety and cosmetic appearance, to provide evidence for clinical decision-making.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 412 patients with hematological malignancies who underwent UAP implantation at Xiangya Hospital of Central South University between December 2021 and December 2024. Based on the implantation method, patients were divided into the tunnel needle-transverse incision group (n=200) and the puncture point-transverse incision group (n=212). Intraoperative variables (operative time, intraoperative pain score, catheter kinking at the pocket, intraoperative blood loss) and postoperative indicators (incidence of complications and incision aesthetic satisfaction) were compared between the two groups.Results There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the two groups (all P>0.05), indicating comparability. The puncture point-transverse incision group showed superior performance in operative time [(32.99±4.91) min vs. (41.42±5.35) min], catheter kinking rate (1.4% vs. 8.5%), and incision aesthetic satisfaction (7.99±0.58 vs. 6.26±0.86) compared with the tunnel needle-transverse incision group (all P<0.05). Although the puncture point group had slightly more intraoperative bleeding [(4.52±1.02) mL vs. (4.16±0.83) mL], the difference, while statistically significant, was of limited clinical relevance. No significant differences were observed between the two groups in intraoperative pain scores or incidence of postoperative complications (both P>0.05).Conclusion The puncture point-transverse incision technique offers significant advantages in terms of operative efficiency, reduced catheter kinking, and improved incision aesthetics, without compromising safety. It represents a promising alternative to the traditional tunnel needle-transverse incision method and has strong potential for broader clinical adoption.The puncture point-transverse incision technique offers advantages such as shorter operative time, lower catheter kinking rate, and higher incision aesthetic satisfaction. It is a promising alternative to the traditional tunnel needle-transverse incision technique and has good potential for clinical application and promotion.
-
Expression and mechanistic role of macrophage-enriched lncRNA CCL3-AS1 in carotid plaque instability
WANG Siting, XIE Hejian, YANG Shujun, XIE Wei
2025,34(6):1196-1208, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250071
Abstract:
Background and Aims Carotid plaque instability is a critical pathological basis for ischemic stroke. Identifying key molecular markers to evaluate plaque stability has important clinical implications. Recent studies have emphasized the regulatory roles and predictive value of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in plaque stability. In our previous transcriptome sequencing analysis of human stable and unstable carotid plaques, we identified lncRNA C-C motif chemokine ligand 3 antisense RNA 1(CCL3-AS1) as significantly upregulated in unstable plaques, suggesting a potential association with plaque instability. Therefore, this study aimed to validate CCL3-AS1 expression in an expanded plaque sample cohort and to explore its role and underlying molecular mechanism in carotid plaque destabilization.Methods Carotid plaque specimens were obtained from patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy and classified into stable and unstable groups (n=15 per group) based on HE and Sirius red staining. qRT-PCR was used to validate the expression of candidate lncRNA CCL3-AS1. The localization and co-expression of CCL3-AS1 with macrophages in plaques were determined by RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) combined with immunofluorescence staining. In vitro, THP1-derived macrophages were transduced with lentivirus or treated with antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) to overexpress or knock down CCL3-AS1, respectively, and the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) were assessed. In vivo, an unstable carotid plaque model was established by tandem ligation of the right carotid artery in apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE-/-) mice, followed by local overexpression of CCL3-AS1. The effects on plaque morphology, macrophage infiltration, and MMP-9 expression were evaluated. Additionally, bioinformatic prediction using the catRAPID v2.1 omics platform was performed to identify potential RNA-binding proteins interacting with CCL3-AS1. RNA stability assays and RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation (RIP) were conducted to verify the regulatory mechanism of MMP-9 expression.Results CCL3-AS1 was significantly upregulated in unstable carotid plaques and was predominantly localized to the cytoplasm of plaque-infiltrating macrophages. In vitro, overexpression of CCL3-AS1 markedly increased the expression of MCP-1, TNF-α, IL-1β, iNOS, and MMP-9 in macrophages, whereas knockdown had the opposite effect. In the ApoE-/- mouse model of unstable carotid plaques, CCL3-AS1 overexpression led to fibrous cap rupture, increased infiltration of pro-inflammatory macrophages, enhanced MMP-9 secretion, and promoted plaque instability. Co-expression analysis revealed a strong correlation between CCL3-AS1 and MMP-9 expression (r=0.89, P=0.001). RNA stability assays demonstrated that CCL3-AS1 delayed the degradation of MMP-9 mRNA. Bioinformatic prediction identified heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP-K) as a potential binding partner of CCL3-AS1. RIP and FISH co-localization confirmed the interaction, suggesting that CCL3-AS1 enhances MMP-9 mRNA stability through binding to hnRNP-K, thereby promoting its expression.Conclusion As a macrophage-enriched inflammatory lncRNA, CCL3-AS1 may promote carotid plaque instability by enhancing MMP-9 expression via hnRNP-K-mediated mRNA stabilization. This lncRNA represents a potential molecular target for early intervention and stratification of ischemic stroke.
-
LI Huazhi, SUN Haitao, CAO Guang, ZHANG Yajing
2025,34(6):1209-1218, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240537
Abstract:
Background and Aims Studies have shown that the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) FGD5-AS1 functions as an oncogene in gastric cancer (GC). Our previous bioinformatics analysis revealed potential binding sites between FGD5-AS1 and microRNA-142-3p (miR-142-3p), as well as between miR-142-3p and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1). Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the expression and functional role of the FGD5-AS1/miR-142-3p/PDK1 axis in GC cells.Methods Dual-luciferase reporter assays were used to verify the targeting relationships between FGD5-AS1 and miR-142-3p, and between miR-142-3p and PDK1. qRT-PCR was conducted to measure the expression levels of FGD5-AS1, miR-142-3p, and PDK1 in GC tissues. A knockdown model of FGD5-AS1 (sh-FGD5-AS1) and an miR-142-3p inhibitor were constructed and transfected, alone or in combination, into BGC823 GC cells. Cellular behaviors, including proliferation (CCK8, EdU), apoptosis (flow cytometry), migration, and invasion (Transwell assays), were assessed, along with related protein expression (Western blot). A subcutaneous xenograft model in nude mice was used to evaluate the effect of FGD5-AS1 on tumor growth in vivo.Results The dual-luciferase assays demonstrated that miR-142-3p mimics significantly reduced the luciferase activity of wild-type (WT) FGD5-AS1 and PDK1 reporters (both P<0.05), but had no effect on mutant (MUT) reporters, confirming a direct binding relationship. Knockdown of FGD5-AS1 led to upregulation of miR-142-3p and downregulation of PDK1 in GC cells, with reduced proliferation, migration, and invasion, and enhanced apoptosis (all P<0.05); these effects were reversed by the miR-142-3p inhibitor. In vivo, FGD5-AS1 knockdown significantly inhibited tumor growth in nude mice and decreased Ki-67 and PDK1 expression in tumor tissues (all P<0.05).Conclusion FGD5-AS1 may act as a ceRNA that sponges miR-142-3p, thereby relieving its suppression on PDK1, and promoting GC cell proliferation and invasion as well as tumor progression. The FGD5-AS1/miR-142-3p/PDK1 axis plays a critical role in the development of GC and may serve as a potential therapeutic target.
-
SONG Xingchao, MA Xiao, YANG Weibin, XU Anzhi, SONG Qiuyu
2025,34(6):1219-1227, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240644
Abstract:
Background and Aims Laparoscopic anatomical liver segmentectomy has been widely applied in the surgical treatment of hepatic tumors due to its safety, feasibility, and effectiveness. The combination of indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence-guided positive staining and intraoperative laparoscopic ultrasound has become an important technique for precision liver resection, particularly in accurately delineating hepatic segment/subsegment boundaries and achieving negative surgical margins. This study reports a case of anatomical resection of the right posterior segment and the dorsal subsegment of the right anterior segment of the liver, guided by laparoscopic ultrasound combined with ICG positive staining, to evaluate its clinical feasibility and outcomes.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on an elderly female patient with a hepatic space-occupying lesion who underwent laparoscopic anatomical resection of the right posterior segment and right anterior dorsal subsegment using intraoperative ultrasound combined with ICG fluorescence-guided positive staining.Results Preoperative three-dimensional reconstruction revealed that the tumor was located in the right posterior segment and right anterior dorsal subsegment. Intraoperatively, under laparoscopic ultrasound guidance, the anterior-ventral branch of the right portal vein was punctured and injected with ICG to achieve precise staining of the right anterior-ventral subsegment. The resection was performed along the fluorescent boundary, enabling accurate anatomical removal of the targeted liver segments. Intraoperative blood loss was approximately 100 mL without transfusion. Pathology confirmed a moderately differentiated small-duct type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with negative margins (R0 resection). The patient recovered well and was discharged on postoperative day 19. Follow-up CT at 6 months showed no evidence of recurrence.Conclusion During anatomical resection of the right posterior segment and right anterior dorsal subsegment of the liver, laparoscopic ultrasound combined with ICG fluorescence-guided positive staining can accurately define segmental boundaries, enhance surgical safety, and ensure complete tumor resection, thus offering significant value in achieving R0 resection.
-
LU Chenbin, TONG Linyan, SUN Yuqin, ZENG Weiming, CHEN Qiuxian, LU Jun, CAI Lisheng
2025,34(6):1228-1237, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250022
Abstract:
Background and Aims The completeness of lymph node dissection in laparoscopic radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer directly affects postoperative patient prognosis. Indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence-guided navigation, as an emerging auxiliary technique, enables real-time visualization of lymphatic drainage pathways and enhances surgical precision. This study was performed to evaluate the impact of ICG fluorescence navigation on lymph node dissection, positive lymph node detection, and patient prognosis during laparoscopic D2 radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer.Methods The clinical data of 168 patients who underwent laparoscopic radical gastrectomy at Zhangzhou Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University from January 2021 to December 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. Among them, 51 patients received ICG-guided surgery (ICG group), and 117 underwent conventional surgery (non-ICG group). Perioperative variables, extent of lymph node dissection, positive lymph node detection efficiency, and postoperative survival outcomes were compared between the two groups.Results There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in baseline clinicopathologic characteristics, as well as operative time, intraoperative blood loss, postoperative recovery, and incidence of surgical complications (all P>0.05). The ICG group had a significantly higher mean number of lymph nodes dissected than the non-ICG group (48.62 vs. 37.20, P<0.001), with a greater proportion of patients achieving ≥30 nodes dissected (92.16% vs. 69.23%, P=0.001). Stratified analysis showed a significantly higher number of dissected lymph nodes in the ICG group at D2 stations, the supra-pancreatic region (stations 7, 8, 9, 11), in total gastrectomy, T3-4 stage, and stage Ⅲ patients (all P<0.01). In the ICG group, the number and positivity rate of fluorescent lymph nodes were significantly higher than those of non-fluorescent nodes (30.31 vs. 17.36; 2.03 vs. 0.94, both P<0.05). The diagnostic sensitivity of ICG fluorescence imaging for positive lymph nodes was 68.4%, with a negative predictive value of 94.6% for non-fluorescent nodes. No significant differences were observed between the two groups in terms of adjuvant therapy, overall survival (HR=0.737, P=0.471), or disease-free survival (HR=0.502, P=0.089).Conclusion ICG-guided navigation in laparoscopic radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer is safe and significantly improves lymph node yield, particularly in the supra-pancreatic region, total gastrectomy, and advanced-stage patients. It also enhances positive node detection. However, no survival benefit has been observed in the short term. Further multicenter studies with long-term follow-up are warranted to confirm its clinical value and optimize intraoperative navigation strategies.
-
ZENG Xianqing, WANG Yunlong, ZHANG Jinfeng
2025,34(6):1238-1245, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240286
Abstract:
Background and Aims Poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma (PDTC) is a relatively rare but highly aggressive type of thyroid malignancy. Its biological behavior lies between differentiated and undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma, and it is often characterized by early metastasis, high recurrence rates, and poor survival outcomes. At present, prognostic assessment for PDTC patients primarily relies on traditional indicators such as TNM staging, and there remains a lack of systematic, multi-factorial, and individualized predictive tools. As a visual and quantitative method, the nomogram model has been widely applied in the prognostic evaluation of various tumors; however, its use in PDTC remains limited. This study aims to identify key risk factors associated with poor prognosis in PDTC patients and to construct a risk prediction nomogram model based on multivariate analysis, in order to provide clinical support for individualized postoperative prognostic assessment.Methods A total of 55 PDTC patients who underwent surgical treatment at our hospital from January 2015 to December 2020 were retrospectively enrolled and followed up for three years. Based on tumor recurrence, metastasis, and mortality during the follow-up period, patients were divided into a good prognosis group and a poor prognosis group. Univariate analysis was performed to screen for clinical features associated with prognosis, followed by multivariate logistic regression to identify independent risk factors. A nomogram risk prediction model was constructed using R software (version 3.5.3), and its predictive performance and calibration were evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and Bootstrap validation.Results During the 3-year follow-up, 15 patients experienced tumor progression and 1 patient died, resulting in a poor prognosis rate of 29.1%. Univariate analysis showed statistically significant differences in tumor diameter, TNM stage, local invasion, surgical approach, vascular invasion, and nerve involvement between the two groups (all P<0.05). Multivariate logistic regression identified tumor diameter ≥3 cm, advanced TNM stage, local invasion, subtotal thyroidectomy, vascular invasion, and nerve involvement as independent risk factors for poor prognosis (all P<0.05). The nomogram model constructed based on these variables demonstrated a C-index of 0.794 (95% CI=0.725-0.846), an AUC of 0.817, sensitivity of 82.26%, and specificity of 86.35%, indicating good discriminatory ability and predictive accuracy.Conclusion Tumor diameter, TNM stage, local invasion, surgical approach, vascular invasion, and nerve involvement are important factors influencing postoperative prognosis in PDTC patients. The nomogram model based on these variables exhibits strong predictive performance and may serve as a valuable tool for individualized risk assessment and therapeutic decision-making in clinical practice.
-
BAI Zhihao, LI Jiaxin, YANG Zhen, ZHOU Ning
2025,34(6):1246-1261, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250156
Abstract:
Background and Aims Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, has been increasingly recognized in recent years as being closely associated with various liver-related diseases, such as hepatic encephalopathy, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Abnormal GABA expression is strongly linked to pathological processes including cognitive impairment and neuroinflammation. Although numerous studies have investigated the mechanistic roles of GABA in neurological complications of liver disease, a systematic overview of the field's research trends, collaborative networks, and emerging hotspots remains lacking. This study employs bibliometric methods to comprehensively map the evolution and frontier topics in GABA and liver-related disease research from 2005 to 2024, aiming to inform future research planning and resource allocation in this area.Methods English-language publications from 2005 to 2024 related to GABA and liver-related diseases were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection. Eligible articles were analyzed using VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and the R package "bibliometrix" to visualize and evaluate contributions by countries/regions, institutions, authors, and journals. Additional analyses included keyword clustering, co-citation analysis, and thematic evolution of research topics.Results A total of 237 articles were included, contributed by 1 340 authors across 456 institutions in 47 countries, and published in 168 journals. The United States and China are leading contributors in this field. Although countries such as the United Kingdom and Italy had fewer publications, they demonstrated higher average citation counts, indicating strong research quality. Notably, Spain's Centro Investigación Principe Felipe and the research team led by Felipo Vicente exhibited high academic influence. Neurochemistry International and Hepatology were identified as core journals, with Hepatology having the highest impact factor (12.9). Keyword clustering revealed major research focuses including the regulatory role of GABA in the neural mechanisms of hepatic encephalopathy, the impact of liver-related metabolic disorders on neurotransmitter balance, the development and evaluation of GABA receptor-targeted therapeutics, and the function of the GABAergic system in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. As research deepens, the frequency of emerging keywords has diversified, with recent emphasis on terms such as "quality of life," "gene expression," and "fatty liver disease," reflecting a shift from fundamental mechanisms to clinical translation and interdisciplinary integration.Conclusion The relationship between GABA and liver diseases has become a focal point of interdisciplinary research. Investigations have expanded from pathological mechanisms to therapeutic applications, with growing interest in GABA's roles in hepatic encephalopathy, metabolic dysregulation, and tumor progression. Future studies should explore the specific functions of GABA receptor subtypes, promote the development of precision-targeted therapies, and investigate novel mechanisms such as the gut microbiota-GABA metabolism-brain-liver axis to broaden the clinical and translational potential of GABA in neurological, metabolic, and oncological contexts.
-
HE Nan, LIU Yiwei, LI Qingqing, TANG Xiaobin, WANG Sheng, CHEN Zhong
2025,34(6):1262-1274, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.250139
Abstract:
Carbon dioxide (CO2), a colorless, odorless, low-density negative contrast agent with no nephrotoxicity or allergic reactions, has seen increasingly widespread application in the field of vascular imaging in recent years, particularly in patients with iodine allergy or renal insufficiency. When combined with digital subtraction angiography, CO2 angiography has demonstrated high-quality imaging in various arterial and venous sites such as the abdominal aorta, renal arteries, iliac arteries, lower limb arteries, and inferior vena cava. It has also shown safety and efficacy in clinical scenarios such as peripheral arterial disease, dialysis access evaluation, and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedures. This review systematically summarizes domestic and international research progress on CO2 angiography, outlines its physicochemical properties, injection dosages and parameters, clinical indications, and imaging characteristics, and compares its image quality with that of iodine-based contrast agents. Common complications, their mechanisms, and preventive measures are also discussed. Although the image quality of CO2 is slightly inferior to that of iodine agents, it remains sufficient for most diagnostic and therapeutic needs, with a low overall incidence of mainly mild and transient adverse effects. With the development of automated injection systems and digital variance angiography technology, CO2 imaging quality is expected to continue improving, and its application scope is likely to expand further. Future efforts should focus on strengthening multicenter clinical research and establishing standardized operational protocols to promote the broader adoption and regulated use of this technology.
-
2025,34(6):1275-1281, DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.240656
Abstract:
Lower extremity atherosclerotic occlusive disease (ASO) is a common peripheral arterial disease with a steadily increasing global incidence. As a key pathological change in ASO, arterial calcification plays a crucial role in its pathogenesis, diagnostic evaluation, treatment strategies, and prognosis. In recent years, with the continuous advancement of imaging and biomarker detection technologies, quantitative assessment and clinical research on arterial calcification have deepened, providing new perspectives for individualized diagnosis and treatment. This review begins with the pathophysiological mechanisms of arterial calcification and systematically summarizes current detection methods, its impact on endovascular therapy, and recent progress in prognostic evaluation, aiming to provide theoretical support and practical reference for precision treatment of ASO patients.
Volume 34,2025 Number 6
GUIDELINE AND CONSENSUS
COMMENTARY
MONOGRAPHIC STUDY
BASIC RESEARCH
CLINICAL RESEARCH
REVIEW
-
Chinese Society of Coloproctology, Chinese Medical Doctor Association
Abstract:
Low anterior resection syndrome (LARS) is a common bowel dysfunction syndrome following sphincter-preserving surgery for rectal cancer, characterized by stool storage dysfunction and evacuatory dysfunction. It has become a critical factor adversely affecting patients"" quality of life and long-term clinical outcomes. Currently, the pathogenic mechanisms of LARS remain incompletely elucidated, and high-quality evidence to guide clinical practice is still lacking. However, emerging evidence suggests that strategic optimization across the clinical management pathway—including precision oncology planning, surgical technique selection, multidimensional symptom profiling, proactive prevention protocols, and comprehensive symptom management—may effectively reduce LARS severity and improve survivorship outcomes. Given the absence of consensus guidelines for LARS management among clinicians across China, the Chinese Society of Coloproctology (Chinese Medical Doctor Association) organized domestic experts in relevant fields. Through systematic review of global research findings, integration of international expertise and guidelines, and adaptation to domestic clinical realities, we developed the Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of low anterior resection syndrome (2025 edition). This consensus elaborates on key aspects including the definition, clinical manifestations, risk factors, pathophysiological mechanisms, symptom assessment, treatment modalities, and prevention strategies for LARS, aiming to standardize the diagnosis and management of LARS in China.
-
Abstract:
Robotic surgery represents a major trend in the current surgical treatment of colorectal cancer. Based on the previous edition, the Robotic Surgery Group of the Colorectal Cancer Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, convened national experts to discuss and reach a consensus on standardized practices for robotic colorectal cancer surgery, with the aim of facilitating its broader application and adoption.
-
Xu Jianmin, Gastrointestinal Surgery Group, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association, Colorectal Surgery Group, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association, Colorectal Cancer Committee, Chinese Anti-Cancer Association, Colorectal Oncology Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Expert Committee on Colorectal Cancer, Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology, Colorectal Surgery Committee, Chinese Society of Surgeons, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Tumor Metastasis Committee, Coloproctology Society, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Colorectal Oncology Group, Chinese Society of Oncology, Chinese Medical Association, Division of Metastatic Tumor Therapy, China International Exchange, Promotive Association for Medical, Health Care, Division of Colorectal Diseases, China International Exchange, Promotive Association for Medical, Health Care
Abstract:
To further standardize and improve the management of colorectal liver metastases (CRLM) in China, the Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and comprehensive treatment of colorectal cancer liver metastases (2025 edition) have been systematically updated based on previous versions and the latest international and domestic evidence. The updated guideline refines diagnostic pathways, strengthens multidisciplinary team collaboration, and comprehensively upgrades therapeutic strategies-including surgical resection, neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatments for patients eligible for no evidence of disease (NED) status, and systemic therapy for those who are not. It also expands the scope of genetic testing, incorporates innovative local ablative therapies, and emphasizes standardized follow-up and long-term management. The guideline aims to promote individualized and precision-based treatment, ultimately improving clinical outcomes and patient survival. It serves as a practical, evidence-based reference for healthcare providers managing CRLM across China.
-
Abstract:
Most patients with biliary tract cancer are diagnosed at advanced stage and lose the opportunity for radical surgery resulting in dismal prognosis. In recent years, with advances in therapeutic approaches, conversion therapy has gradually been implemented in some cases of initially unresectable biliary tract cancer, enabling a subset of patients to achieve opportunities for radical surgery. To further standardize conversion therapy of biliary tract cancer and improve the overall efficacy, the Branch of Biliary Surgery, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association and Working Group of Biliary Surgeons, Chinese College of Surgeons, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, based on the latest evidence-based medical evidence and specific practices in the treatment of biliary tract cancer in China, organized discussion among experts in the field. Following the discussion, the "Expert consensus on conversion therapy of biliary tract cancer (2025)" was developed. This consensus aims to address key issues in the field of biliary tract cancer conversion therapy, standardize diagnostic and therapeutic procedures and protocols,and lay the foundation for further advancing research and practice in this area.